GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Auto DevOps
What is Auto DevOps
GitLab Auto DevOps is a built-in CI/CD feature that automatically detects your project’s language, framework, and configuration to generate a complete pipeline. It follows best practices across build, test, and deployment stages—integrating security scans, code quality checks, and container analysis—so you can focus on writing code instead of maintaining CI/CD scripts.
Auto DevOps provides:
- Automated build and containerization
- Comprehensive testing (unit, integration, security)
- Review Apps for testing merge request changes
- Continuous delivery or deployment after merge
Note
Auto DevOps offers sensible defaults, but you can customize the pipeline via CI/CD templates or project-specific .gitlab-ci.yml overrides.
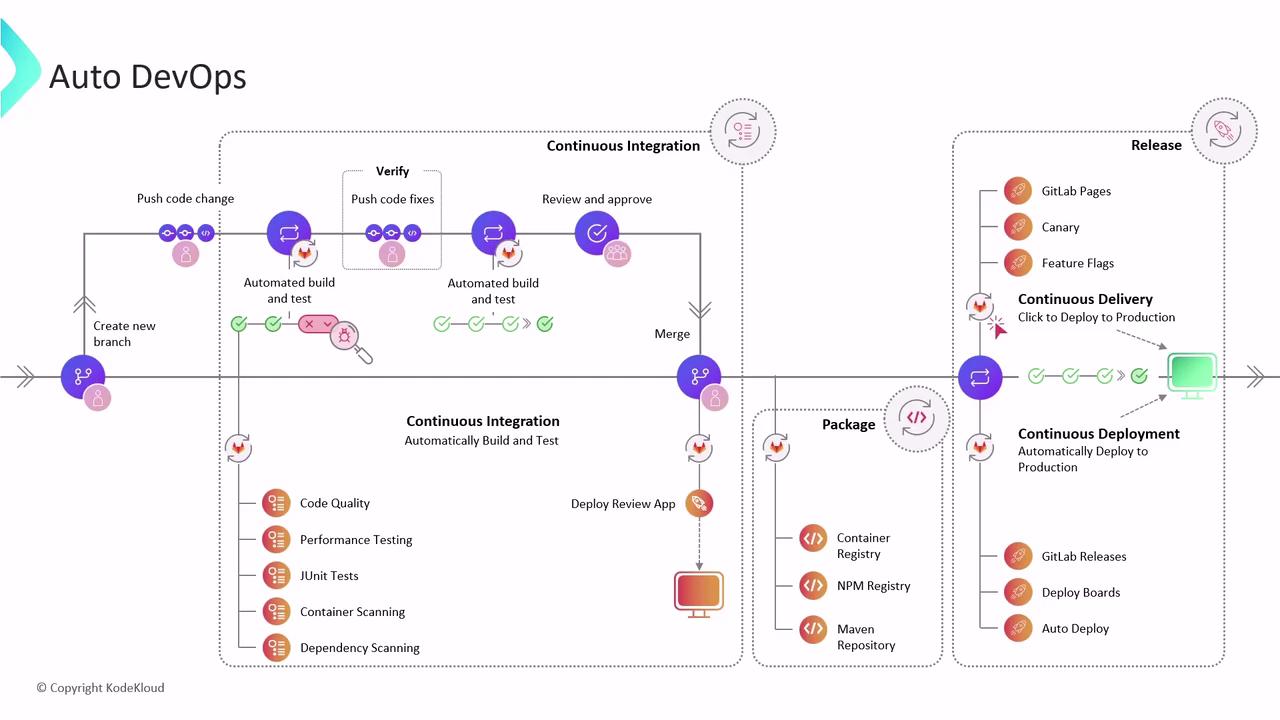
How Auto DevOps Works at the Project Level
When you enable Auto DevOps in Settings > CI/CD, GitLab inspects your repository and applies predefined CI/CD templates. The default pipeline includes three core stages:
1. Build Stage
- Detects a
Dockerfilein your repo and builds a container image. - Falls back to Heroku buildpacks if no Dockerfile is found.
- Outputs a ready-to-use Docker image for subsequent stages.
2. Test Stage
Runs your test suite and adds built-in checks:
| Check Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Code Quality | Analyzes source code for maintainability and style issues. |
| Static Application Security Testing (SAST) | Scans code for common vulnerabilities. |
| Secret Detection | Searches for accidentally committed credentials. |
| Dependency Scanning | Reviews Gemfile.lock, package.json, etc., for vulnerable dependencies. |
| Container Scanning | Scans the built Docker image for OS-level vulnerabilities. |
Supported languages include Ruby, Node.js, Java (Maven/Gradle), Python, Go, and more. All reports appear in the pipeline UI for immediate feedback.
3. Kubernetes Deployment
If you register a Kubernetes cluster in Operations > Kubernetes, Auto DevOps can deploy your app automatically. Supported cluster providers include:
- Amazon EKS (Elastic Kubernetes Service)
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Self-managed (Bare Metal) clusters
Review Apps and Security Testing
When a merge request is opened, Auto DevOps spins up a Review App—a temporary, live environment to validate changes before merge. This deployment uses the Helm Auto Deploy chart, which you can customize.
Once the Review App is live, Auto DevOps runs Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) using OWASP ZAP. ZAP crawls the application, identifies vulnerabilities, and produces a comprehensive report with severity levels and remediation advice.
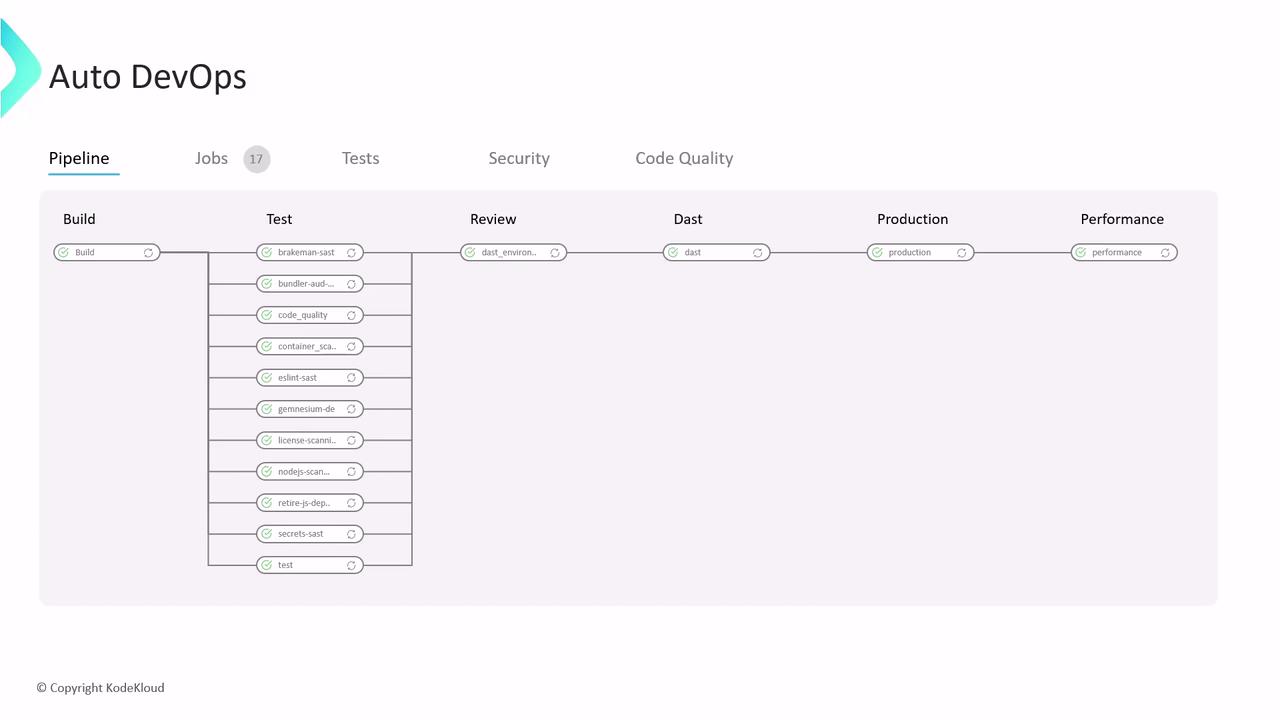
Post-Merge Deployment and Performance Testing
After you merge to the default branch, Auto DevOps can deploy your application to staging or production based on your configuration. Post-deployment, it executes browser-based performance tests to benchmark page load times against previous releases—ensuring optimal user experience.
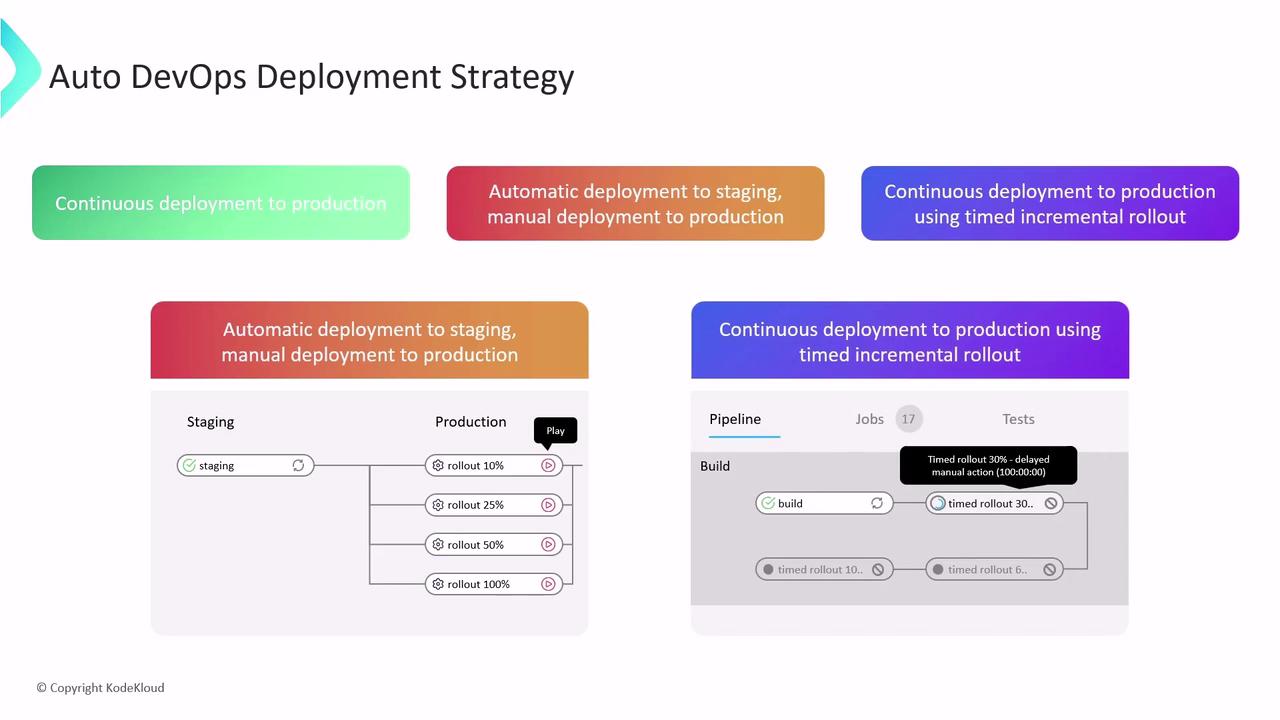
Deployment Strategies
Choose from three release workflows to match your team’s requirements:
| Strategy | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Continuous Deployment to Production | Deploys every successful pipeline run directly to production without manual steps. |
| Automatic Staging + Manual Production Deploy | Automatically updates staging; requires manual approval to promote changes to production (e.g., click the play button). |
| Timed Incremental Rollout | Performs staged deployments automatically with configurable delays (default: 5 minutes between stages). |
Warning
Ensure your rollback procedures are tested and documented. Timed rollouts reduce risk but require proper monitoring and alerts.
Links and References
- GitLab Auto DevOps documentation
- GitLab CI/CD Overview
- Kubernetes Basics
- OWASP ZAP Proxy
- Heroku Buildpacks
Watch Video
Watch video content