AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Designing for Reliability
Turning up Reliability on MigrationTransfer Services
Welcome, future solutions architects! In this article, presented by Michael Forrester, we explore how to enhance reliability across various AWS migration and transfer services. This guide outlines service features, reliability considerations, and best practices to ensure smooth transitions to the cloud.
Overview of Migration and Transfer Services
AWS offers a host of services that facilitate data and workload migration. We begin by examining the role of the Application Discovery Service and the Migration Hub. The Migration Hub provides a centralized dashboard for tracking migration data. However, it offers limited options for adjusting reliability directly.
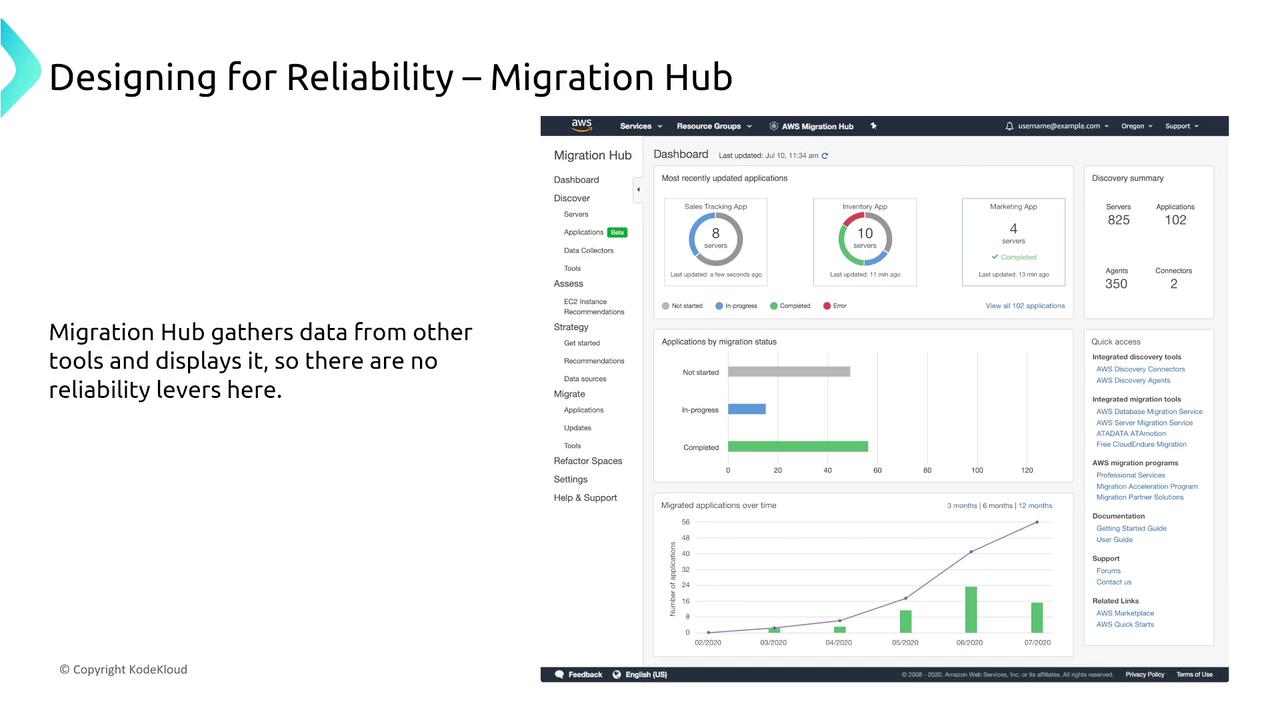
Moving forward, the focus shifts to the Application Discovery Service, which is crucial for detailed system analysis and planning.
AWS Application Discovery Service
Unlike the Migration Hub, the AWS Application Discovery Service actively detects and collects configuration and performance data from your on-premises applications. It supports multiple discovery methods, including agents, agentless collectors, and manual entries.
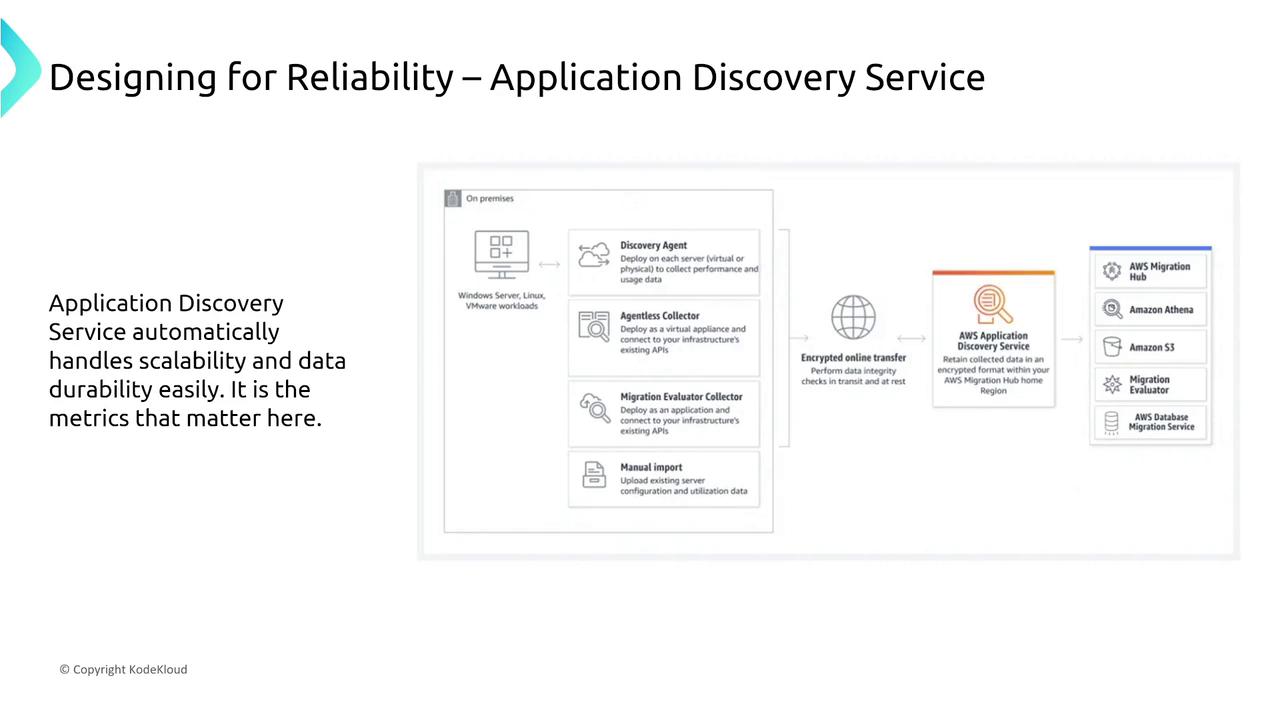
To maintain service reliability, AWS recommends using tools like CloudWatch for metrics, CloudTrail for auditing, and X-Ray for tracing. Note that while the service is robust, it offers limited custom reliability knobs.
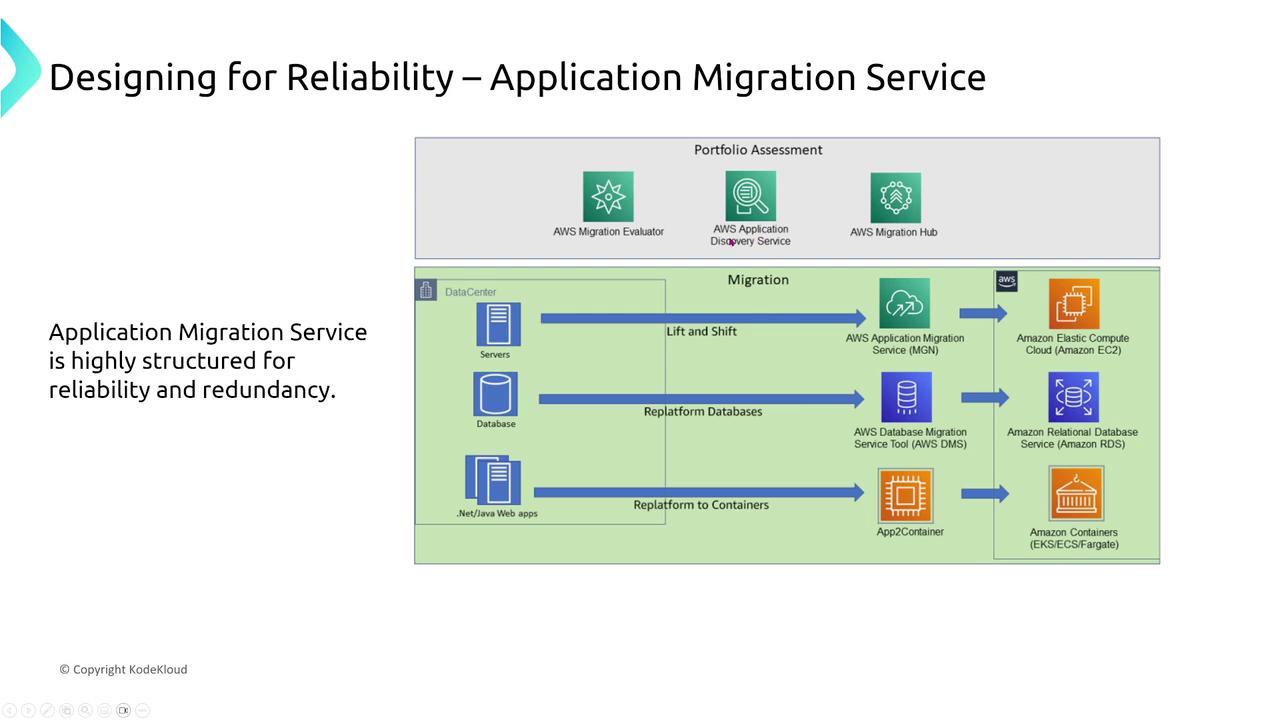
AWS Application Migration Service
The AWS Application Migration Service is built to simplify and automate the migration process. It facilitates the lift-and-shift of servers from your data center to Amazon EC2, ensuring a controlled and repeatable workflow. Being highly managed, this service minimizes manual intervention while emphasizing redundancy and reliability.
Note
Because the process is nearly automated, there are few custom adjustments for reliability. Instead, AWS ensures a predefined, repeatable workflow.
AWS Database Migration Service (DMS)
The AWS Database Migration Service (DMS) transfers data between databases using a replication instance and change data capture. While efficient, the replication instance introduces a single point of failure. Multi-AZ support is available; however, it does not include automatic failover during failures in full load scenarios. Instead, manual intervention to restart the replication job is required.
Warning
Ensure you have procedures in place to manually restart replication jobs in case of a failure, despite using Multi-AZ configurations.
Elastic Disaster Recovery Service (EDR)
Formerly known as CloudEndure, the Elastic Disaster Recovery Service delivers near-real-time, block-by-block replication from on-premises systems to AWS. EDR utilizes a staging VPC and scalable replication servers, making it an excellent solution for meeting strict Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO).
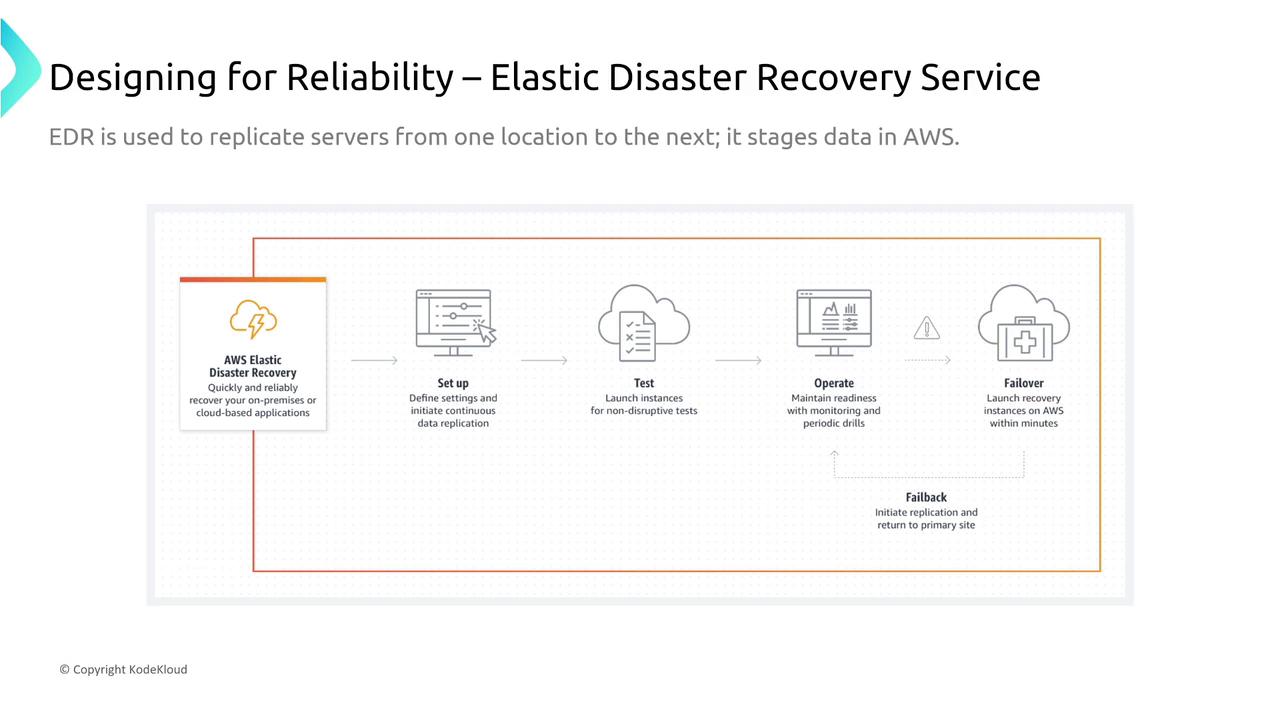
Replication occurs at the block level with on-the-fly transformations during transit. The service’s auto-scaling and auto-replacement features further enhance its reliability.
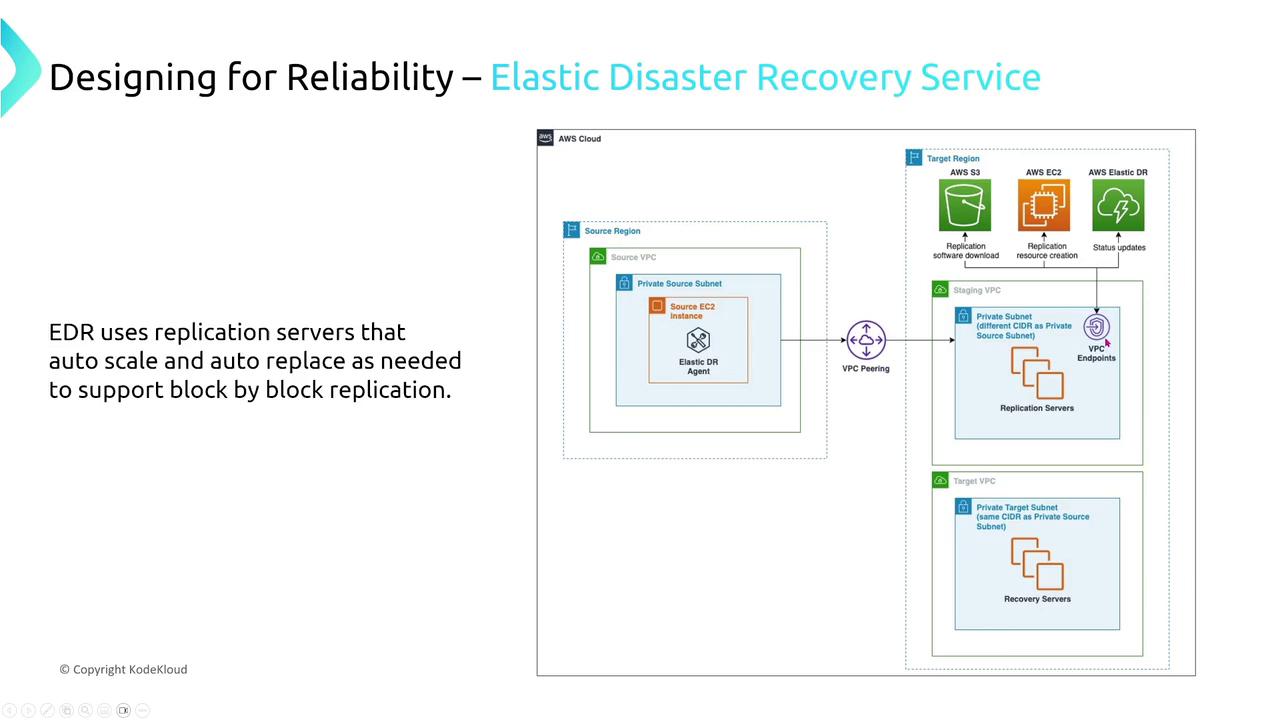
EDR is particularly beneficial for organizations with rigorous business continuity requirements.
Mainframe Modernization
Mainframe modernization involves migrating legacy mainframe workloads to modern AWS services such as EC2, Lambda, or other managed services. In this context, the reliability of your solution is determined more by the target AWS service than by the modernization process itself.
Note
Think of mainframe modernization as the orchestration layer. The inherent reliability is primarily provided by the target AWS services.
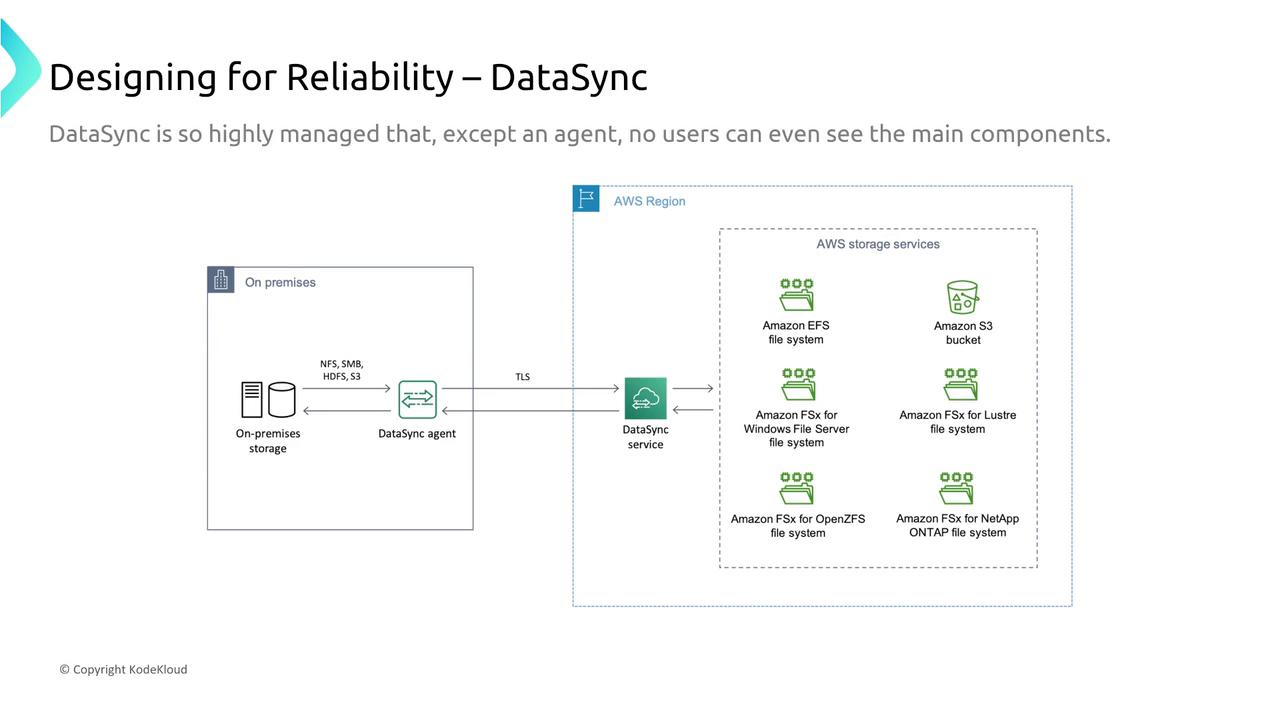
AWS Data Transfer and DataSync
AWS DataSync is designed for secure and efficient data transfers between on-premises storage and AWS storage services. By using a dedicated DataSync agent, it ensures file-level logging and monitoring via S3, CloudWatch, and CloudTrail. For protocol-based transfers (FTP, FTPS, SFTP, or SCP), the service offers built-in reliability features and visibility.
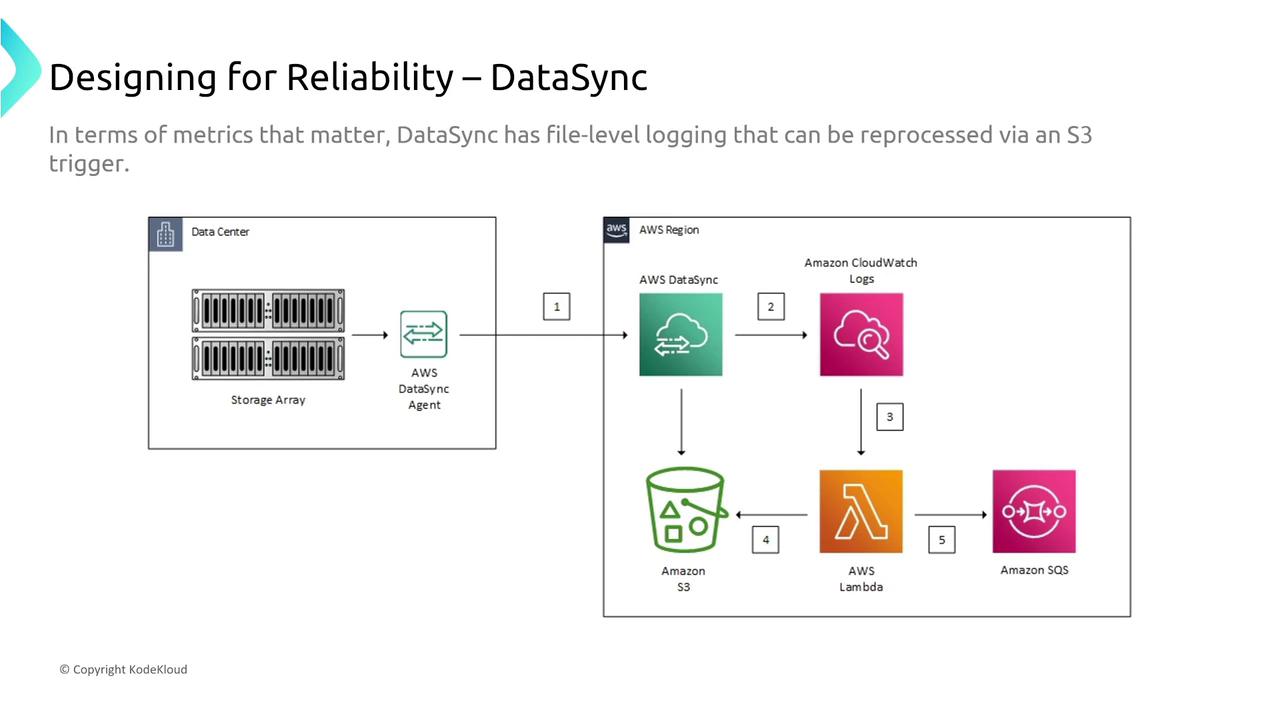
Monitoring options such as CloudWatch logs, DataSync task logs, and additional trace tools help in ensuring smooth operations during data transfers.

Detailed logging and visualization of data flow allow teams to quickly troubleshoot issues.
AWS Snow Family Storage Devices
For physical data migration, the AWS Snow Family—comprising devices like Snowcone and Snowball Edge—is engineered for reliable and secure data transfer in challenging environments. These rugged devices are pre-hardened for transit and are ideal for moving large volumes of data from remote or harsh locations.
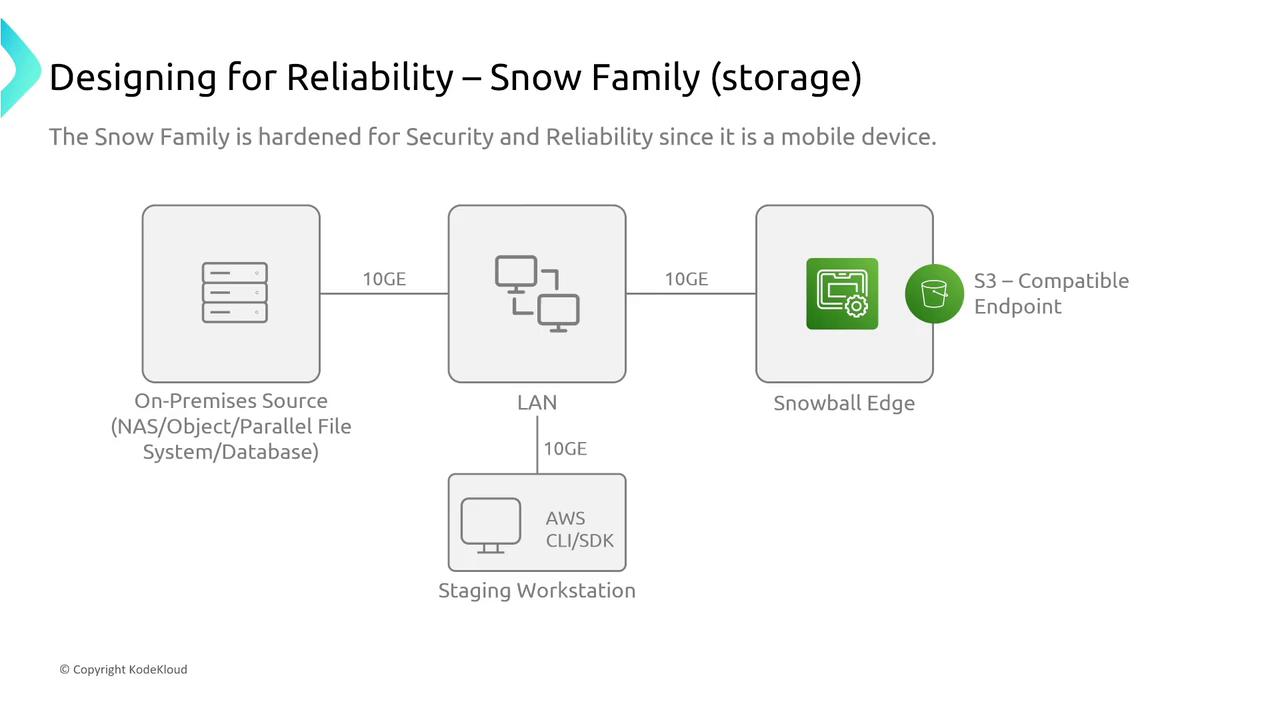
For example, the Snowball Edge offers up to 210 terabytes of NVMe storage and is built to withstand the demands of mobile deployment, ensuring durability without the need for adjustable reliability settings.
Conclusion
In summary, AWS migration and transfer services are designed as highly managed solutions with intrinsic reliability, though they offer few manual configuration options. Services like Application Migration, Application Discovery, and DataSync leverage AWS monitoring tools—such as CloudWatch, CloudTrail, and X-Ray—to maintain operational excellence. At the same time, services like EDR and DMS require careful planning to accommodate their unique recovery processes.
Effective monitoring and proactive management are key to ensuring reliable migrations and transfers. For further information on AWS services and best practices, consider exploring the AWS Documentation or AWS Migration Hub.
Thank you for reading this guide on enhancing reliability in migration and transfer services. We look forward to sharing more insights in our next lesson.
Watch Video
Watch video content