AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Designing for Security
Understanding the seven foundations of Security
Welcome to this lesson on the Well-Architected Framework. In this tutorial, Michael Forrester will guide you through seven critical areas of cloud security. Unlike broader design principles that help conceptualize your strategy, these seven areas are concrete categories you can actively work on to secure your cloud environment.
Below are the seven areas of cloud security:
- Security Foundations
- Identity and Access Management
- Detection
- Infrastructure Protection
- Data Protection
- Application Security
- Incident Response
There is significant overlap among these areas, but each one emphasizes a specific aspect of cloud security.
1. Security Foundations
This section establishes the baseline for all subsequent security measures. It involves planning activities such as defining roles, identifying critical services, and determining the necessary protection levels—whether that means 24/7 monitoring or security during specific timeframes. By setting clear objectives for system updates, threat identification, and account management, the security foundations guide your overall strategy.
2. Identity and Access Management
This category focuses on controlling who can access your cloud resources and what permissions are granted. In AWS, for example, this is achieved using IAM (Identity and Access Management). A robust identity and access management process not only prevents unauthorized entry but also facilitates secure operations for authorized users.
![]()
3. Detection
Detection involves deploying tools and processes to identify security issues early. This includes monitoring for unexpected configuration changes, analyzing logs and metrics, and tracking vulnerabilities. The goal is to provide centralized and actionable information that can trigger timely alerts and remediation efforts.
4. Infrastructure Protection
Infrastructure Protection is dedicated to defending the underlying cloud infrastructure. This area involves implementing various defenses—such as network security, continuous network inspections, and vulnerability assessments for compute assets. Protecting essential components like network switches, storage systems, and compute instances is vital to prevent exploitation.
5. Data Protection
Data Protection focuses on safeguarding your data independently of the underlying infrastructure. This includes encryption of data at rest and in transit, key lifecycle management, and implementing data classification based on sensitivity. Maintaining data integrity and confidentiality—using built-in cloud features or additional security measures—is a top priority.

6. Application Security
Application Security ensures that workloads and the software development lifecycle are protected at every phase. By integrating security measures into application design, development, deployment, and maintenance, you can mitigate vulnerabilities. Practices such as penetration testing, code reviews, and screening third-party components are key to maintaining a secure application environment.
Note
In addition to securing the infrastructure, focusing on application security helps ensure that your code remains safe from new vulnerabilities throughout its lifecycle.
7. Incident Response
Incident Response is about preparing for and managing security breaches effectively. This involves creating a comprehensive incident response plan, conducting regular training sessions, and running simulations to test your procedures. The purpose is not only to remediate issues quickly when they occur but also to refine your processes continuously through lessons learned.
Applying the Seven Areas of Cloud Security
An understanding of these seven areas allows you to map specific security requirements to the appropriate focus area. For instance:
- To protect data stored in Amazon S3, emphasize Data Protection by enabling S3 bucket object encryption.
- To log user activity, implement Detection strategies such as using S3 access logs.
- To control resource access, focus on Identity and Access Management, utilizing AWS IAM policies.
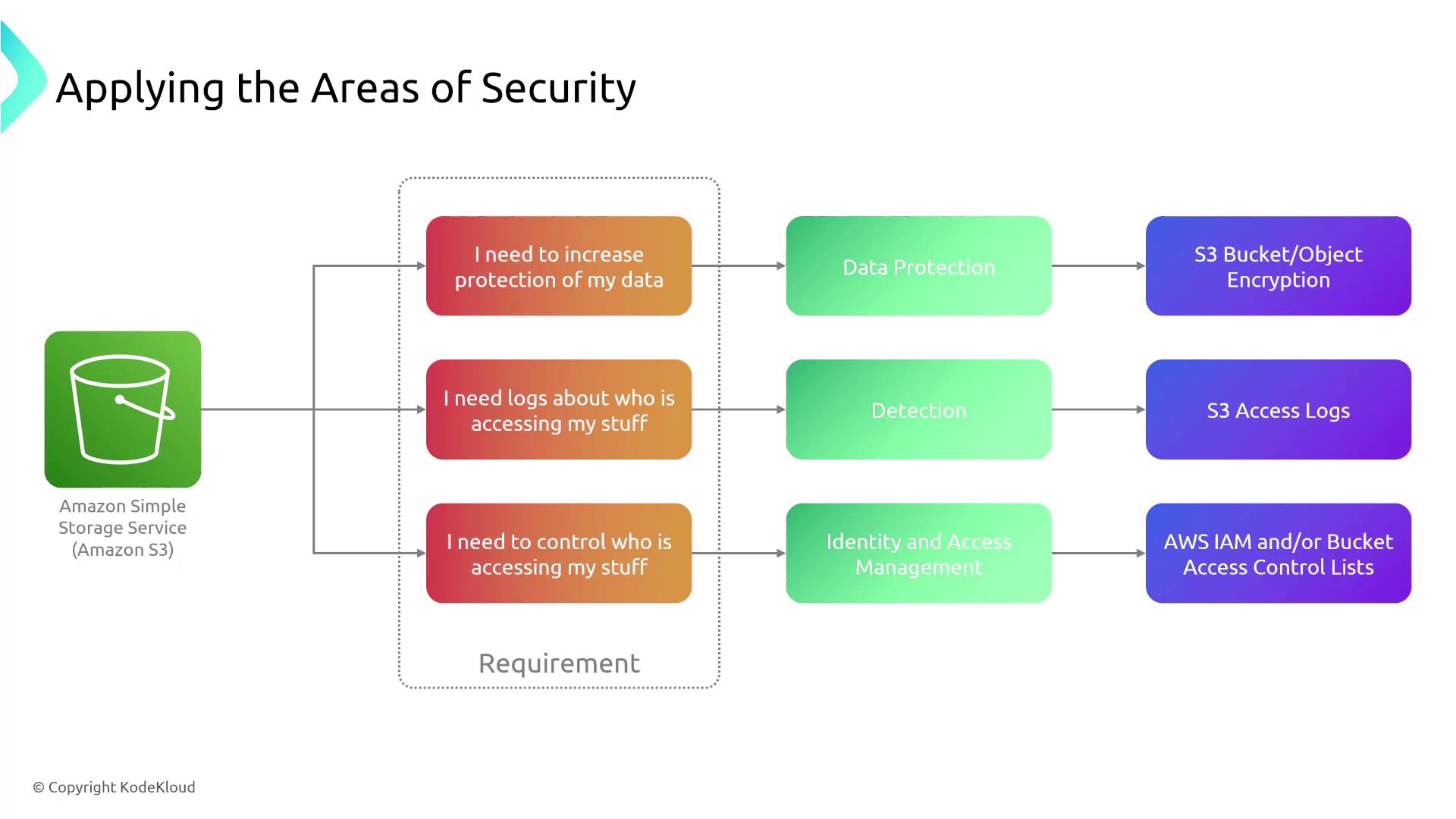
The purple-highlighted service features in the diagrams indicate which AWS service or feature to enable for meeting these security needs. These seven areas work together with cloud design principles to help evaluate and enhance the security posture of AWS services.
For example, if you are strengthening data protection for a database, you might implement encryption and enable detailed access logs. Conversely, if your focus is on user authentication for S3, you would utilize IAM services for effective access control. Although these categories are not part of the formal exam, they are essential for conducting a thorough security analysis and designing robust solutions.

If you have any questions, please feel free to reach out on Slack. Thank you for reading, and we look forward to seeing you in the next lesson.
Watch Video
Watch video content