Introduction to OpenAI
Introduction to AI
Integrating Multimodal Inputs in Generative AI
In this lesson, you’ll learn how generative AI models process and synthesize multiple data types—text, images, charts, audio, and video—to deliver richer, context-aware outputs. We’ll cover:
- Defining multimodal inputs
- Core integration techniques
- Key applications and examples
- Challenges and best practices
- Future directions
1. Overview of a Multimodal AI Model
The diagram below shows how a multimodal AI model ingests text, images, and charts, then fuses them into a unified representation to power diverse outcomes—answers to complex questions, mixed-media content, and detailed insights.
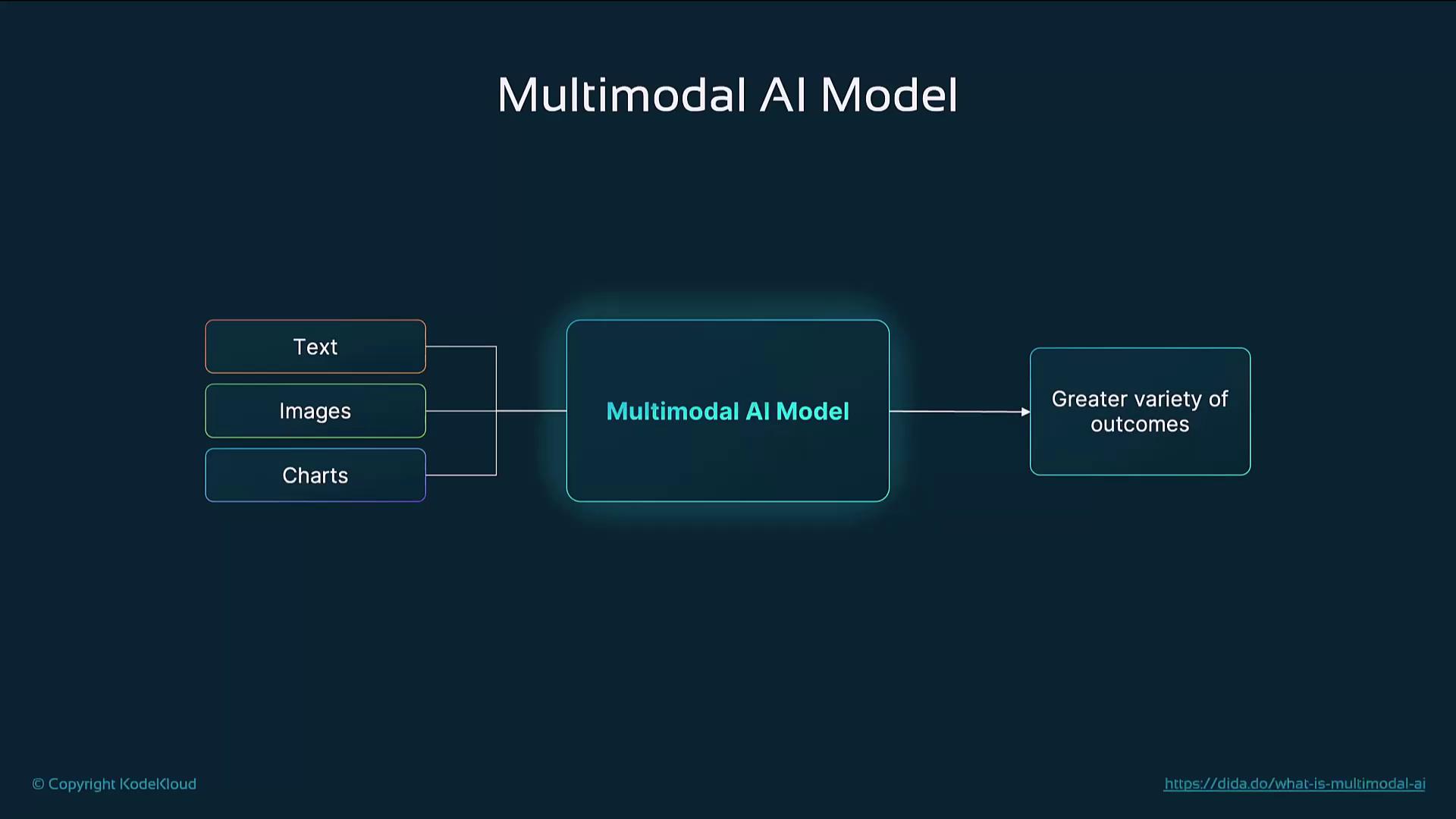
2. What Are Multimodal Inputs?
Multimodal inputs combine distinct data streams—text, images, audio, and video—into a single AI pipeline. Unlike single‐modality models that learn from one data type at a time, multimodal models leverage cross-modal relationships to generate more meaningful, context‐rich outputs.
For example, given an image of a dog and the prompt “a dog playing fetch,” a multimodal model can produce:
- A vivid narrative describing the scene
- An enhanced or stylized version of the image
- A brief animation simulating the dog’s play
Below is a visual comparison of single‐modality versus multimodal architectures:
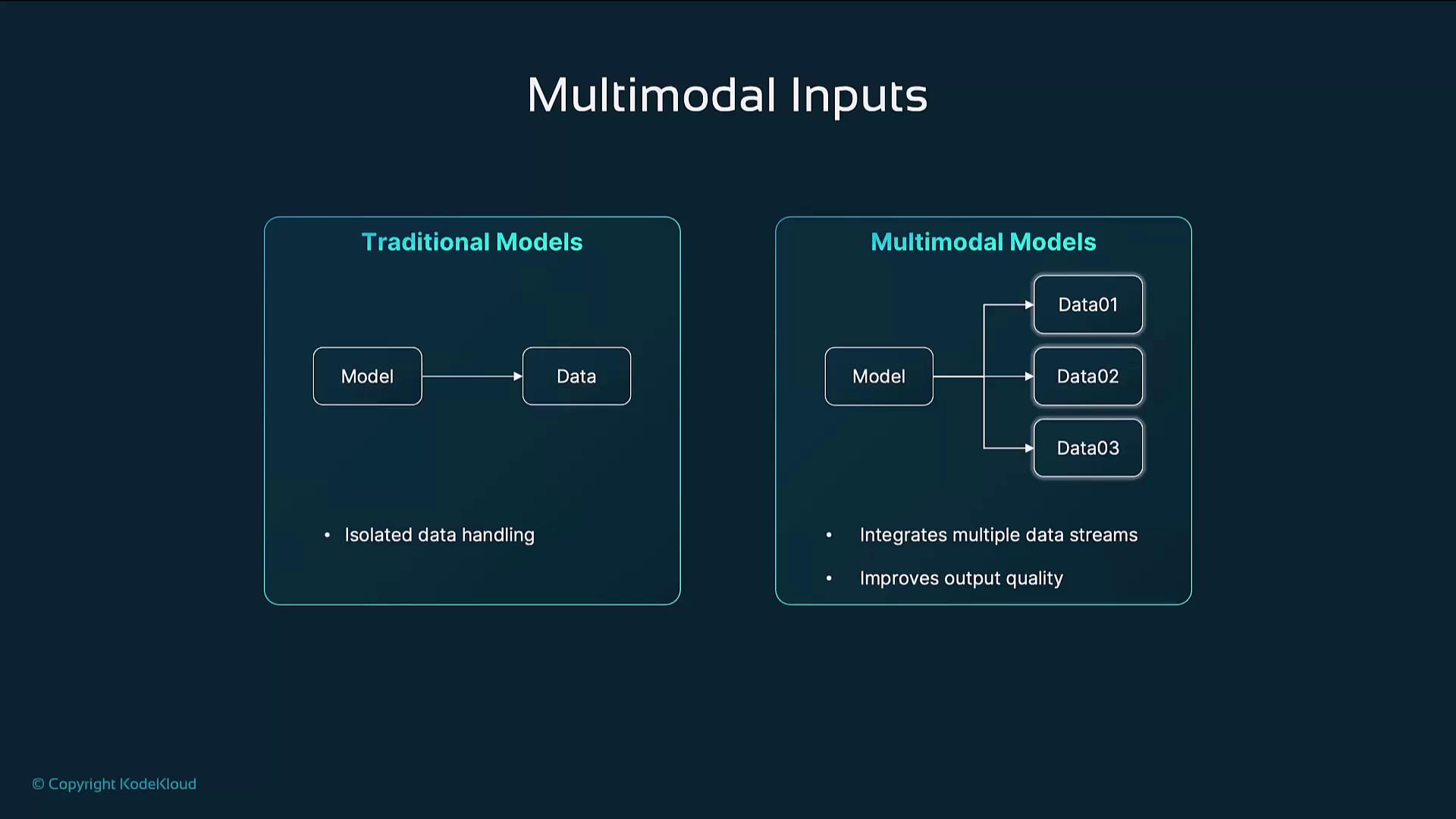
3. Techniques for Integrating Multimodal Inputs
3.1 Shared Embedding Space
Map each modality into a common vector space so that semantic features align across data types. For instance, CLIP encodes text descriptions and images into the same embedding space, enabling tasks like text-to-image retrieval or zero-shot classification.

Note
A well-designed shared embedding space ensures that similar concepts—across words and pixels—occupy nearby positions, improving retrieval and generation tasks.
3.2 Cross-Attention Mechanisms
Cross-attention layers let the model highlight relevant segments in one modality while processing another. In image captioning, the text generator “attends” to critical image regions. DALL·E uses cross-attention to align prompts like “a two-story house shaped like a shoe” with the correct visual features during synthesis.
3.3 Multimodal Transformers
Extend transformer architectures by assigning separate encoders for each modality, then fuse their outputs into a joint representation. Models like VisualGPT or Flamingo ingest text alongside images to generate captions, stories, or even novel visuals.

4. Applications of Multimodal Generative AI
| Application | Description | Example Model |
|---|---|---|
| Text-to-Image Generation | Converts textual prompts into high-quality images by linking semantic embeddings with pixels. | DALL·E |
| Video Generation | Produces animated sequences from a static image plus text, adding motion and narrative context. | vid2vid variants |
| Visual Question Answering (VQA) | Answers user queries by interpreting images or videos in tandem with natural language questions. | VQA systems |
| Multimodal Virtual Assistance | Combines voice commands and visual inputs (e.g., photos) to perform context-aware tasks. | Smart home agents |
5. Challenges and Considerations
Multimodal integration comes with its own set of hurdles:
- Alignment of Modalities
Synchronizing embeddings across text, images, audio, and video can be complex. - Computational Complexity
Training and inference on multiple data streams require substantial GPU/TPU resources. - Data Availability
Building large, well-curated multimodal datasets is time-intensive and expensive.

Warning
Insufficient alignment or low-quality data in any modality can degrade overall performance. Ensure balanced, high-fidelity datasets before training.
6. Future Directions
Research is driving toward more immersive and responsive multimodal experiences:
Real-Time Multimodal Interaction
Instantaneous responses to combined voice, gesture, and visual cues—ideal for gaming and AR/VR.Advanced Multimodal Creativity
Generating fully cohesive artworks that blend text, images, audio, and video into unified narratives.

References
- OpenAI CLIP
- DALL·E
- vid2vid: High-Resolution Video-to-Video Translation
- Flamingo: a Visual Language Model
Watch Video
Watch video content