GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Continuous Deployment with GitLab
Manually Promote to Staging Environment via agentK
To streamline manual promotions to staging, use GitLab’s Kubernetes Agent (AgentK) to authenticate your CI/CD jobs. This guide walks through deploying to the staging namespace and updating your pipeline to leverage the Agent’s built-in KUBECONFIG context.
Prerequisites
- A configured GitLab Kubernetes Agent with
ci_accessenabled inconfig.yaml - Defined CI/CD variables:
DEV_KUBE_CONFIG,NAMESPACE,MONGO_*,DOCKER_USERNAME - The
stagingnamespace created on your cluster
1. Verify the Staging Namespace Is Empty
Confirm there are no existing resources in staging:
kubectl -n staging get all
No resources should be returned.
You can also verify in GitLab under Environments:
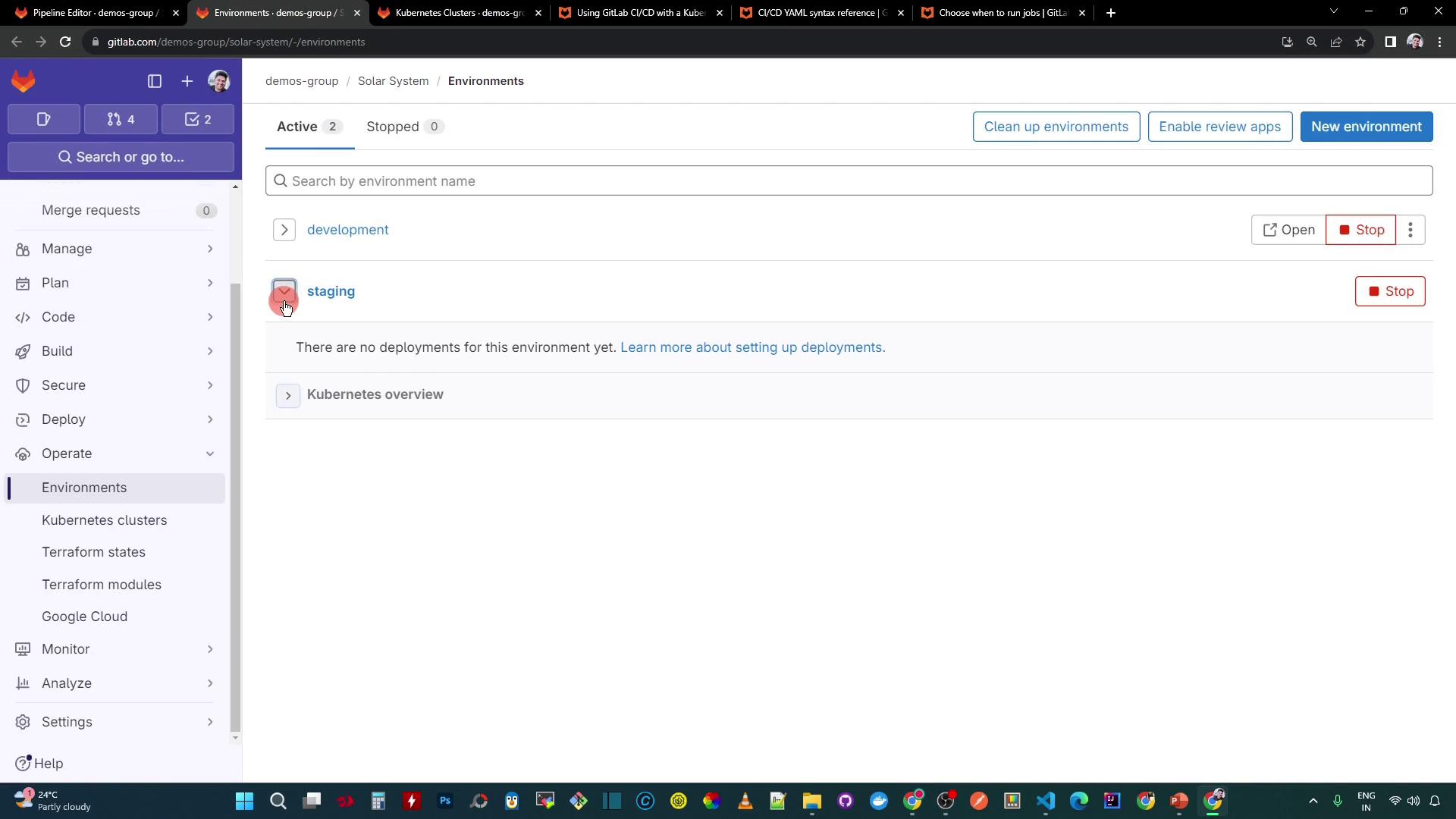
2. Review the Current Development Deploy Job
Our .gitlab-ci.yml defines a k8s_dev_deploy job that uses a self-managed KUBECONFIG. It builds the image, injects secrets, and applies manifests:
variables:
DOCKER_USERNAME: siddhanth67
IMAGE_VERSION: $CI_PIPELINE_ID
K8S_IMAGE: $DOCKER_USERNAME/solar-system:$IMAGE_VERSION
MONGO_URI: mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83j.mongodb.net/superData
MONGO_USERNAME: superuser
MONGO_PASSWORD: $M_DB_PASSWORD
k8s_dev_deploy:
stage: dev-deploy
image: alpine:3.7
before_script:
- wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(wget -q -O - https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
- chmod +x ./kubectl && mv ./kubectl /usr/bin/kubectl
- apk add --no-cache gettext && envsubst -V
script:
- export KUBECONFIG=$DEV_KUBE_CONFIG
- kubectl version -o yaml
- kubectl config get-contexts
- kubectl get nodes
- |
export INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx get svc ingress-nginx-controller \
-o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}")
- echo "Ingress IP: $INGRESS_IP"
- kubectl -n $NAMESPACE create secret generic mongo-db-creds \
--from-literal=MONGO_URI=$MONGO_URI \
--from-literal=MONGO_USERNAME=$MONGO_USERNAME \
--from-literal=MONGO_PASSWORD=$MONGO_PASSWORD \
--save-config --dry-run=client -o yaml \
| kubectl apply -f -
- for f in kubernetes/manifest/*.yaml; do envsubst < $f | kubectl apply -f -; done
environment:
name: development
url: https://$INGRESS_IP.nip.io
artifacts:
reports:
dotenv: app_ingress_url.env
3. Connect the GitLab Kubernetes Agent
In config.yaml, enable CI access so each job automatically receives the Agent’s kubeconfig:
ci_access:
groups:
- id: path/to/group/subgroup
Now $KUBECONFIG is populated by the Agent in every CI job.
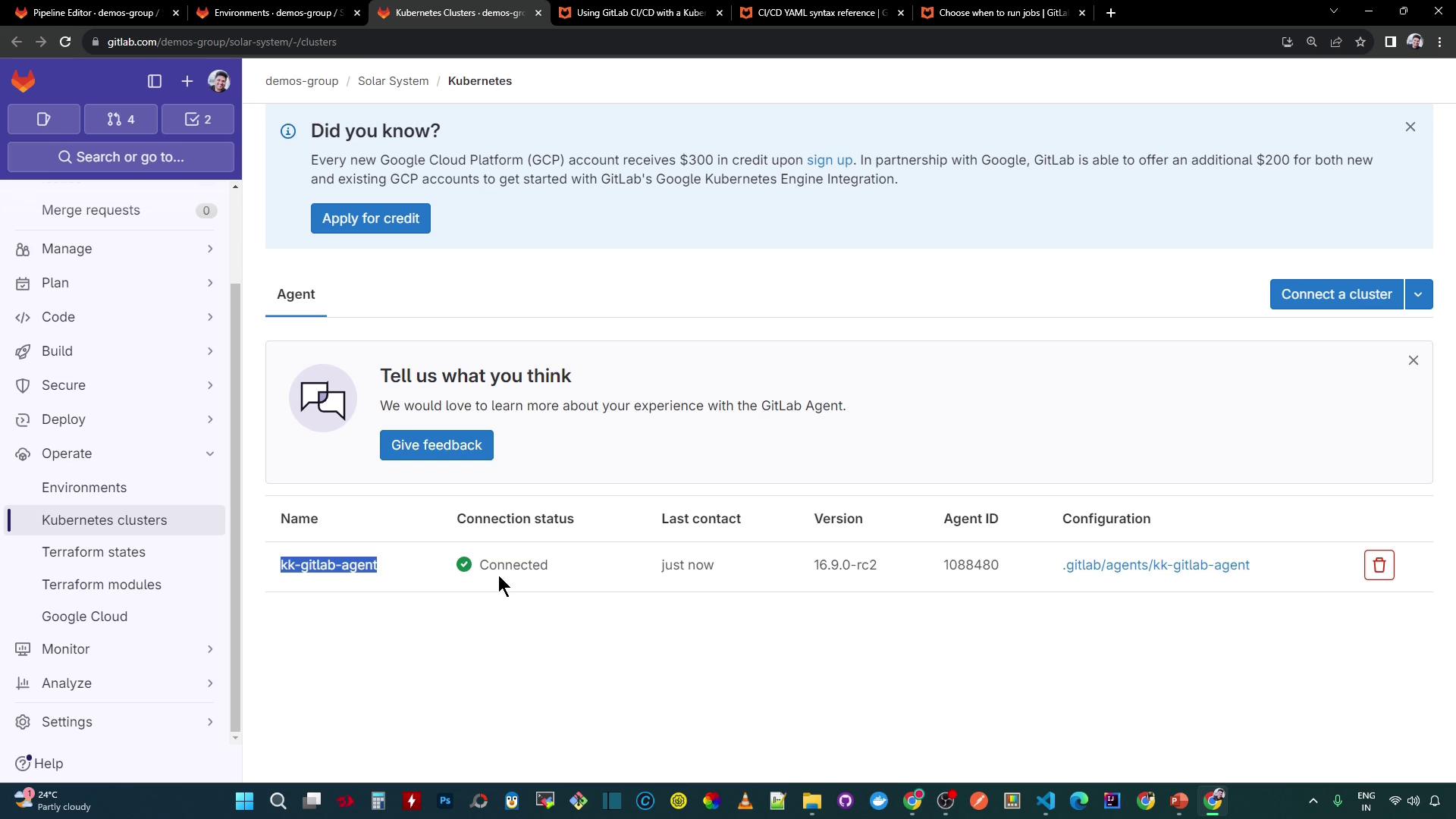
4. Minimal Deploy Example
A concise example using bitnami/kubectl to switch context:
deploy:
image: bitnami/kubectl:latest
entrypoint: ['']
script:
- kubectl config get-contexts
- kubectl config use-context path/to/agent/project:agent-name
- kubectl get pods
For more details, see the GitLab Kubernetes deployments guide.
5. Add the Staging Deploy Job
Copy the k8s_dev_deploy job, rename it to k8s_stage_deploy, and update it to use the Agent’s $KUBECONFIG. Remove custom kubeconfig logic. Add when: manual so it only runs on demand.
Note
Ensure you have added stage-deploy to the top-level stages list and set NAMESPACE: staging.
k8s_stage_deploy:
stage: stage-deploy
image: alpine:3.7
when: manual
before_script:
- wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/$(wget -q -O - https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
- chmod +x ./kubectl && mv ./kubectl /usr/bin/kubectl
- apk add --no-cache gettext && envsubst -V
script:
# Inspect and switch the Agent context
- cat $KUBECONFIG
- kubectl config get-contexts
- kubectl config use-context demos-group/solar-system:kk-gitlab-agent
- kubectl get po -A
# Deploy application
- |
export INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx get svc ingress-nginx-controller \
-o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}")
- echo "Ingress IP: $INGRESS_IP"
- kubectl -n $NAMESPACE create secret generic mongo-db-creds \
--from-literal=MONGO_URI=$MONGO_URI \
--from-literal=MONGO_USERNAME=$MONGO_USERNAME \
--from-literal=MONGO_PASSWORD=$MONGO_PASSWORD \
--save-config --dry-run=client -o yaml \
| kubectl apply -f -
- for f in kubernetes/manifest/*.yaml; do envsubst < $f | kubectl apply -f -; done
- kubectl -n $NAMESPACE get all,secret,ing
- echo "INGRESS_URL=$(kubectl -n $NAMESPACE get ing \
-o jsonpath="{.items[0].spec.tls[0].hosts[0]}")" >> app_ingress_url.env
artifacts:
reports:
dotenv: app_ingress_url.env
environment:
name: staging
url: https://${INGRESS_URL}
6. Add Integration Tests for Staging
Verify your /live and /ready health endpoints:
k8s_stage_integration_testing:
stage: stage-deploy
image: alpine:3.7
needs:
- k8s_stage_deploy
before_script:
- apk add --no-cache curl jq
script:
- echo "Testing URL: $INGRESS_URL"
- curl -s -k https://$INGRESS_URL/live | jq -r .status | grep -i live
- curl -s -k https://$INGRESS_URL/ready | jq -r .status | grep -i ready
7. Pipeline Visualization
Your CI pipeline now spans four stages (test, containerization, dev-deploy, stage-deploy) and includes manual promotion:

8. Manual Promotion in GitLab
The k8s_stage_deploy job is set to manual:
9. Trigger the Manual Job
Navigate to CI/CD → Pipelines, then click the ▶️ icon next to k8s_stage_deploy. You can override variables before starting:
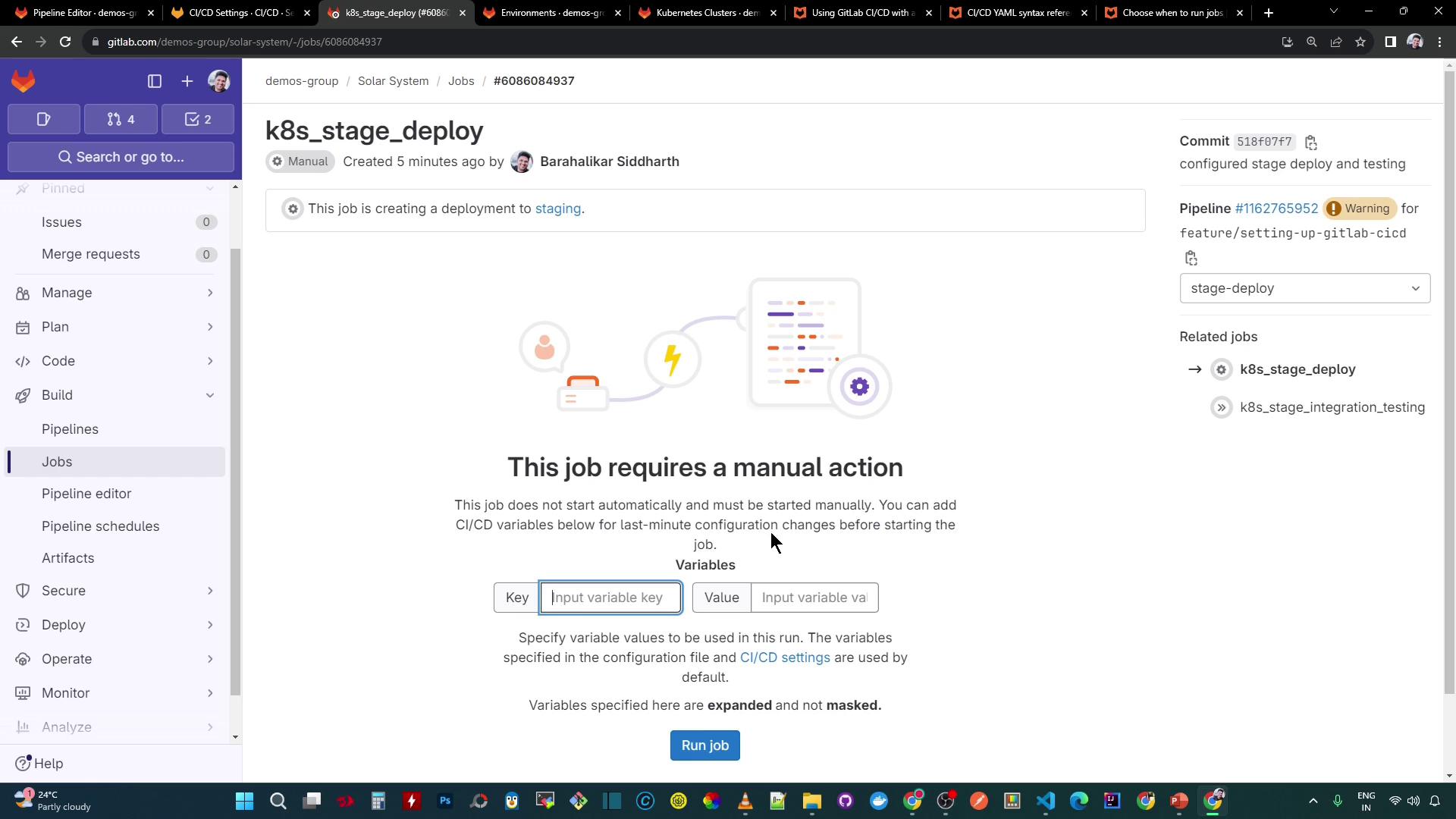
Once k8s_stage_deploy completes, k8s_stage_integration_testing will run automatically.
10. Inspect the Deployment Logs
Important log snippets include:
$ cat $KUBECONFIG
apiVersion: v1
kind: Config
...
contexts:
- name: demos-group/solar-system:kk-gitlab-agent
context:
cluster: gitLab
user: agent:108840
$ kubectl config use-context demos-group/solar-system:kk-gitlab-agent
Switched to context "demos-group/solar-system:kk-gitlab-agent".
$ kubectl get po -A
...
$ export INGRESS_IP=$(kubectl -n ingress-nginx get svc ingress-nginx-controller \
-o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}")
$ echo $INGRESS_IP
139.84.208.48
$ kubectl -n staging create secret generic mongo-db-creds ... | kubectl apply -f -
secret/mongo-db-creds created
$ kubectl -n staging get all,secret,ing
...
You should see your pods, services, deployments, and replicasets in staging.
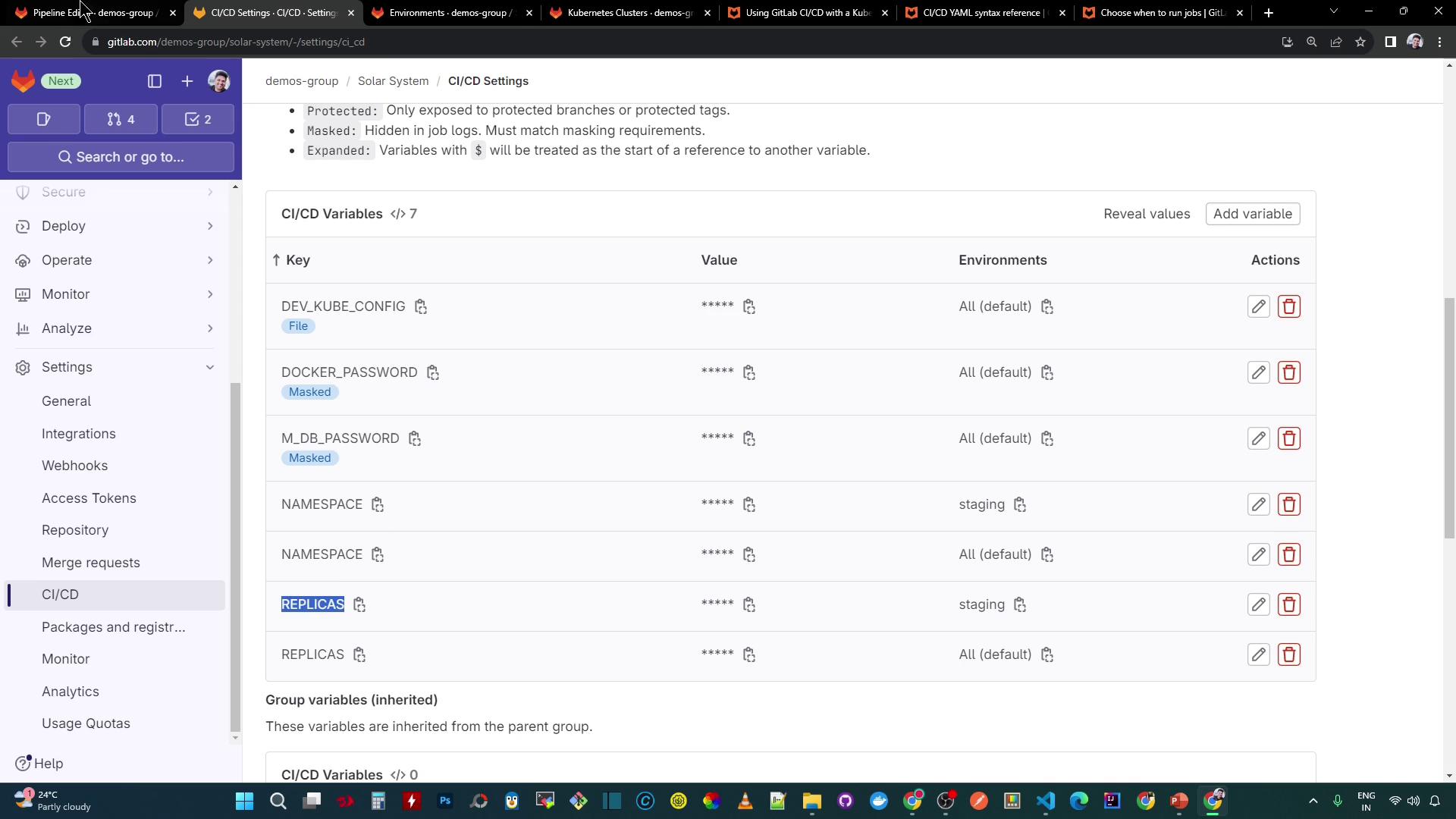
11. Review CI/CD Environment Variables
In Settings → CI/CD, scope variables to your environments (e.g., staging):
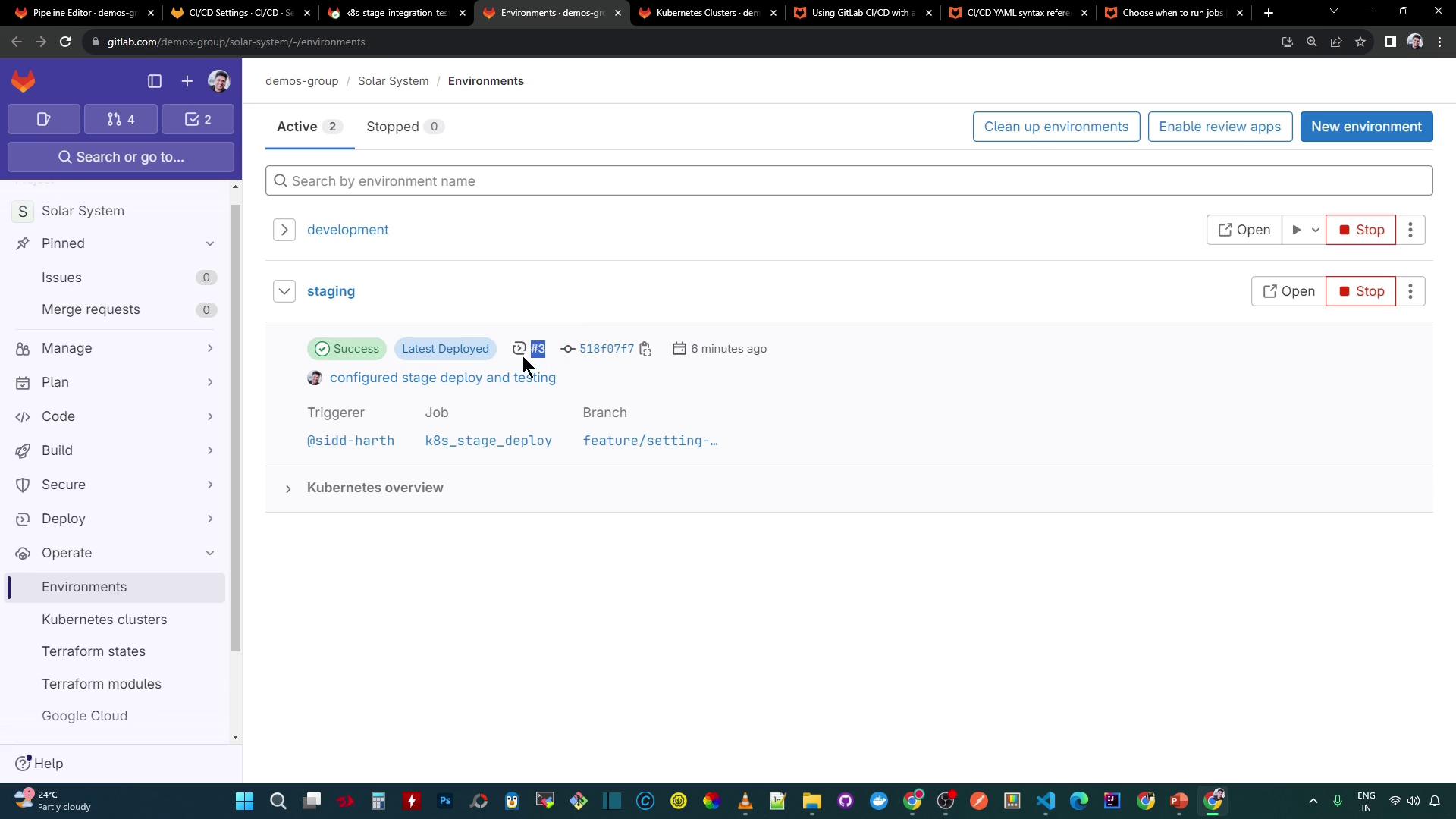
12. Validate Deployment in GitLab UI
The Environments dashboard now reflects your successful staging deploy:
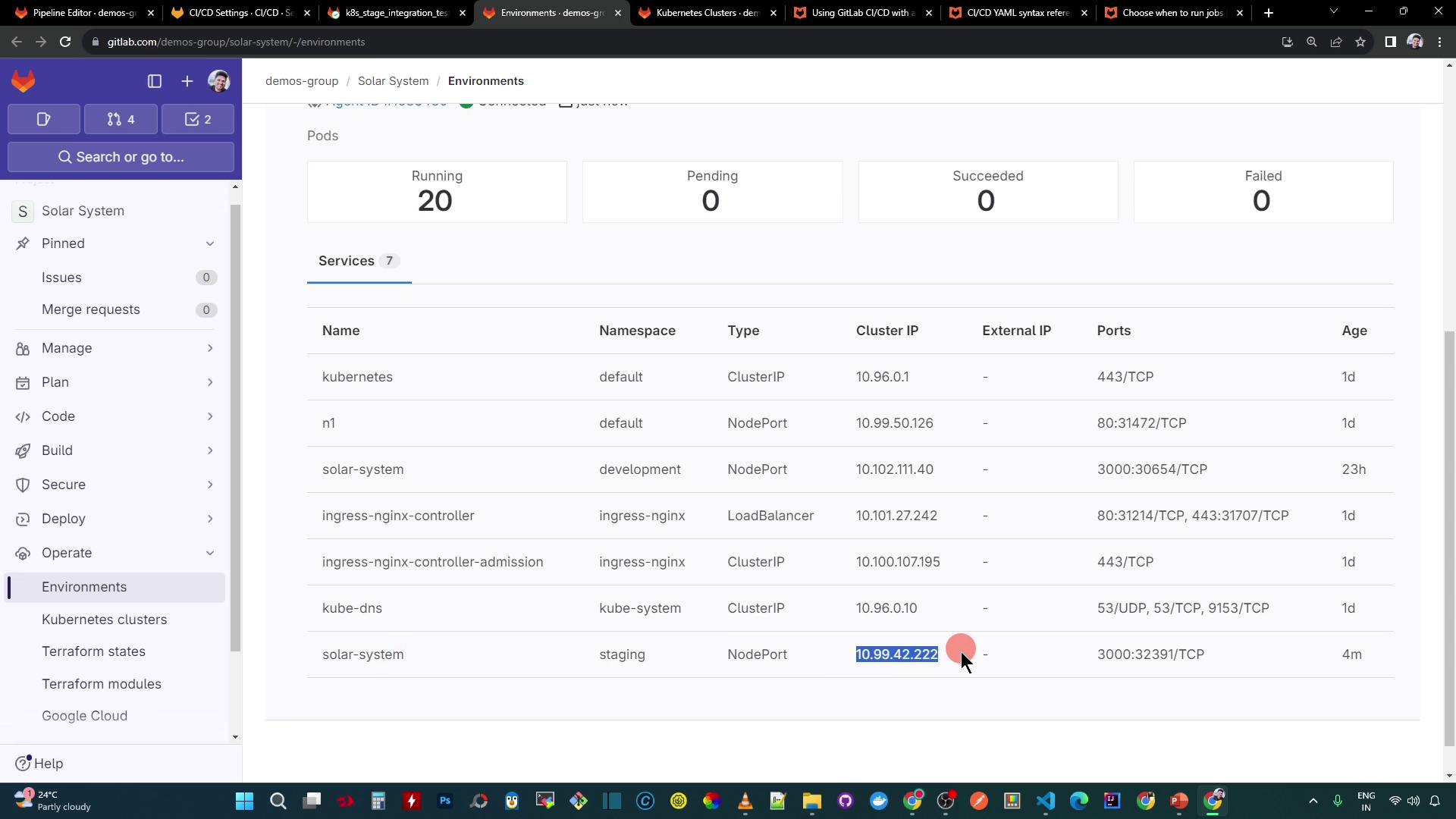
Under Kubernetes services, your service appears with its external IP:
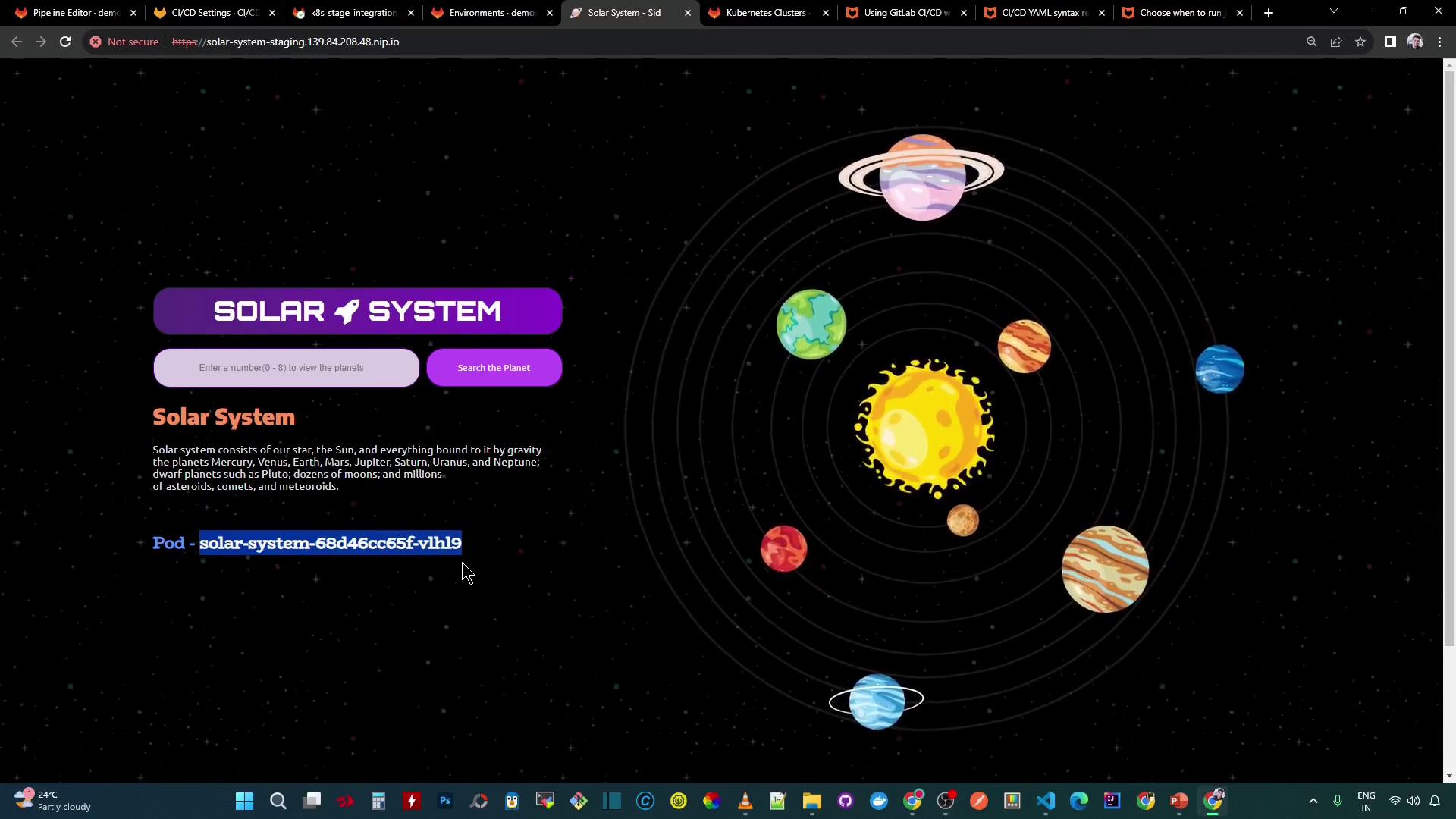
Opening the application displays the Solar System UI:
13. Confirm Locally via kubectl
Finally, verify in your terminal:
kubectl -n staging get all
You should now see pods, services, deployments, and replicasets matching your manifests.
By leveraging the GitLab Kubernetes Agent, you’ve simplified authentication, enforced manual approvals for staging, and successfully deployed your application to the staging namespace.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab