return (redirect) and rewrite directives to forward requests, enforce HTTPS, and transform URLs on the fly. Whether you’re migrating a domain, cleaning up paths, or preserving legacy links, these patterns will help you maintain SEO value and user experience.
Table of Contents
- Why Redirect vs Rewrite?
- 1. Redirecting with
return - 2. Common HTTP Status Codes
- 3. Transforming URLs with
rewrite - Links and References
Why Redirect vs Rewrite?
- Redirect (
return) issues an HTTP status code (e.g., 301) back to the client and changes what appears in their browser’s address bar. - Rewrite silently alters the URI before Nginx processes it, keeping the user’s URL intact.
1. Redirecting with return
1.1. Entire Domain Redirect
To forward every request from one domain to another: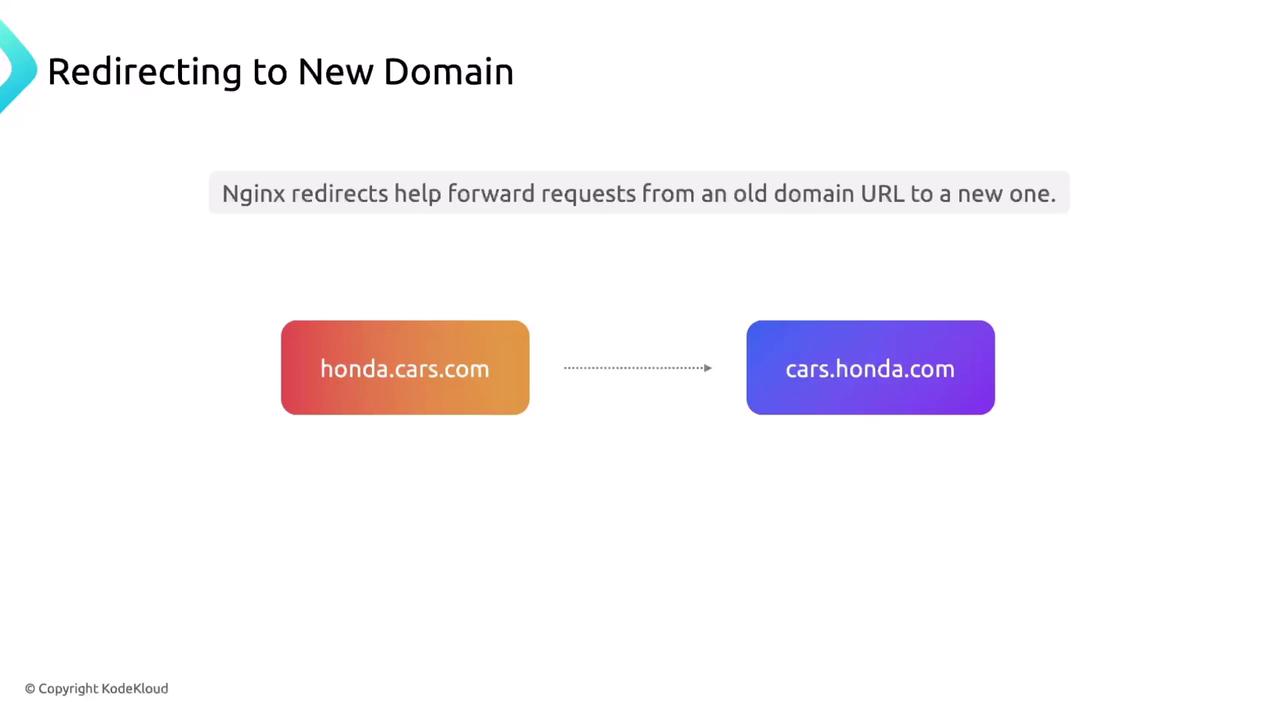
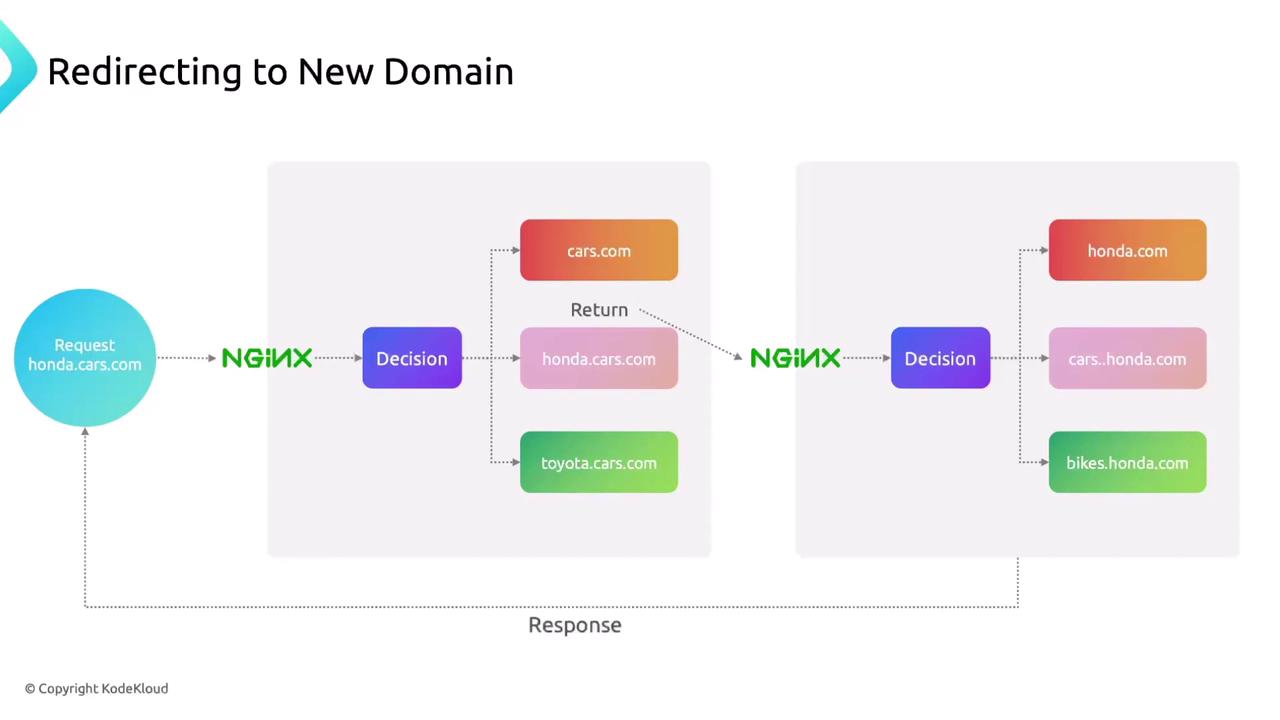
Use
301 for permanent redirects to transfer SEO equity. For temporary redirects, replace 301 with 302.1.2. HTTP → HTTPS Redirect
Force all HTTP traffic to HTTPS:$host becomes the requested domain name, and $request_uri includes the full path and query string.

1.3. Single-Page Redirect
For path-specific forwarding, wrap only that URI:2. Common HTTP Status Codes
Inspect redirects and responses in your browser’s DevTools (Network tab):
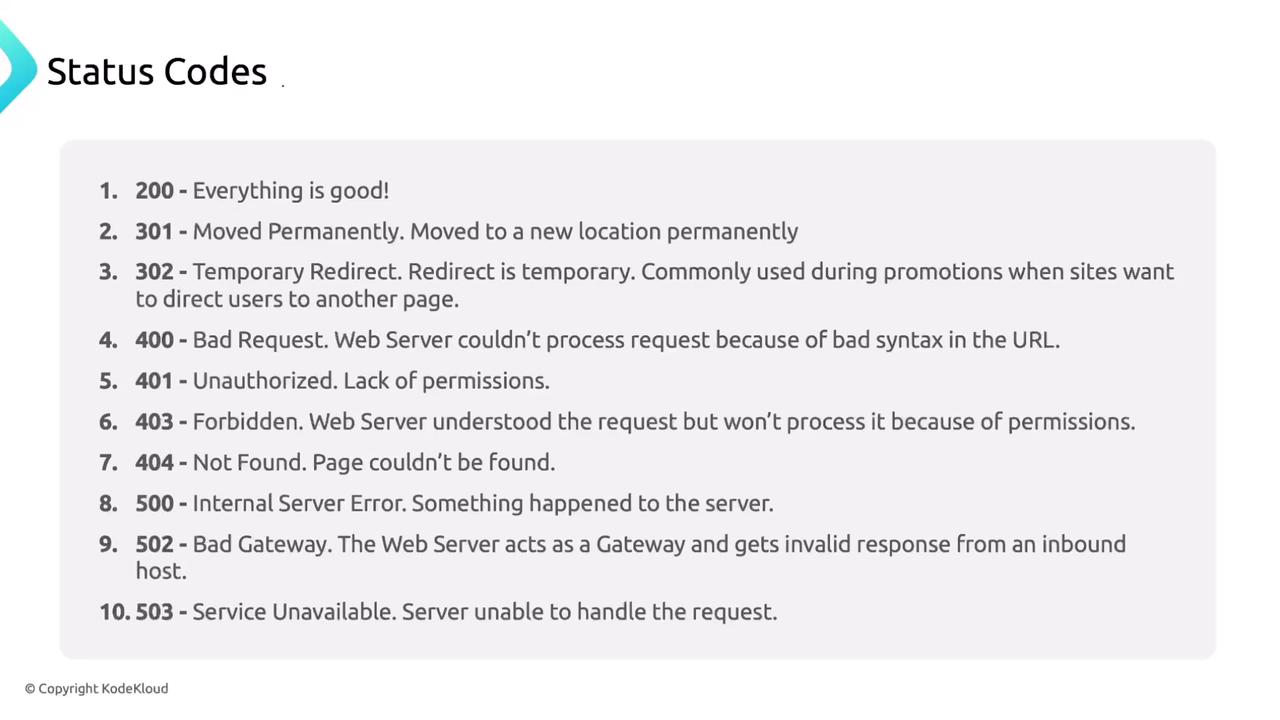
| Status Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 200 | OK |
| 301 | Moved Permanently |
| 302 | Found (Temporary Redirect) |
| 400 | Bad Request |
| 401 | Unauthorized |
| 403 | Forbidden |
| 404 | Not Found |
| 500 | Internal Server Error |
| 502 | Bad Gateway |
| 503 | Service Unavailable |
3. Transforming URLs with rewrite
Rewrites let you modify incoming URLs before Nginx searches for files or forwards to upstream servers—ideal for cleanup rules or legacy support.


3.1. Simple Rewrite Example
Map/sports-car-civic-type-r → /type-r:
3.2. Rewriting Directory Paths
When you rename a folder from/pics → /images, keep existing links functional:
/pics/type-r.jpg will be served /images/type-r.jpg without broken links.
Misconfigured regex or overlapping
rewrite rules can cause redirect loops. Test your configuration with nginx -t and in a staging environment first.3.3. Regex Cheat Sheet
| Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| ^ | Start of string | ^/old matches /old |
| $ | End of string | /page$ matches /page |
| . | Any single character | a.b matches acb |
| * | Zero or more of the preceding token | .* captures anything |
| [] | Character class | [a-z] |
| () | Capture group | (.*) |