GitLab CI/CD: Architecting, Deploying, and Optimizing Pipelines
Self Managed Runners
Run Jobs on the installed Shell Executor
In this guide, you’ll learn how to configure and optimize a CI/CD pipeline on a self-hosted GitLab Runner using the Shell executor. We’ll walk through:
- Defining a basic pipeline.
- Selecting your self-managed runner with tags.
- Troubleshooting shell-profile issues.
- Installing Node.js on the runner VM.
- Caching npm dependencies between runs.
- Customizing the runner’s cache directory.
1. Basic Pipeline Configuration
Begin by creating a simple .gitlab-ci.yml that runs unit tests against your Node.js project. This example sets up environment variables, uses stages, and caches node_modules to speed up subsequent runs.
workflow:
name: Shell Executor Demo
variables:
MONGO_URI: 'mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData'
MONGO_USERNAME: superuser
MONGO_PASSWORD: SuperPassword
stages:
- test
unit_test:
stage: test
cache:
policy: pull-push
key:
files:
- package-lock.json
prefix: node-modules
paths:
- node_modules
before_script:
- npm install
script:
- npm test
| Section | Purpose |
|---|---|
variables | Secure strings for database connection |
stages | Defines workflow steps (only test here) |
cache | Speeds up npm install by reusing modules |
before_script | Pre-test setup commands |
script | Actual test command |
2. Selecting the Self-Managed Runner
To ensure jobs land on your Shell executor, add the same tags you used during runner registration:
unit_test:
tags:
- nodejs
- linux
- local
stage: test
cache:
policy: pull-push
key:
files:
- package-lock.json
prefix: node-modules
paths:
- node_modules
before_script:
- npm install
script:
- npm test
Note
Runner tags must match exactly (case-sensitive). Review Settings > CI/CD > Runners in your project to confirm tag names.
Your project’s CI/CD settings should display your tagged runner:
After committing these changes, GitLab will automatically trigger a new pipeline.
3. Troubleshooting Shell-Executor Profiles
If the job fails during prepare environment, you might see:
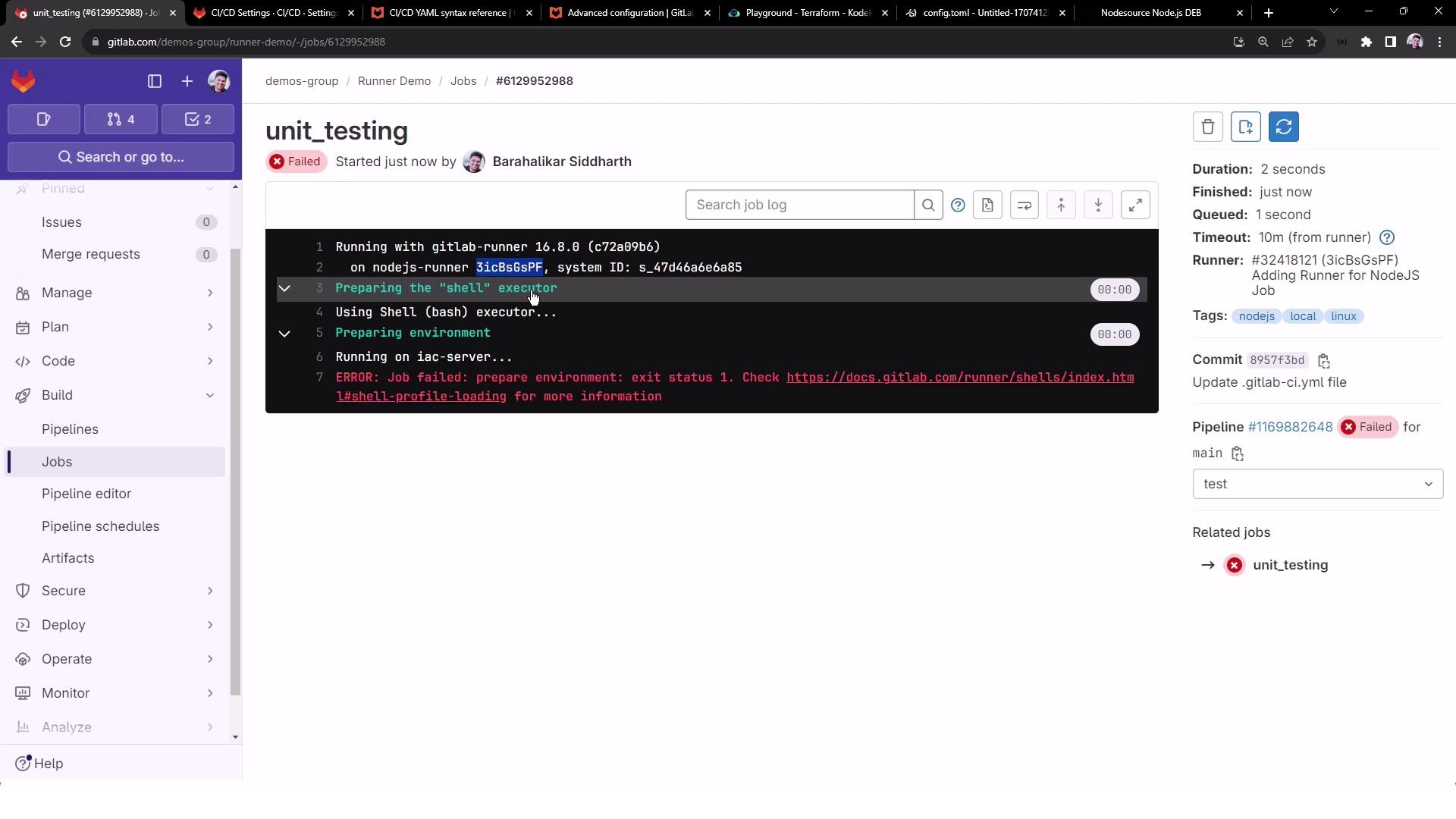
Preparing environment
Running on iac-server...
ERROR: Job failed: prepare environment: exit status 1.
Check https://docs.gitlab.com/runner/shells/index.html#shell-profile-loading
This usually means your shell’s logout or profile scripts are clearing the console. On the runner VM, edit ~/.bash_logout:
# ~/.bash_logout: executed when a login shell exits
# if [ "$SHLVL" -eq '1' ]; then
# [ -x /usr/bin/clear_console ] && /usr/bin/clear_console -q
# fi
Comment out any clear_console lines, commit the update, and rerun the pipeline.
Warning
Modifying shell profiles on production runners can affect all jobs. Always back up files before editing.
4. Installing Node.js on the Runner
Since the Shell executor uses your VM’s environment, you must install Node.js globally:
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg
# Add NodeSource repository (replace 'nodistro' with your distro codename, e.g., 'jammy')
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/gpgkey/nodesource-repo.gpg.key \
| sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg
NODE_MAJOR=20
echo "deb [signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/nodesource.gpg] \
https://deb.nodesource.com/node_${NODE_MAJOR}.x nodistro main" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.list
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y nodejs
Verify:
node -v # e.g., v20.x.x
npm -v # e.g., 9.x.x
Rerun your pipeline—npm install and npm test should now succeed.
5. Caching Dependencies for Faster Builds
Your pipeline’s cache settings will automatically save node_modules on success:
Saving cache for successful job
Creating cache node-modules-<hash>-protected...
node_modules: found 5735 matching files
Created cache locally
Inspect the runner’s cache directory:
cd /home/gitlab-runner/cache/<project-path>/node-modules-<hash>-protected
unzip cache.zip
ls node_modules
On future runs, the cache is restored:
Restoring cache
Successfully extracted cache
$ npm install
up to date in 1s
| Cache Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| pull-push | Downloads & uploads cache for every job run |
| key | Uniquely identifies cache based on package-lock |
| paths | Directories to cache (e.g., node_modules) |
6. Customizing the Runner’s Cache Directory
By default, caches live under GitLab Runner’s home folder. To change it, update /etc/gitlab-runner/config.toml:
[[runners]]
name = "nodejs-runner"
url = "https://gitlab.com"
id = 32418121
token = "glrt-..."
executor = "shell"
cache_dir = "/home/gitlab-runner/builds" # custom path
[runners.cache]
MaxUploadedArchiveSize = 0
Restart the service:
sudo gitlab-runner restart
Subsequent cache archives will appear under your new cache_dir:
For a deep dive into advanced runner settings, consult the official docs:
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content