AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Designing for Security
Design Principles of the Security
Welcome back to this lesson. I’m Michael Forrester, and today we will cover several core security design principles encouraged by AWS. These principles are essential not only for passing the exam but also for designing robust and secure solutions on AWS.
When implementing, deploying, or designing services on AWS, it's critical to ask questions such as:
- What aspects of security enhance the service?
- Which design principles strengthen overall security—and which could possibly degrade it if misapplied?
- What is the ultimate security goal we are trying to achieve?

For example, when evaluating a service's security posture, identify the elements that bolster its protection.
![]()
Similarly, for reliability, you may ask what factors enhance or diminish it. In security, the following key questions arise:
- What principles increase security?
- What principles might compromise it?
- What is our security end goal?
![]()

Design principles act as filters to determine whether a particular approach strengthens, remains neutral, or undermines your security posture.
Encryption Example
Storing data in raw format without encryption exposes it to unauthorized reading by anyone with access. Encrypting data not only ties into robust access controls but is a fundamental security measure in itself.
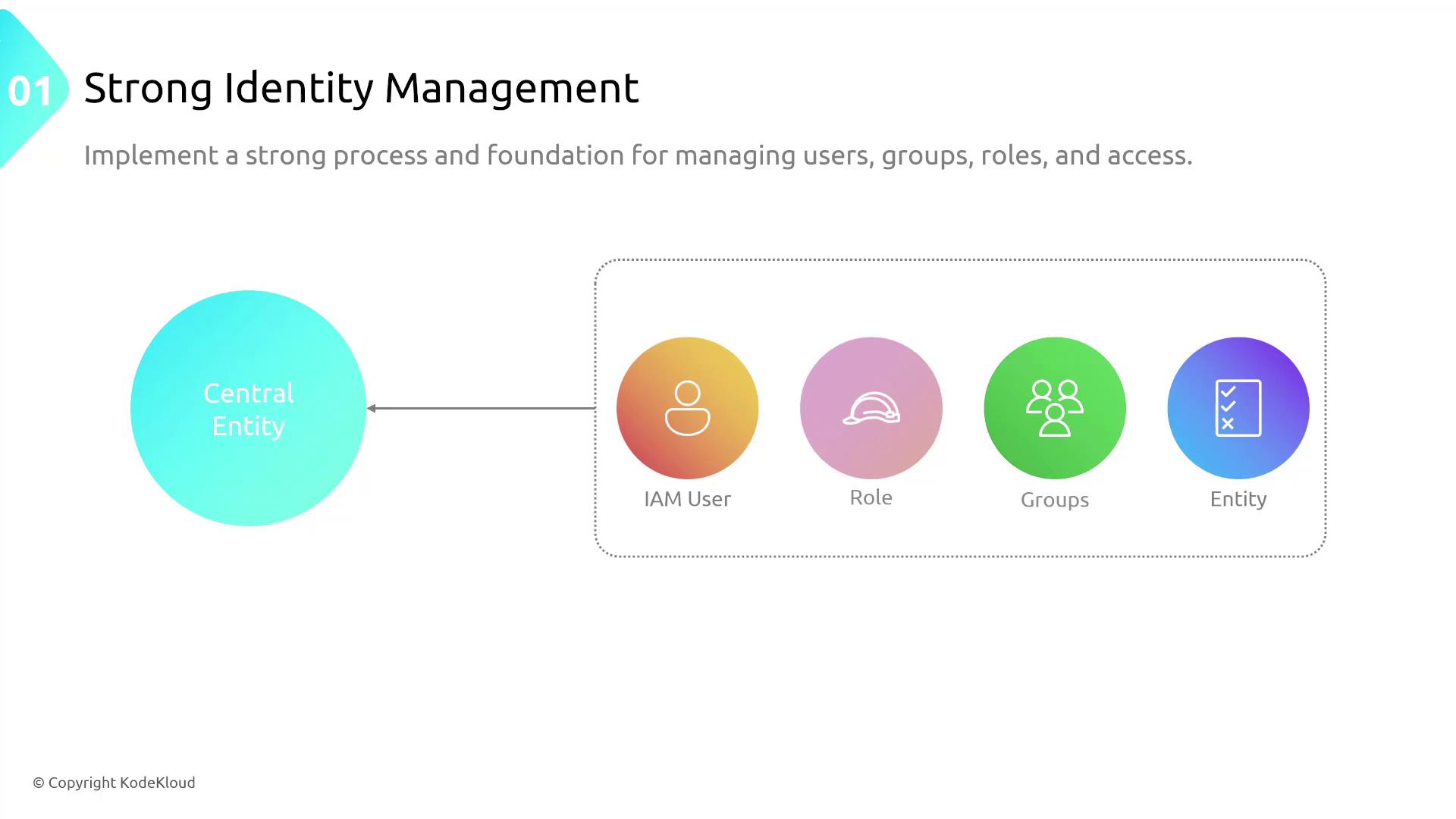
A foundational security requirement is strong identity management. This involves robust processes to manage users, groups, and roles, and to enforce strict conditions for resource access. In AWS, this responsibility is typically handled by IAM and AWS Organizations.
Imagine an AWS account where a user, role, or group requires specific permissions. Securing that access begins with strong identity management.
Next, ensure that security is implemented at every layer of your infrastructure and applications. Effective security extends beyond the network perimeter—it must incorporate public firewalls, network defenses, host-level protection, and application-level controls.
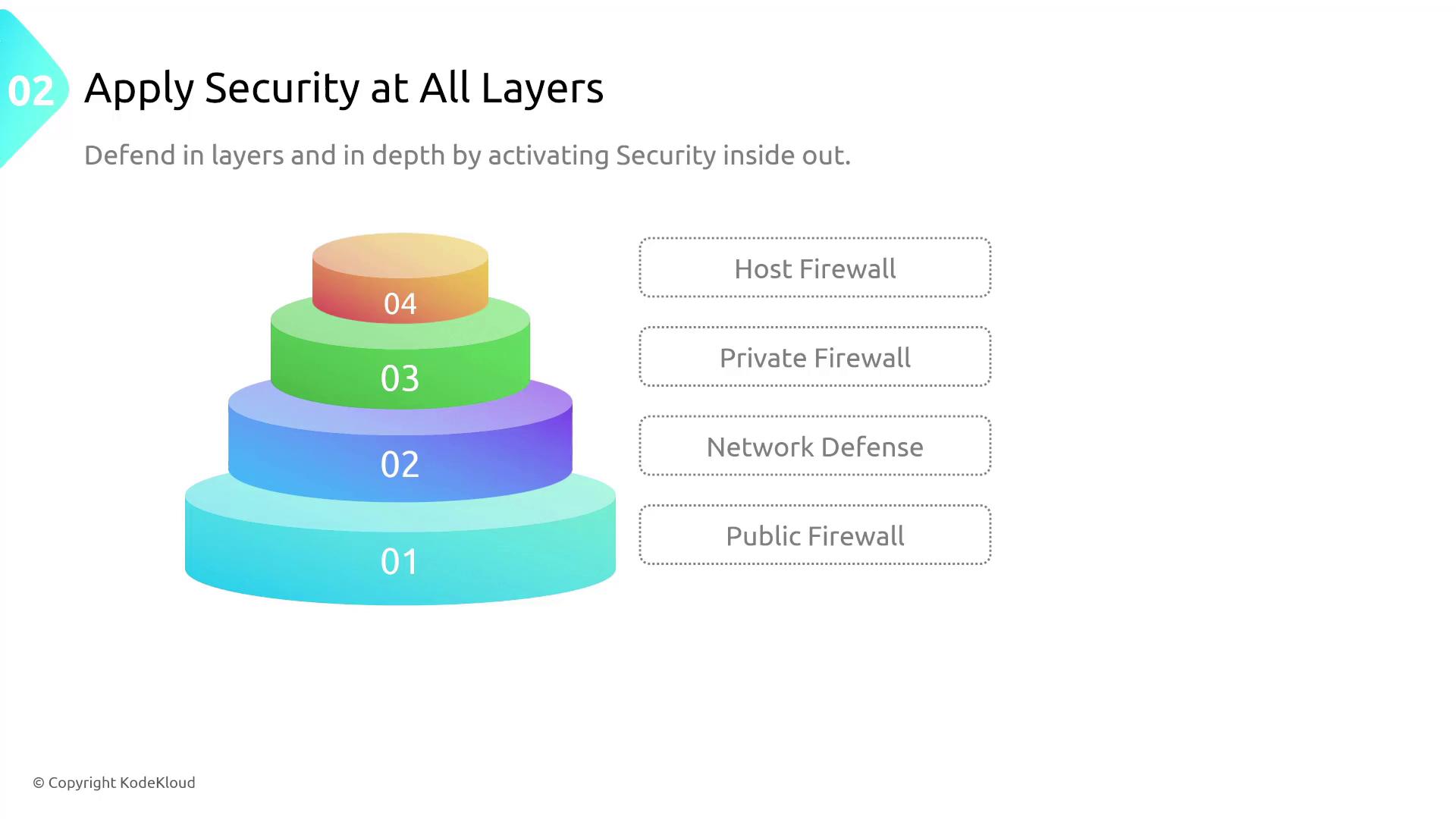
Layered security, or defense in depth, ensures that if one control fails, additional controls continue to protect your system.
A well-defined response to security events is another critical principle. Early in my career, I made the error of deleting a compromised machine immediately, which inadvertently erased crucial forensic evidence. A comprehensive incident response (IR) plan enables systematic handling of security incidents while preserving vital forensic data.
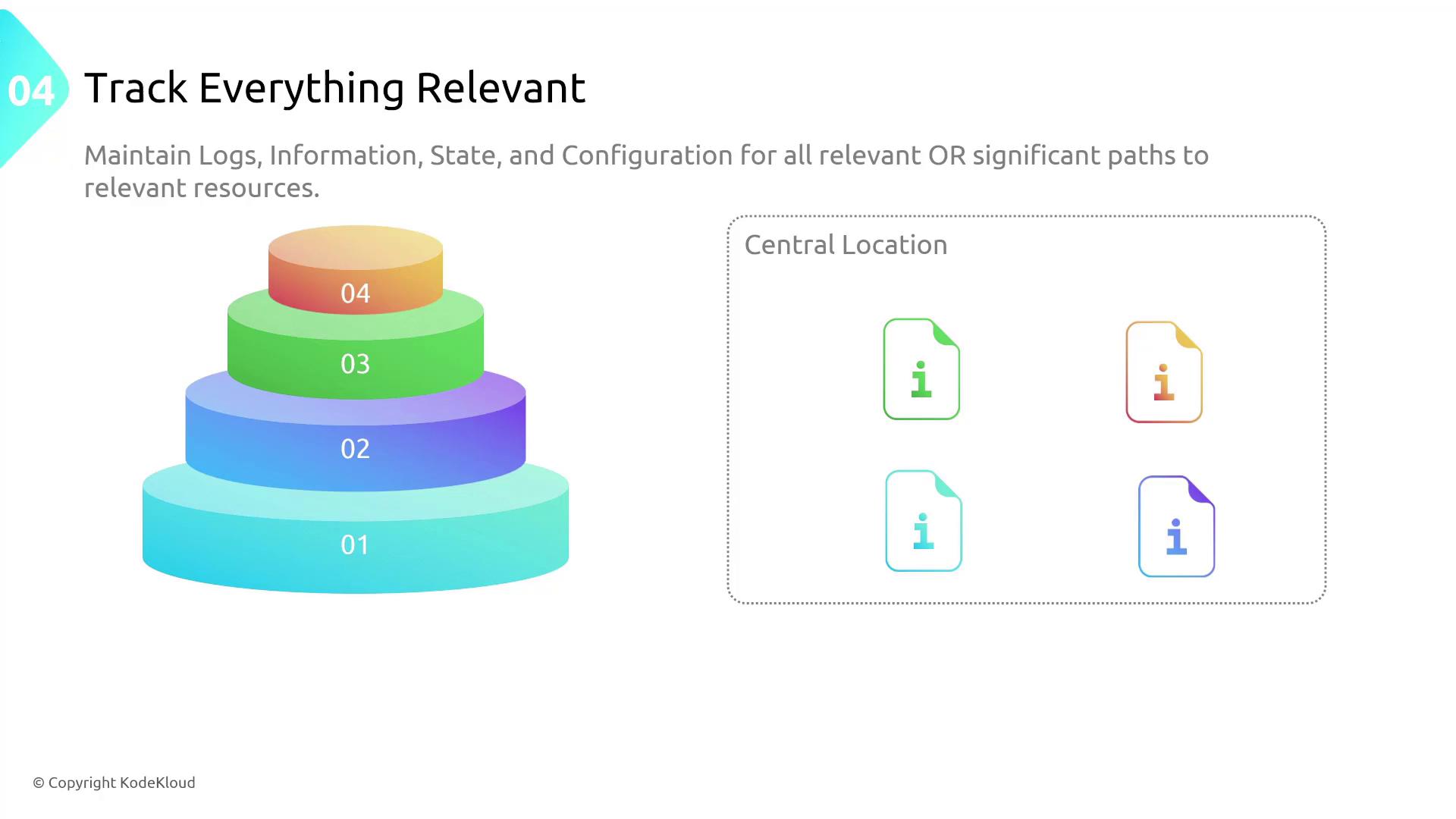
Tracking all relevant data is also essential. Even seemingly insignificant data or activities should be logged. Collect metrics, logs, configuration details, and state information in a centralized and secure location with access restricted to authorized personnel. This practice promotes integrity and accountability.
Reducing direct human contact with sensitive processes and data is vital. When intervention is necessary, rely on controlled tools that restrict direct access and help mitigate the risk of errors. For instance, rather than granting direct access to raw data, use tools that enforce role-based controls.

Automating best practices is the next step. Tasks such as patching, security scans, and even auto-scaling should be automated. By integrating security scans into CI/CD pipelines, you ensure that these checks occur automatically during code merges and deployments, thereby reducing human error and improving reliability.

Finally, protect your data in all states: at rest, in transit, and in use. Encrypt data on your storage devices, secure network transfers, and, where feasible, encrypt data even during processing. This approach is critical not only for databases but also for code repositories, files, and other sensitive information.
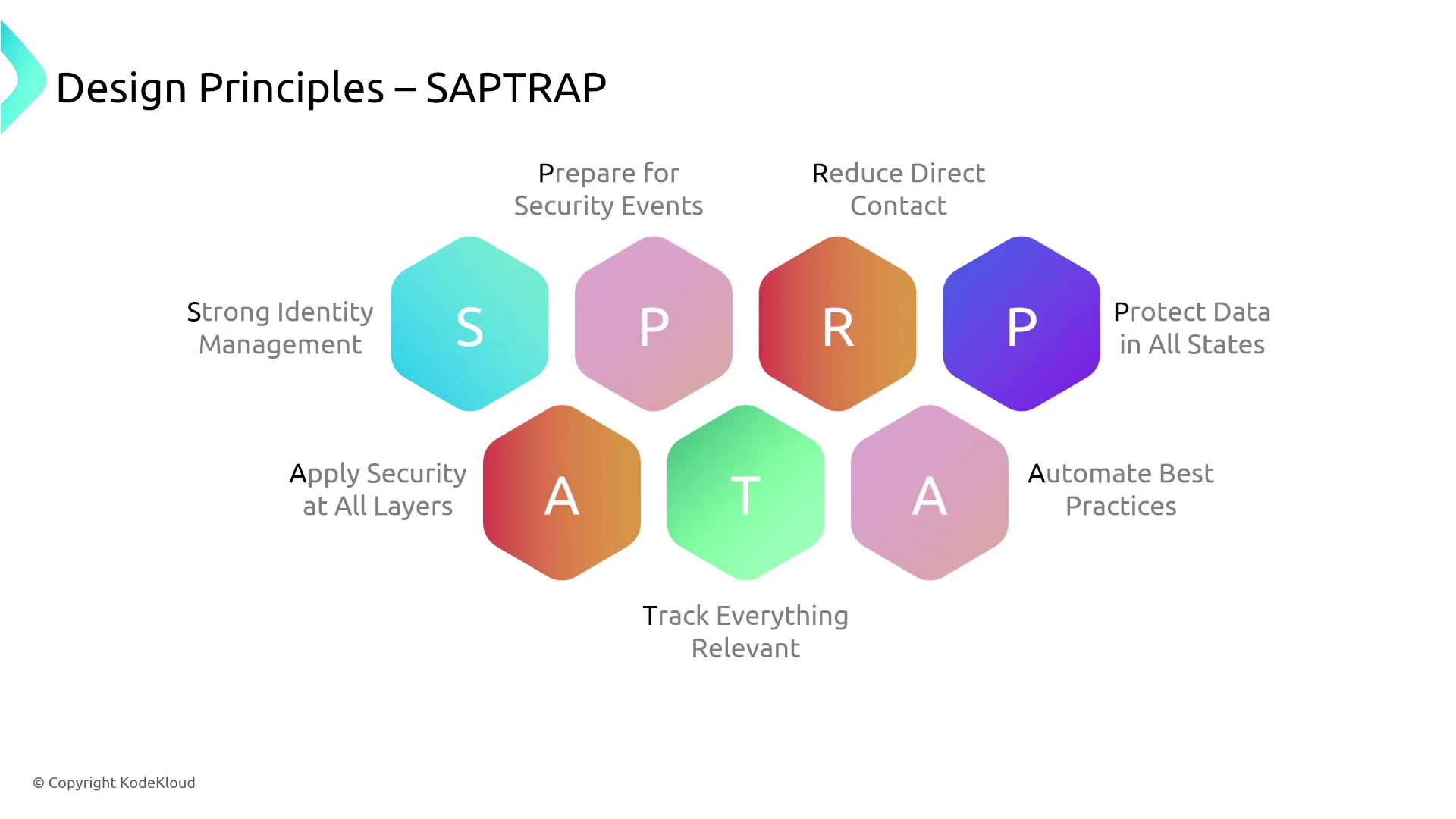
The SAPTRAP Mnemonic
To summarize these principles, remember the mnemonic "SAPTRAP":
| Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| Strong Identity Management | Robust user, group, and role management through services like IAM and AWS Organizations. |
| Apply Security at All Layers | Extend security measures from public firewalls to host and application-level controls. |
| Prepare for Security Events | Develop and follow an incident response plan to handle security breaches effectively. |
| Track Everything Relevant | Log and monitor all metrics, access logs, and configuration details centrally. |
| Reduce Direct Contact | Minimize manual interventions by using automated tools that enforce role-based access. |
| Automate Best Practices | Integrate automation in security checks, patch management, and scalability processes. |
| Protect Data in All States | Encrypt data at rest, in transit, and during processing to ensure complete data protection. |
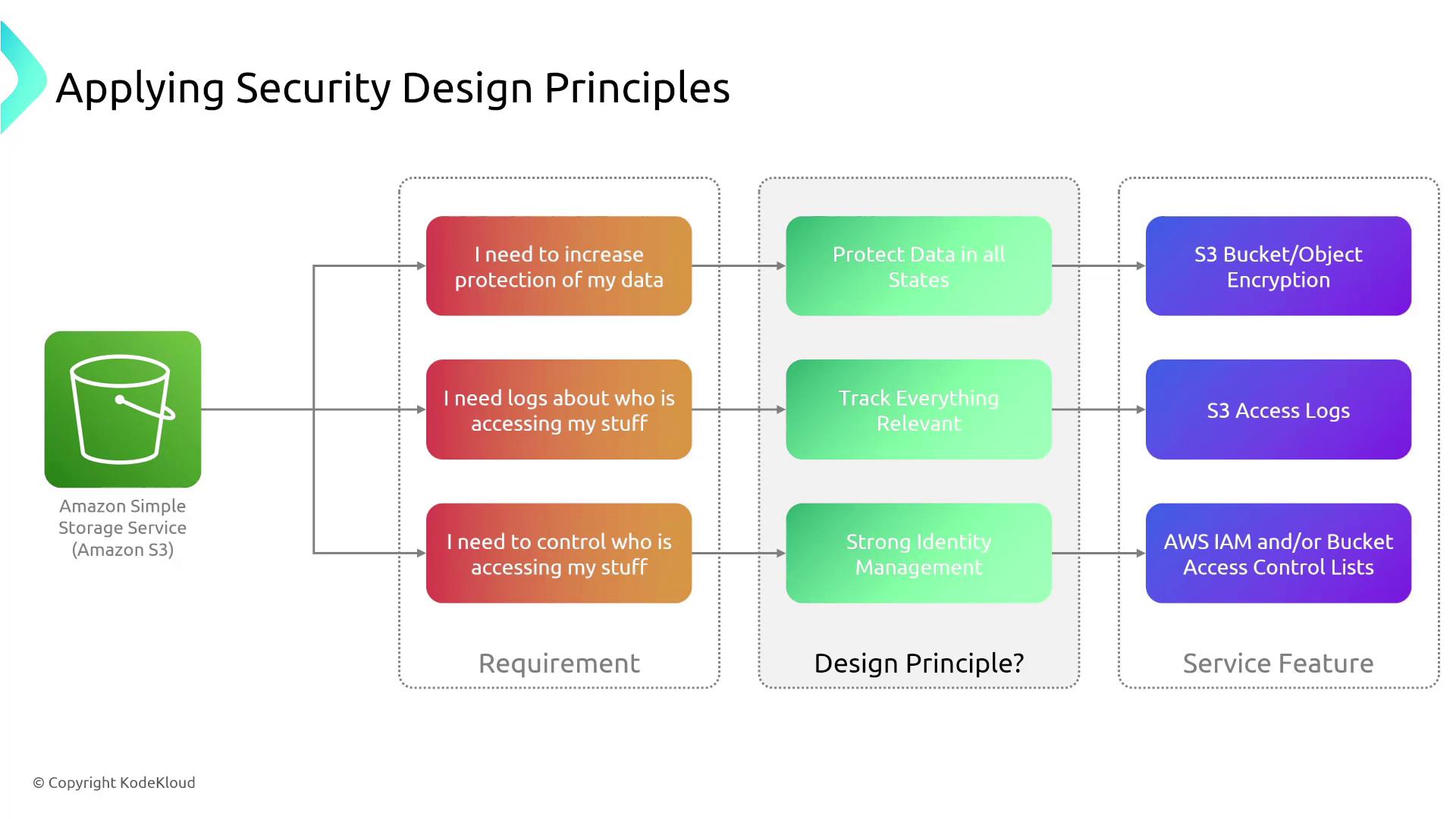
Real-World Example: Amazon S3
Let’s apply these principles to a real-world scenario involving Amazon S3. Suppose a client requires enhanced protection for their S3 data. They would benefit from:
- Enhanced Encryption: Protect data at rest and in transit. While AWS now enables encryption by default for new buckets, older buckets might require manual intervention.
- Access Logging: Enable S3 access logging to capture critical details like IP addresses and access patterns, which help in detecting potential security issues.
- Strong Identity Management: Use IAM policies (instead of access control lists) to enforce strict access control and maintain robust security practices.
Summary
Design principles serve as guiding values that help balance security, reliability, and cost in your solutions. Incorporating practices like:
- Automating best practices,
- Protecting data in all states,
- Enforcing strong identity management, and
- Applying layered security
ensures that your AWS environment remains secure and resilient against threats.
Key Takeaway
While these principles may not appear exactly as-is on the exam, applying concepts like defense in depth and stringent identity management is critical for your security strategy.
Review the SAPTRAP mnemonic to reinforce these concepts and integrate them into your design methodologies. Thank you for joining this lesson on security design principles. We’ll move on to the next section shortly.
Watch Video
Watch video content