GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Self Managed Runners
Install Group Runner on Linux Machine with Docker Executor
Enable all projects in a GitLab group to share a single runner powered by Docker. This guide walks you through creating a group-level runner, registering it on a Linux host, and verifying its status.
Table of Contents
- Create a Group-Level Runner
- Register the Runner on Your Linux Host
- Check Runner Status in GitLab
- Review the Runner Configuration
- Verify Runner in a Project
- Links and References
1. Create a Group-Level Runner
Sign in to GitLab and navigate to your target group (e.g.,
demos).In the left sidebar, select CI/CD > Runners.
Under Group runners, click New group runner.
Enter the runner details:
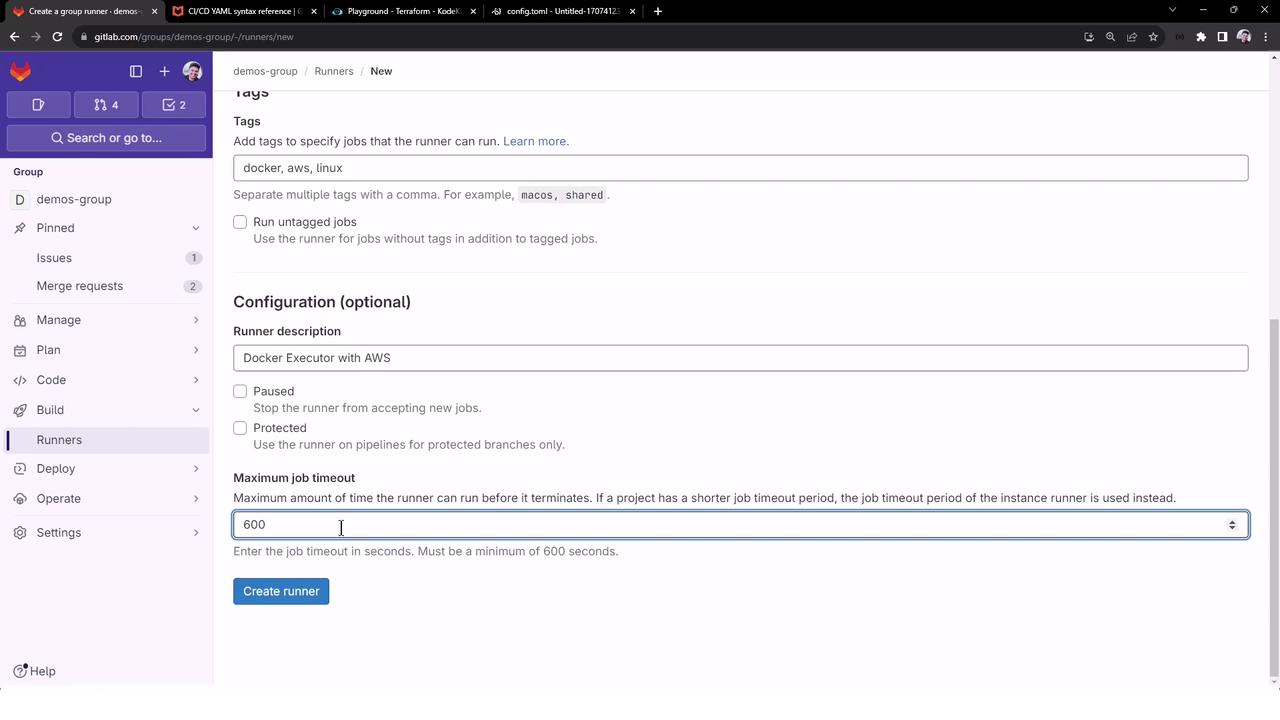
Field Value Runner description Docker executor with AWS on Linux Tags docker,aws,linuxMaximum job timeout 10 minutes 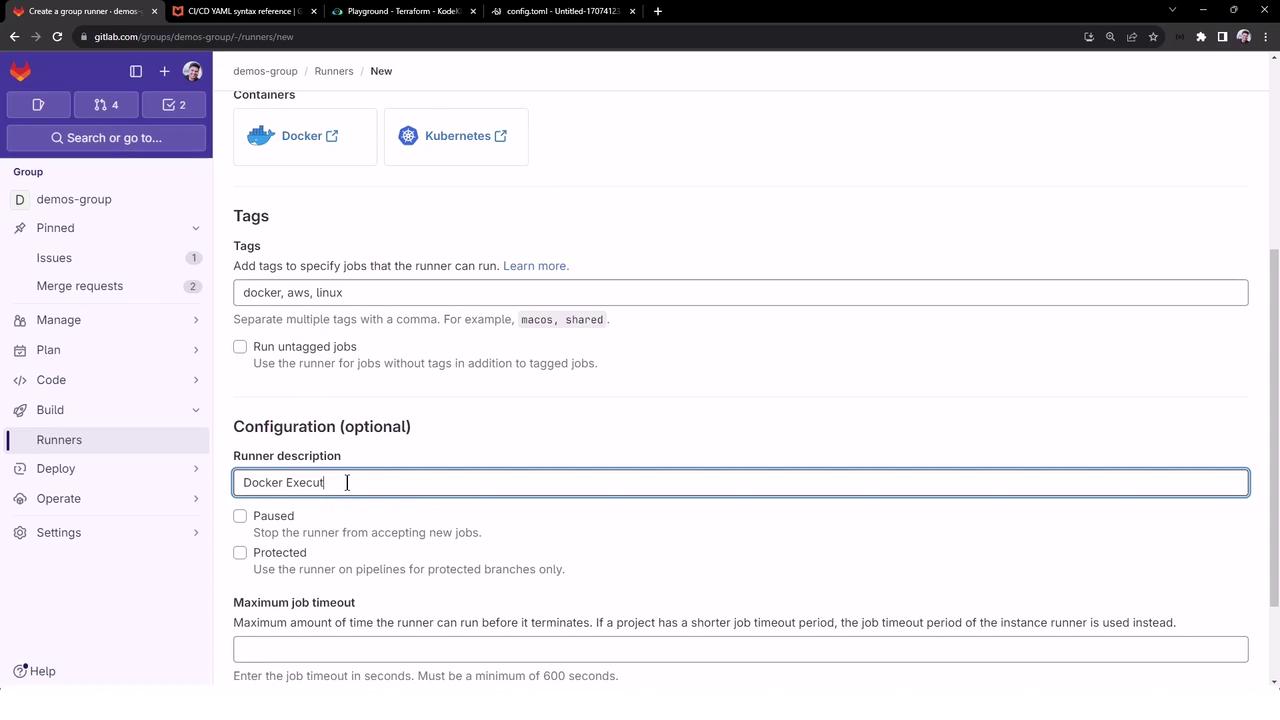
Click Create runner. GitLab will display a registration token—copy it for the next step.
Warning
Keep your registration token secure. Anyone with this token can register additional runners to your group.
2. Register the Runner on Your Linux Host
If GitLab Runner is not yet installed, install and start it as a system service:
# Download the latest GitLab Runner binary
sudo curl -L --output /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner \
https://gitlab-runner-downloads.s3.amazonaws.com/latest/binaries/gitlab-runner-linux-amd64
# Make it executable
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner
# Create a dedicated service user
sudo useradd --comment 'GitLab Runner' --create-home gitlab-runner --shell /bin/bash
# Install and start GitLab Runner as a service
sudo gitlab-runner install --user=gitlab-runner --working-directory=/home/gitlab-runner
sudo gitlab-runner start
Register the group runner using the token you copied:
gitlab-runner register \
--url https://gitlab.com \
--token <YOUR_REGISTRATION_TOKEN>
When prompted:
- Enter a name for the runner:
aws-docker-runner - Enter an executor:
docker - Enter the default Docker image:
ruby:2.7
Note
You can customize the default image per job in your .gitlab-ci.yml using the image: keyword.
3. Check Runner Status in GitLab
After registration, GitLab lists the runner under Group > CI/CD > Runners, but it will show “Never contacted” until the service connects.
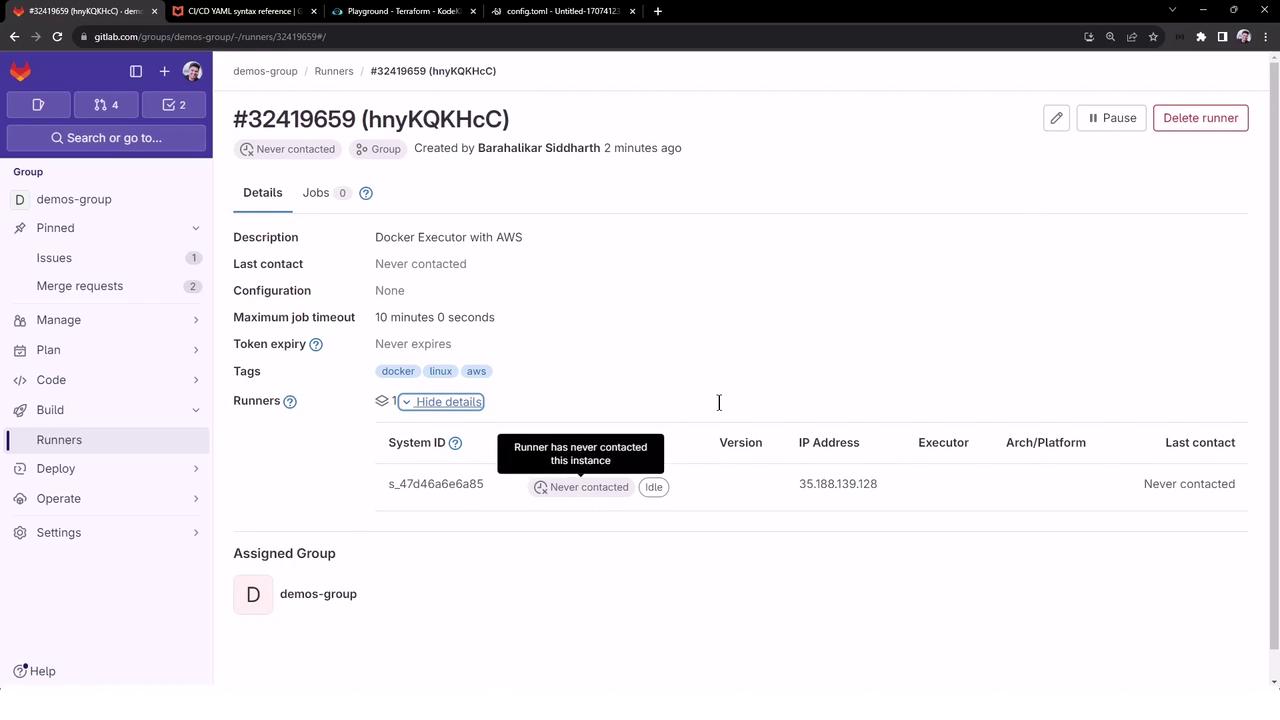
On your Linux host, verify both shell and Docker runners are registered:
gitlab-runner list
# Sample output:
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux pid=123610 revision=c72a09b6 version=16.8.0
ConfigFile=/etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml
Executor=shell Token=glrt-3iCBsGsPFN6WBGmaps5B URL=https://gitlab.com
Executor=docker Token=glrt-hnyKQKHcCoxosWLEssKc URL=https://gitlab.com
Once the runner service starts successfully, the status will update to online in GitLab.
4. Review the Runner Configuration
Open /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml to inspect both runners:
concurrent = 1
check_interval = 0
[[runners]]
name = "nodejs-runner"
url = "https://gitlab.com"
id = 32418121
token = "glrt-3iCBsGsPFN6WBGmaps5B"
executor = "shell"
cache_dir = "/home/gitlab-runner/builds"
[[runners]]
name = "aws-docker-runner"
url = "https://gitlab.com"
id = 32418122
token = "glrt-hnyKQKHcCoxosWLEssKc"
executor = "docker"
[runners.cache]
MaxUploadedArchiveSize = 0
[runners.docker]
tls_verify = false
image = "ruby:2.7"
privileged = false
disable_entrypoint_overwrite = false
oom_kill_disable = false
disable_cache = false
volumes = ["cache"]
shm_size = 0
network_mtu = 0
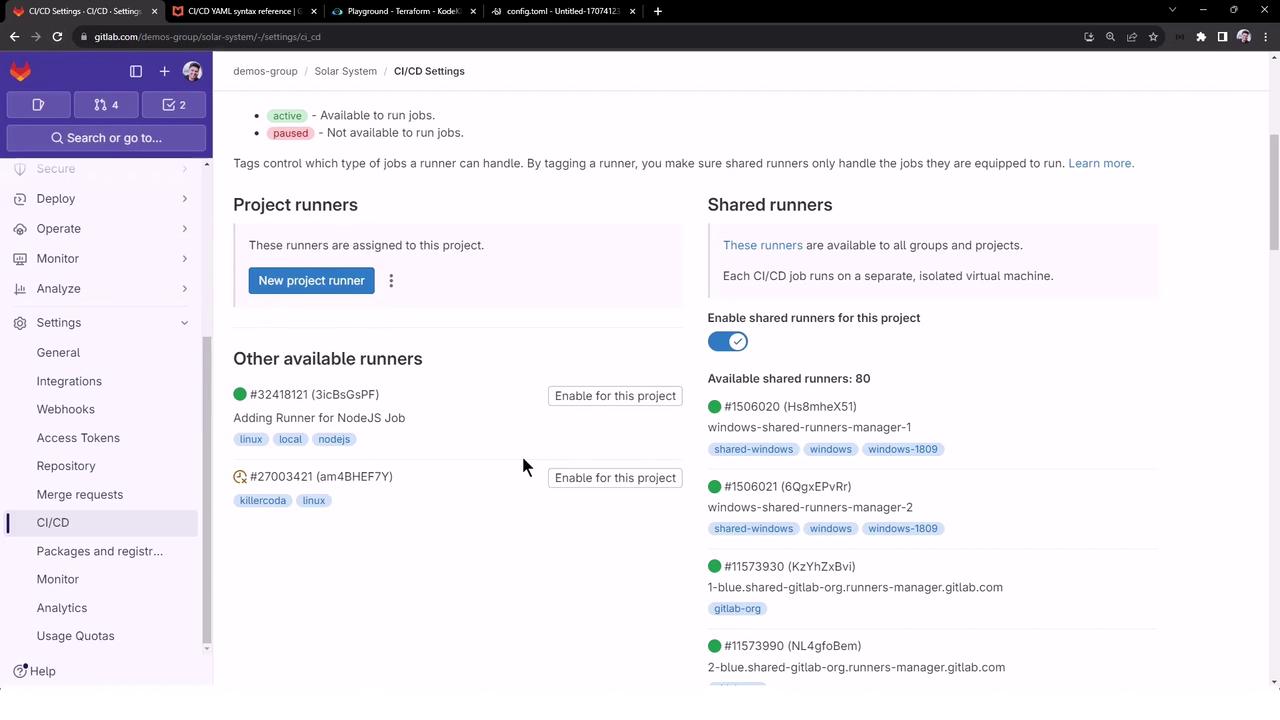
5. Verify Runner in a Project
The group runner is now available to every project in the demos group.
- Open a project (e.g., Solar System).
- Navigate to Settings > CI/CD > Runners.
- Optionally disable shared runners to ensure jobs use your group runner exclusively.
Jobs tagged with docker, aws, and linux will now execute on your Docker-based group runner.
6. Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content