Skip to main contentIn this article, we explore how NAT Gateways enable secure communication between private subnets and the internet. NAT Gateways allow instances within private subnets to initiate outbound connections while blocking unsolicited inbound traffic, thereby keeping internal servers shielded from external threats.
Consider a scenario where a server hosted in a private subnet requires internet access to download updates and security patches. One might think of attaching an Internet Gateway to the VPC and creating a route for the subnet. However, this would expose the server to the internet, making it public and vulnerable. Instead, the solution is to configure a NAT Gateway so that the server can access the internet for outbound requests without accepting inbound connections initiated from the internet.
How NAT Gateways Work
NAT Gateways offer a secure channel for outbound internet requests from private subnets while preventing unsolicited inbound traffic. Essentially, the NAT Gateway allows instances to initiate connections but blocks external entities from starting a conversation with them.
To set up a NAT Gateway, you need the following components:
- Internet Gateway: Attach an Internet Gateway to your VPC.
- Public Subnet: Create a public subnet with a default route pointing to the Internet Gateway.
- NAT Gateway Deployment: Deploy the NAT Gateway in the public subnet so that it functions as a mediator for outbound internet requests.
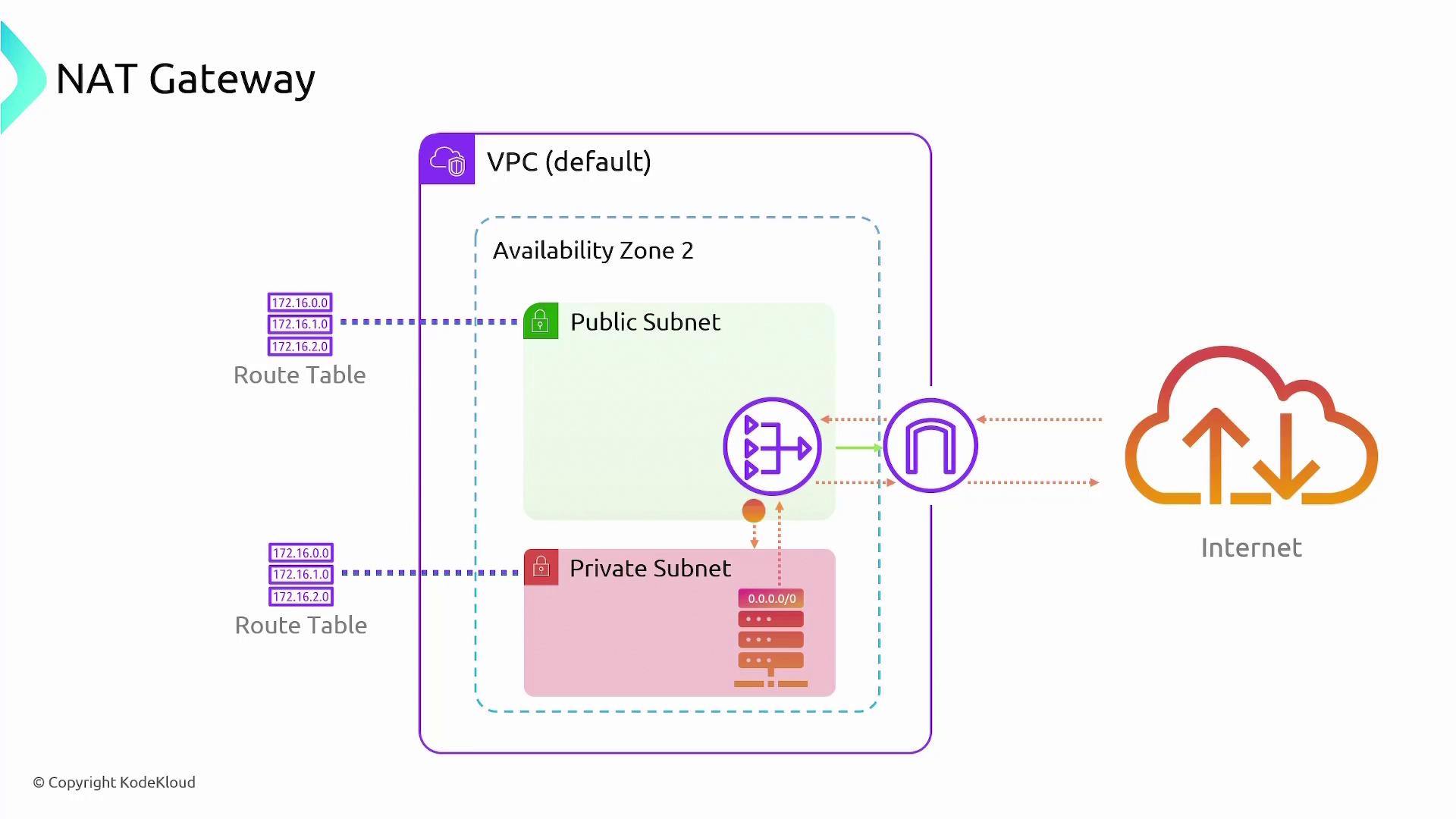
After deploying the NAT Gateway, update the route table for your private subnet with a default route that points to the NAT Gateway. This ensures that when the private server sends a request, the packets are directed from the private subnet to the NAT Gateway. The NAT then forwards these packets to the Internet Gateway, facilitating internet communication while keeping the private server off the public internet.
The following diagram illustrates a typical NAT Gateway setup within a VPC, including public and private subnets, route tables, and internet connectivity:
NAT Gateway Configuration and Operation
Key aspects of NAT Gateway configurations include:
- Dependency on an Internet Gateway: Even though a NAT Gateway is used, an Internet Gateway is necessary for external connectivity.
- Deployment on Public Subnets: NAT Gateways are deployed within public subnets and thus receive a public IP address. This setup is essential for routing outbound traffic to the internet.
- Routing Setup: Ensure that the private subnet’s route table directs all outbound traffic to the NAT Gateway.
- Fully Managed Service: Being a managed service by AWS, NAT Gateways require minimal ongoing management, with AWS handling maintenance and scaling.
- Billing Considerations: NAT Gateway usage is billed based on hourly usage and the volume of data processed.
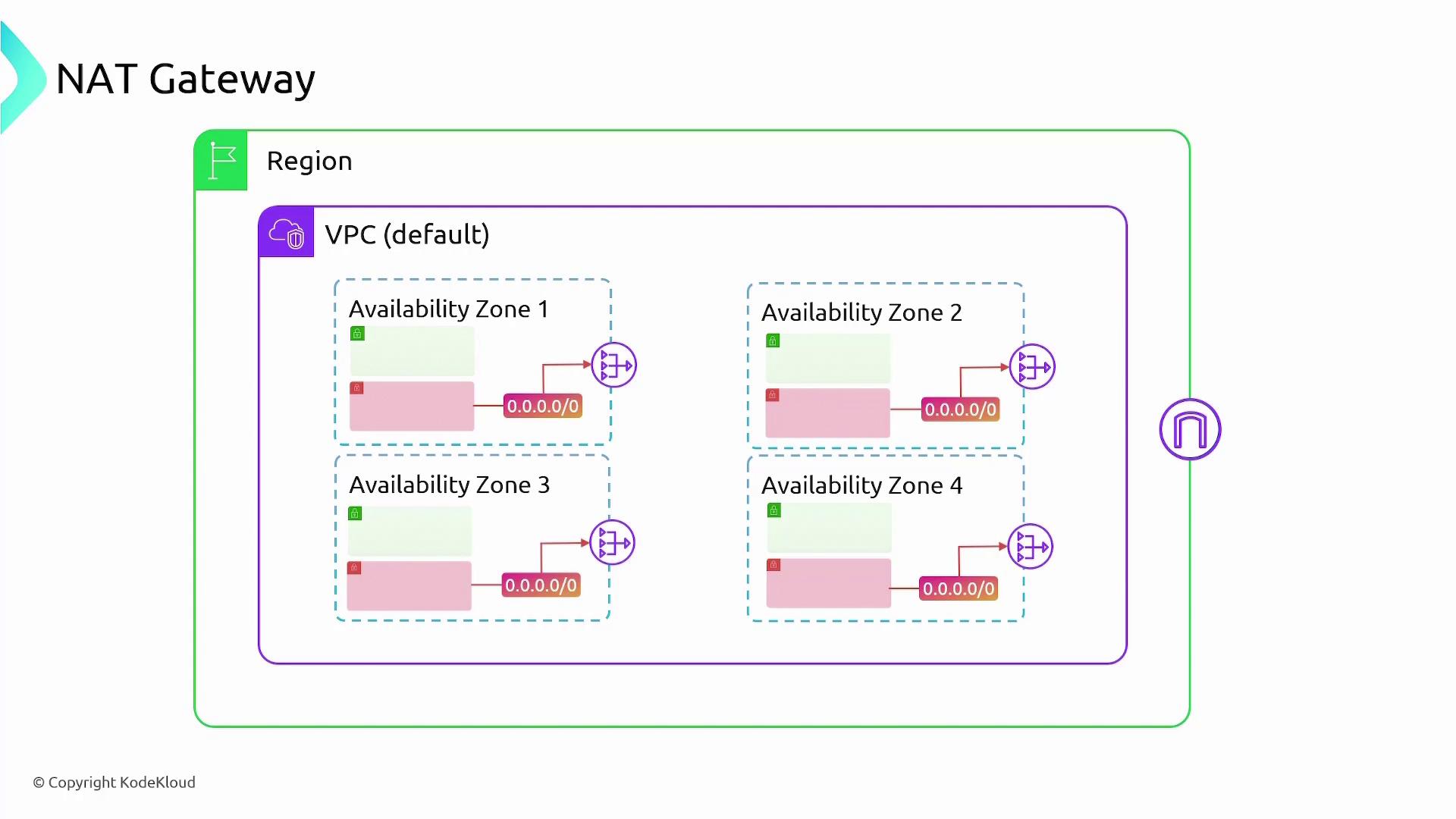
High Availability Note:
For maintaining high availability, it is recommended to deploy NAT Gateways across multiple Availability Zones. Since NAT Gateways are not region-resilient and are tied to specific Availability Zones, using multiple gateways mitigates the risk of service disruption in case of an outage in any single zone.
The diagram below demonstrates the deployment of one NAT Gateway per Availability Zone, illustrating the redundancy required for high availability:
Summary of NAT Gateway Features
NAT Gateways provide a secure method for routing outbound internet traffic from private subnets without exposing your instances to inbound traffic. Below is a concise summary of their features:
- Deployed on public subnets and require an Internet Gateway for internet communication.
- Utilize Elastic IPs (details of which are covered in further documentation).
- Must be deployed individually for each Availability Zone to ensure redundancy.
- Private subnet route tables must direct outbound traffic to the NAT Gateway.
- Operate as fully managed services provided by AWS, with billing based on uptime and data processing volume.
- Designed to automatically handle bursts of high traffic, typically supporting up to 10 Gbps throughput.
The following diagram offers a summary of NAT Gateway features, highlighting their deployment characteristics and operational capabilities:
Further, the NAT Gateway’s routing configuration and AWS management model ensure transparent operation once deployed. This allows private instances to access the internet securely while remaining safeguarded against external unsolicited connections.
Conclusion
NAT Gateways in a VPC provide an essential solution for securely managing outbound internet access from private subnets. By ensuring that internal services can communicate externally without exposure to direct inbound internet traffic, NAT Gateways help maintain the security and integrity of your network architecture. Whether you’re scaling up for high throughput or ensuring availability across multiple Availability Zones, NAT Gateways offer a robust and managed solution for modern cloud environments.