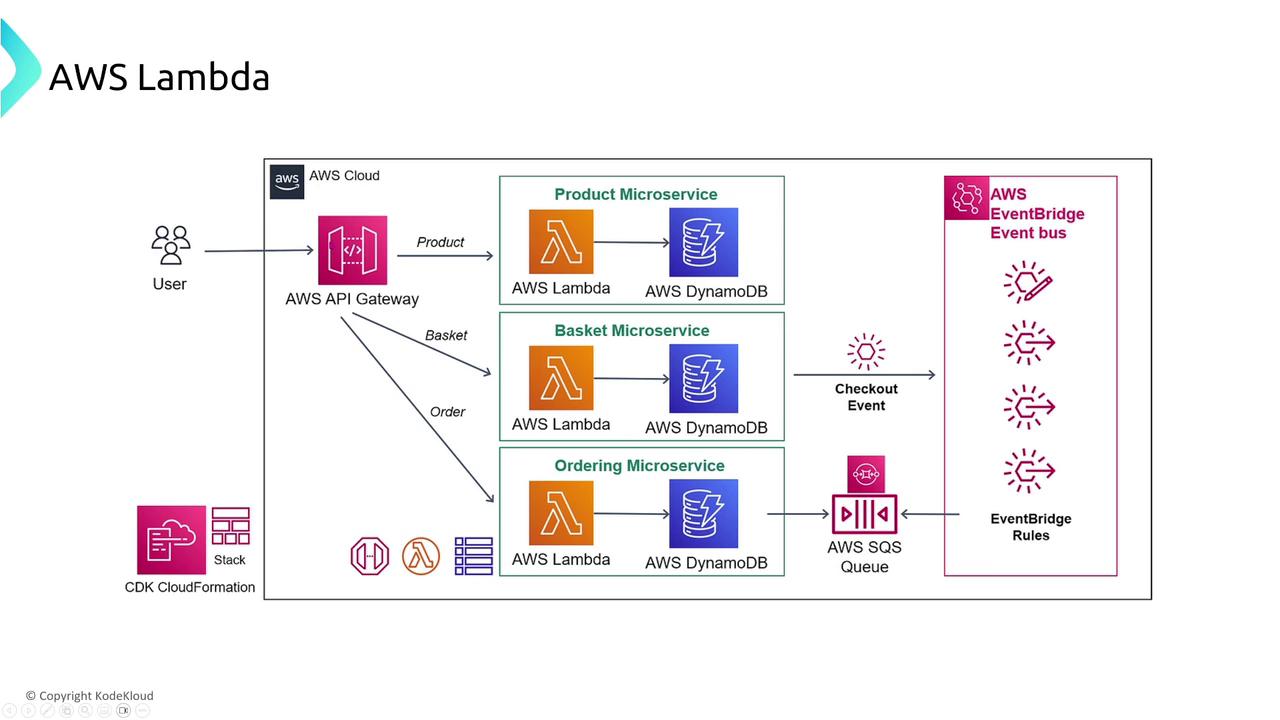
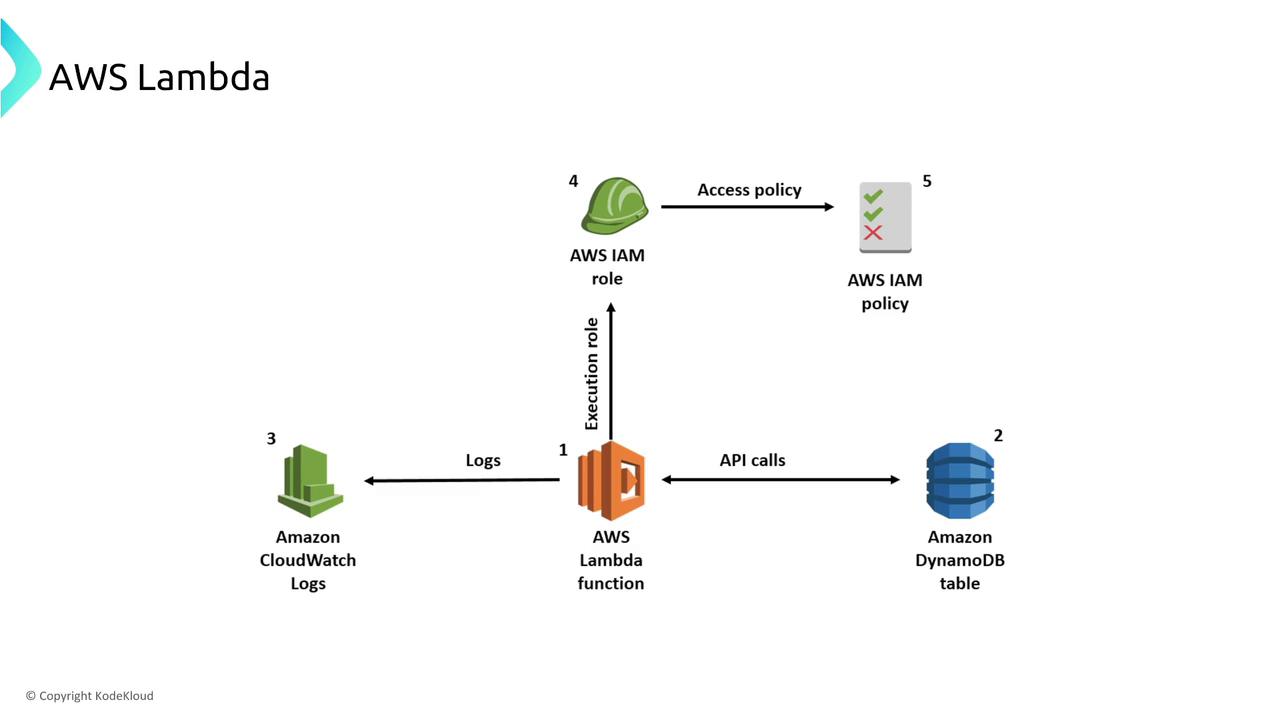
AWS Lambda Performance and Resiliency
One common challenge with Lambda is managing cold starts. A cold start happens when a Lambda function initializes from scratch, which can add latency to function execution. To address this, AWS provides a feature called provisioned concurrency. With provisioned concurrency, you can reserve a set number of Lambda instances to remain “hot,” thereby reducing the latency caused by cold starts.AWS Lambda manages many aspects of scaling, fault tolerance, and performance under the hood. However, you can also customize retry policies and configure dead-letter queues to handle function failures.
AWS Step Functions: Orchestrating Serverless Workflows
AWS Step Functions offer a robust method to coordinate multiple AWS services into complex, serverless workflows. When processing large datasets in parallel, the failure of a single task should not break the entire workflow. The recommended approach is to integrate catchers within the parallel state. These catchers capture errors from individual tasks, allowing the state machine to continue execution by rerouting the error-handling flow.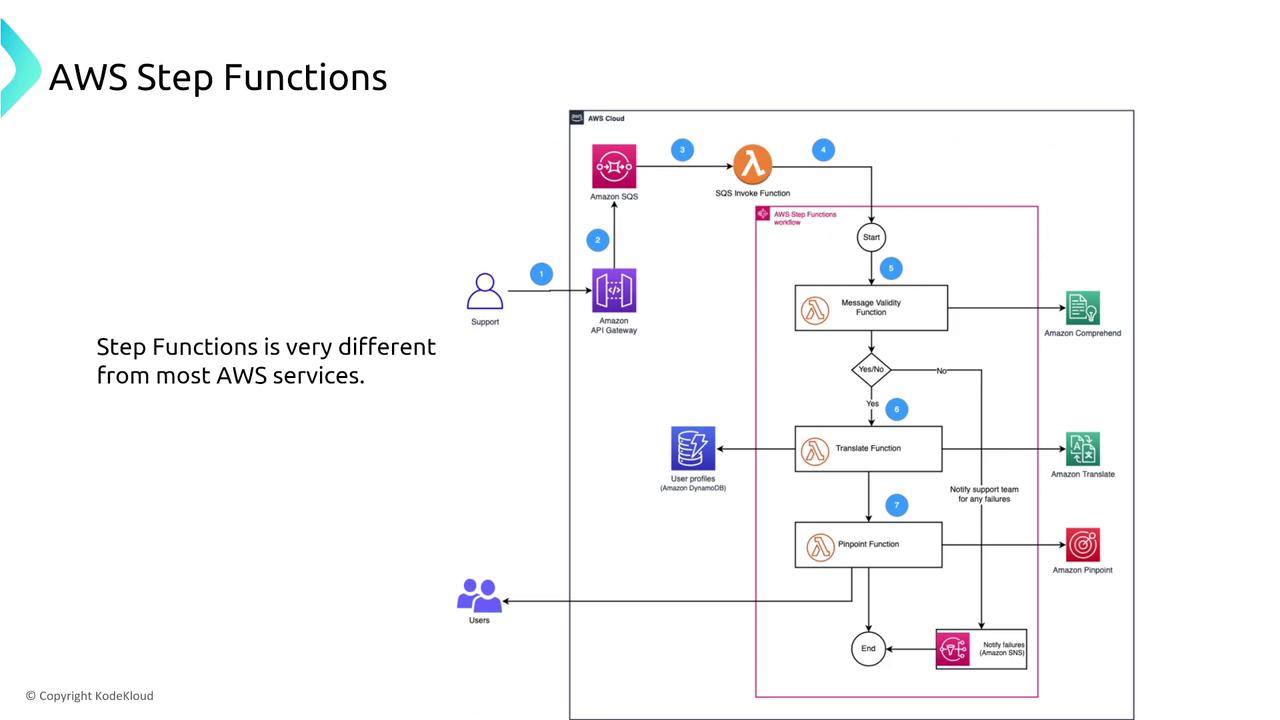
The Serverless Application Model (SAM)
The Serverless Application Model (SAM) is a framework that simplifies the development and deployment of serverless applications. SAM abstracts the underlying infrastructure, with AWS handling many resiliency features. For example, to ensure high availability and quick redeployment across regions, you can define a SAM template and use AWS CloudFormation StackSets.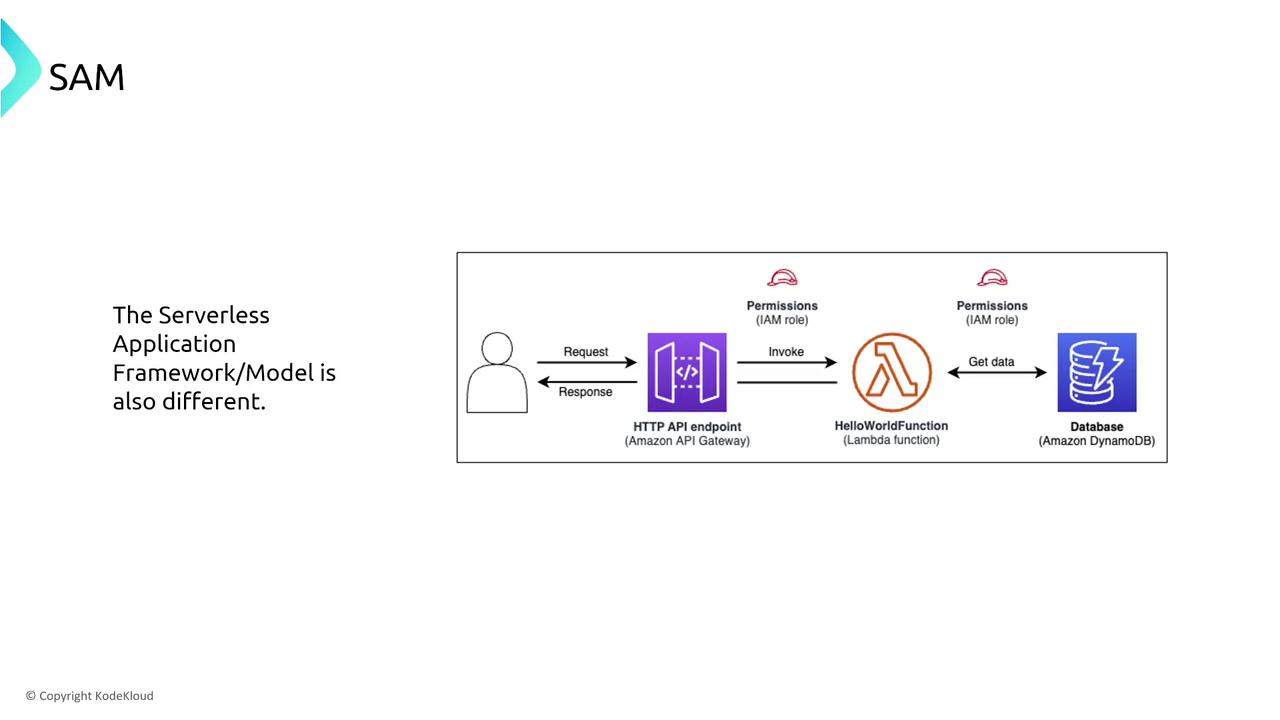
AWS Serverless Application Repository (SAR)
AWS Serverless Application Repository (SAR) provides prebuilt Lambda templates and functions, which can be a great starting point for your serverless projects. While SAR itself has limited options for configuring resiliency directly, you can improve reliability by leveraging semantic versioning. This approach enables clear version control and straightforward rollbacks or forward rollouts in case of deployment issues.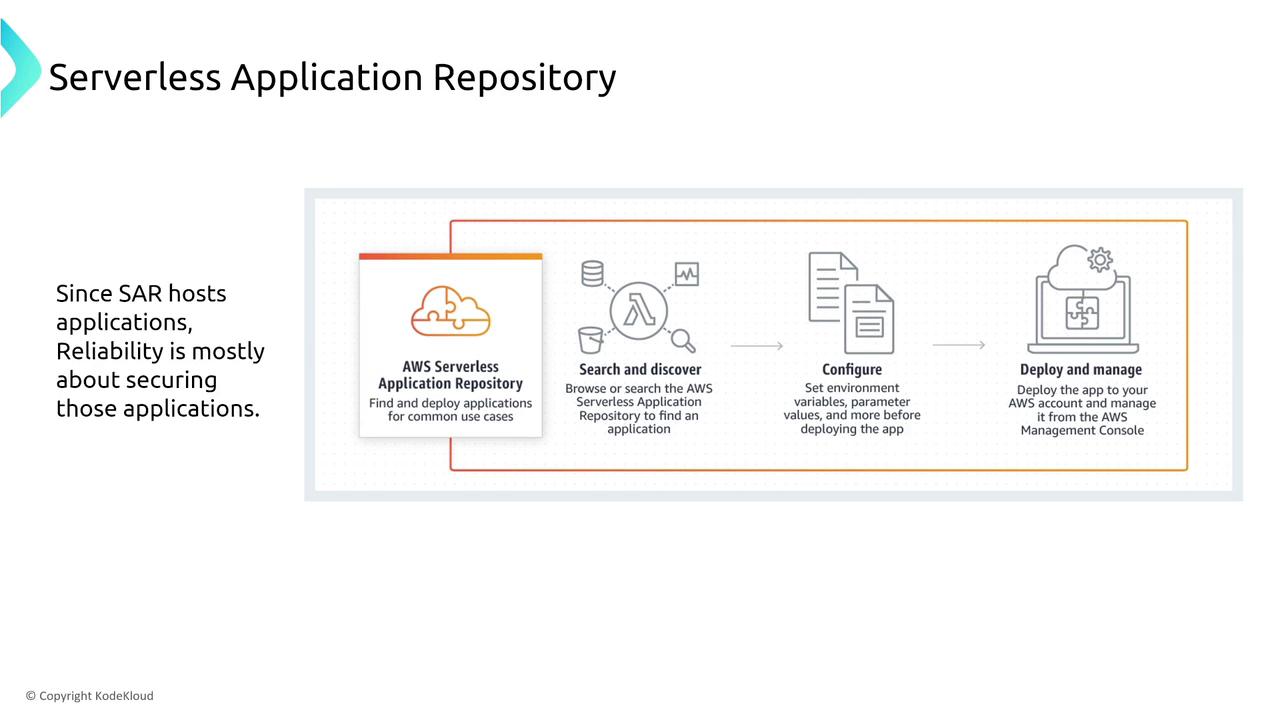
AWS Amplify
AWS Amplify streamlines the deployment and hosting of web applications, particularly those built on serverless architectures. Amplify integrates with a variety of AWS services, including API Gateway, Lambda, and database services, and features tools like GraphQL transform to manage API versioning and maintain backward compatibility.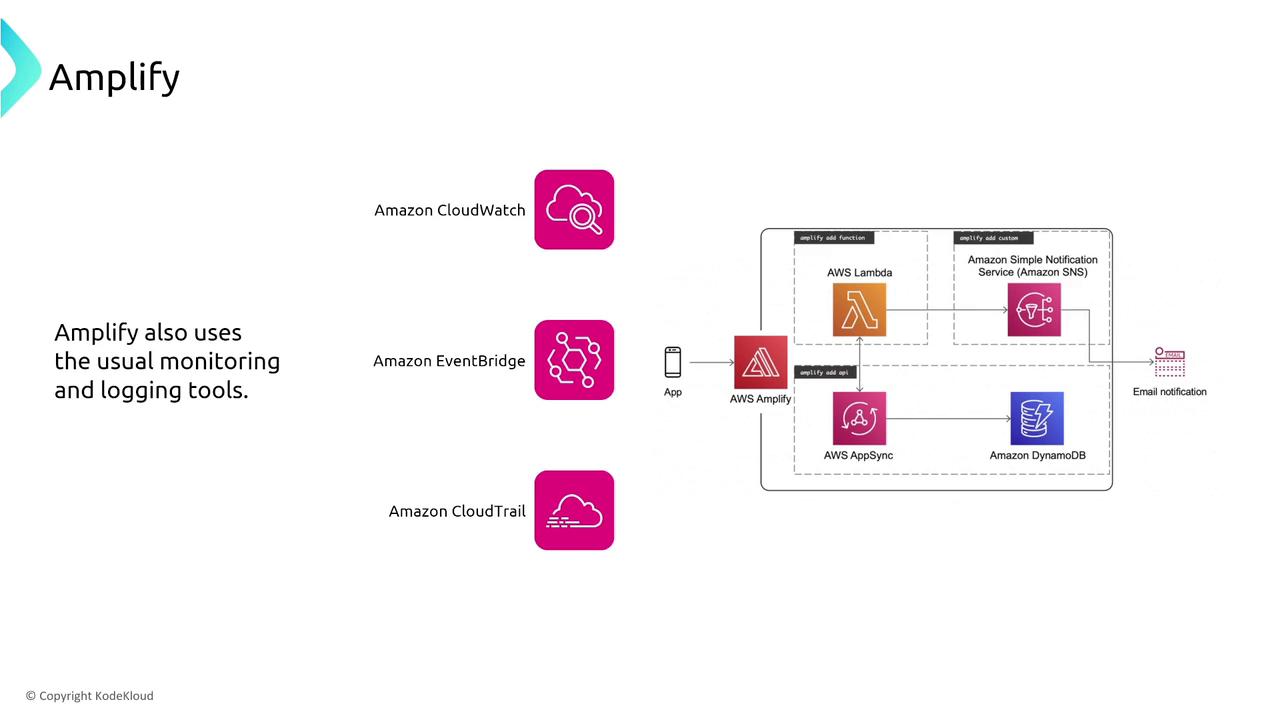
Hybrid Computing – AWS Outposts
Hybrid computing solutions bring the power of AWS services into your on-premises data centers with AWS Outposts. Outposts extends your Amazon VPC into your data center, connecting via AWS Direct Connect for a reliable private link between your on-premises network and AWS cloud services. A reference architecture for AWS Outposts includes an Amazon VPC, an Outpost subnet, and a service anchor that routes traffic over a Direct Connect line to a customer edge router. Local infrastructure components, such as dedicated VLANs and local gateways, integrate AWS services like RDS and EC2. Although Outposts benefit from traditional data center resiliency—such as redundancy across racks and locations—many resiliency settings are determined by your local infrastructure design.

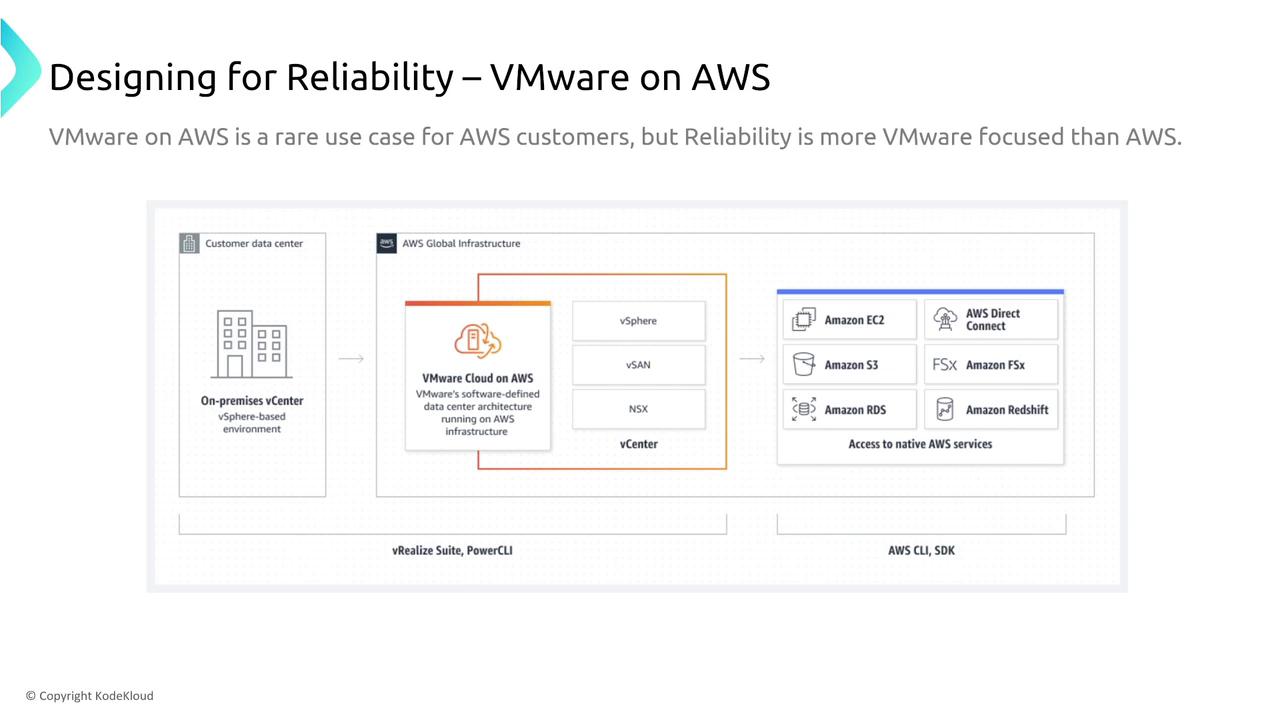
ECS and EKS Anywhere & VMware Cloud
AWS offers container orchestration solutions that extend beyond the cloud. ECS and EKS Anywhere enable you to run containerized applications on-premises while leveraging AWS management and control planes. In these cases, resiliency hinges on the robustness of your local data center architecture, including redundancy, security, and performance measures.
The Snow Family
Within the Snow family, devices are engineered for specific computing and data transfer use cases. For example, Snowmobile is designed primarily for large-scale storage and transfer, while Snowcone offers a compact, portable solution with built-in compute capabilities. Snowball devices incorporate resiliency through features such as RAID and error correction, with settings preconfigured by AWS to ensure security and durability. For scenarios that require reliable data collection and transfer in remote or connectivity-constrained environments, Snowcone is an ideal choice—provided your dataset fits within its storage limitations.Summary
This module explored the resiliency considerations across a diverse range of compute services including:- AWS Lambda: Achieves reliability through automatic scaling, provisioned concurrency, retries, and dead-letter queues.
- AWS Step Functions: Enhances workflow resiliency by incorporating catchers in parallel states to handle individual task failures.
- Serverless Frameworks (SAM and SAR): Utilize CloudFormation StackSets and semantic versioning to support high availability and straightforward rollbacks.
- AWS Amplify: Simplifies web application deployment and integrates seamlessly with AWS monitoring tools to maintain backend API resiliency.
- Hybrid Solutions (AWS Outposts, ECS/EKS Anywhere, VMware Cloud): Require robust local data center architectures while leveraging AWS connectivity.
- Edge Devices (Snow Family): Are preconfigured for resilient operations in data transfer and remote computing use cases.
For additional resources, please refer to:
- AWS Lambda Developer Guide
- AWS Step Functions Documentation
- Serverless Application Model (SAM)
- AWS Outposts
- VMware Cloud on AWS