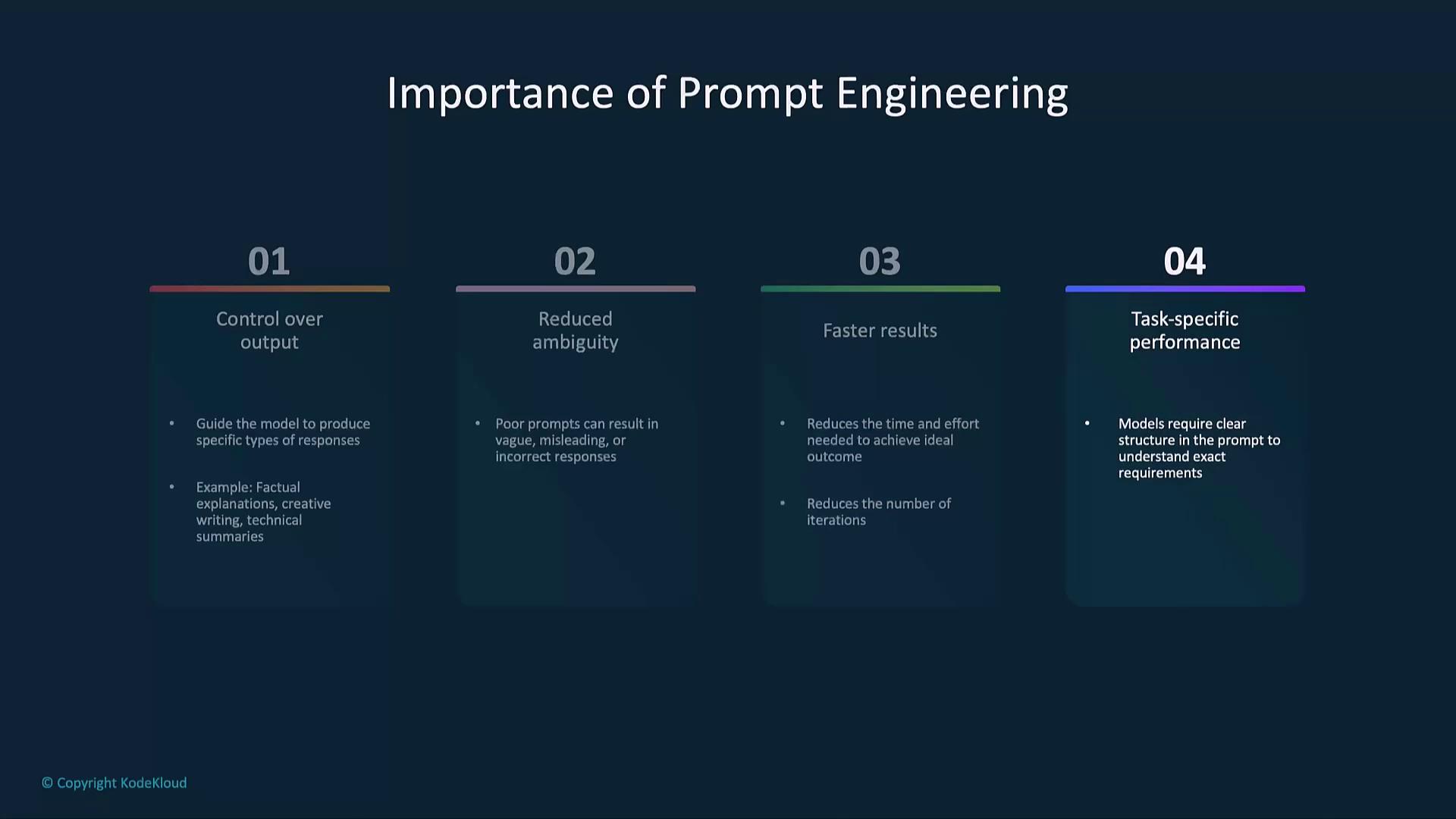
Why Prompt Engineering Matters
Generative AI can tackle diverse tasks, but the clarity and structure of your prompt determine the quality of the response:- Control over tone and format
- Precision to reduce vague answers
- Faster convergence on desired results
- Enhanced performance in specialized domains (e.g., legal, technical)
Core Principles
Clarity & Specificity
Make requests explicit to avoid off-target or incomplete answers.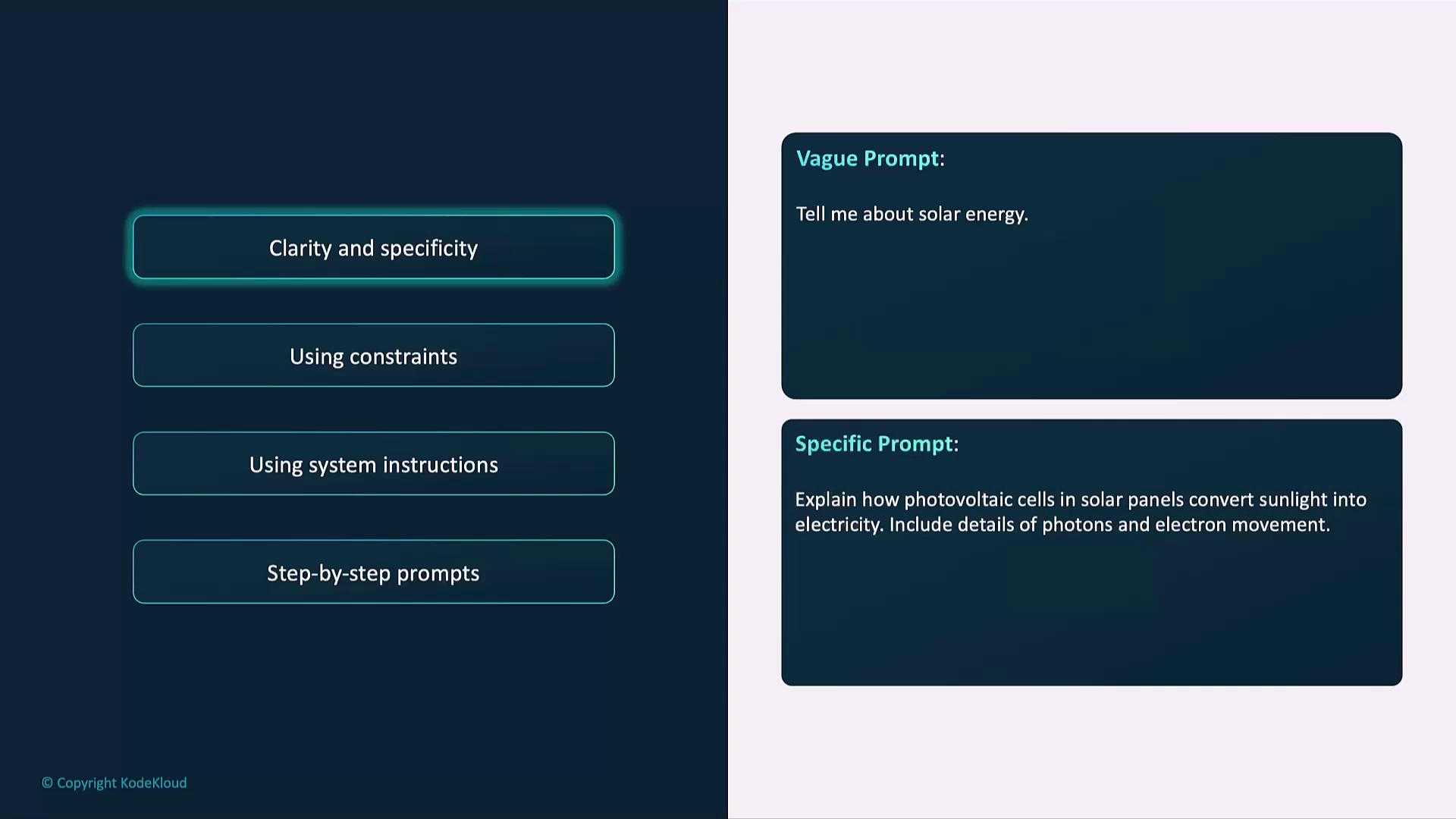
Using Constraints
Define style, length, or format to shape output consistency.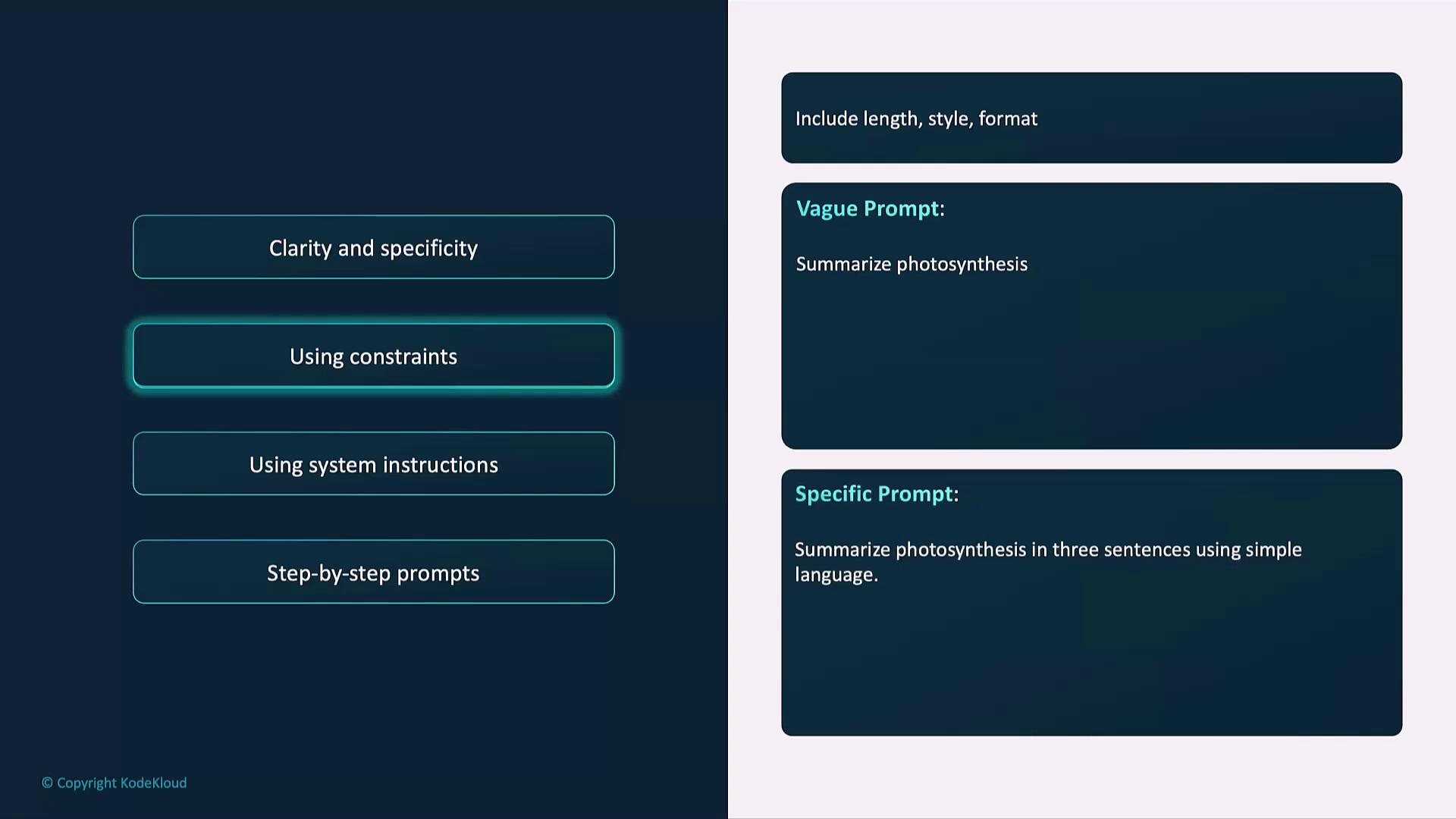
Use bullet points, word limits, or tone specifications (e.g., formal vs. conversational) to guide the model’s style.
System Messages
In chat-based setups, system instructions define the model’s role and behavior before user input.
Step-by-Step Prompts
Break down complex tasks into sequential steps for transparency and logical flow. Example:Advanced Techniques
Few-Shot Learning
Provide annotated examples within the prompt to demonstrate desired format and style.
Zero-Shot Prompts
Rely on explicit instructions without examples—best for straightforward tasks. Example:Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Encourage the model to “think aloud,” revealing intermediate reasoning steps for complex queries.
Common Pitfalls & Solutions
Avoid these mistakes to get the most reliable and focused outputs.
| Mistake | Why It Happens | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Vague prompts | Too broad or unspecific | Specify topic, audience, and depth requirements |
| Missing constraints | No length, tone, or format guidelines | Add word limits, bullet points, or style instructions |
| Untested parameters | Default settings (temperature, top_p) may not suit task | Experiment with lower temperature for accuracy, higher for creativity |
| Ignoring context | Critical details left out | Provide background: audience, purpose, format, and relevant data |