AWS Solutions Architect Associate Certification
Services Security
Demo Setting up CloudTrail for the first time
In this lesson, we demonstrate how to work with AWS CloudTrail effectively. You will learn how to view the past 90 days of events, create a CloudTrail trail to store and forward logs, and review detailed log records in both Amazon S3 and CloudWatch.
Viewing CloudTrail Events
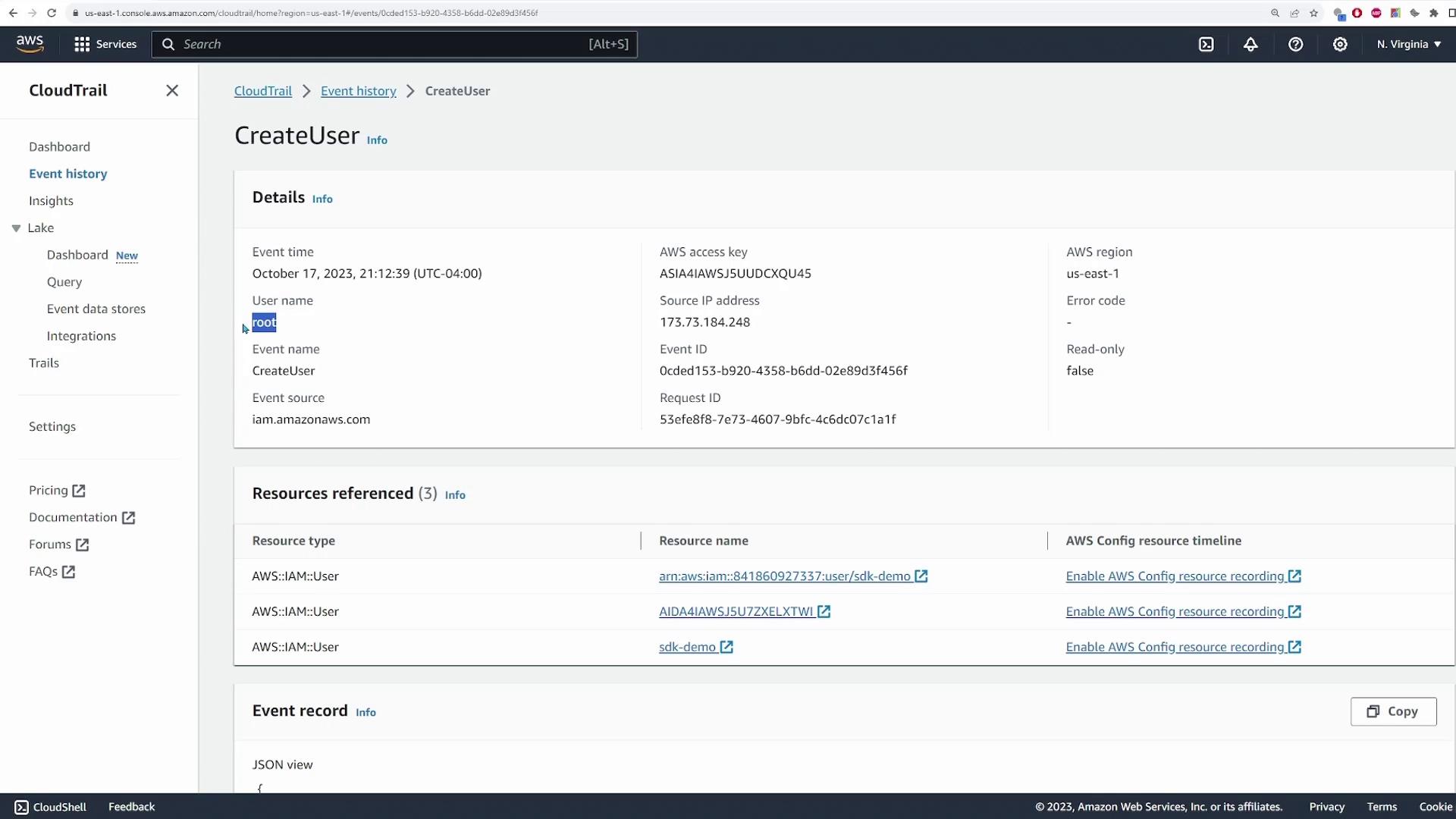
To begin, search for the CloudTrail service in the AWS Console. Once in the CloudTrail dashboard, click on Event History to view recent events. For example, selecting a "CreateUser" event lets you examine critical details such as the event time, the user who initiated the action, the event type, the source IP address, and the access key used.
Expanding a specific event (like the "CreateUser" event) provides a detailed view that includes:
- User identity
- Event time
- Action details
- Event metadata
You also have the option to view the event record in JSON format. Consider the following example of a CloudTrail event for a user creation action:
{
"eventVersion": "1.08",
"userIdentity": {
"type": "Root",
"principalId": "841860927337",
"arn": "arn:aws:iam::841860927337:root",
"accountId": "841860927337",
"accessKeyId": "ASIAIAAWSJ5UUDCXQU45",
"sessionContext": {
"sessionIssuer": {},
"webIdFederationData": {},
"attributes": {
"creationDate": "2023-10-18T00:46:36Z",
"mfaAuthenticated": "true"
}
}
},
"eventTime": "2023-10-18T01:12:39Z",
"eventSource": "iam.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "CreateUser",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"sourceIPAddress": "173.73.184.248",
"userAgent": "AWS Internal",
"requestParameters": {
"userName": "sdk-demo"
}
}
Note
CloudTrail by default displays events for the past 90 days. For long-term log storage or integration with services like Amazon S3 and CloudWatch, you must create and configure a CloudTrail trail.
Setting Up a CloudTrail Trail
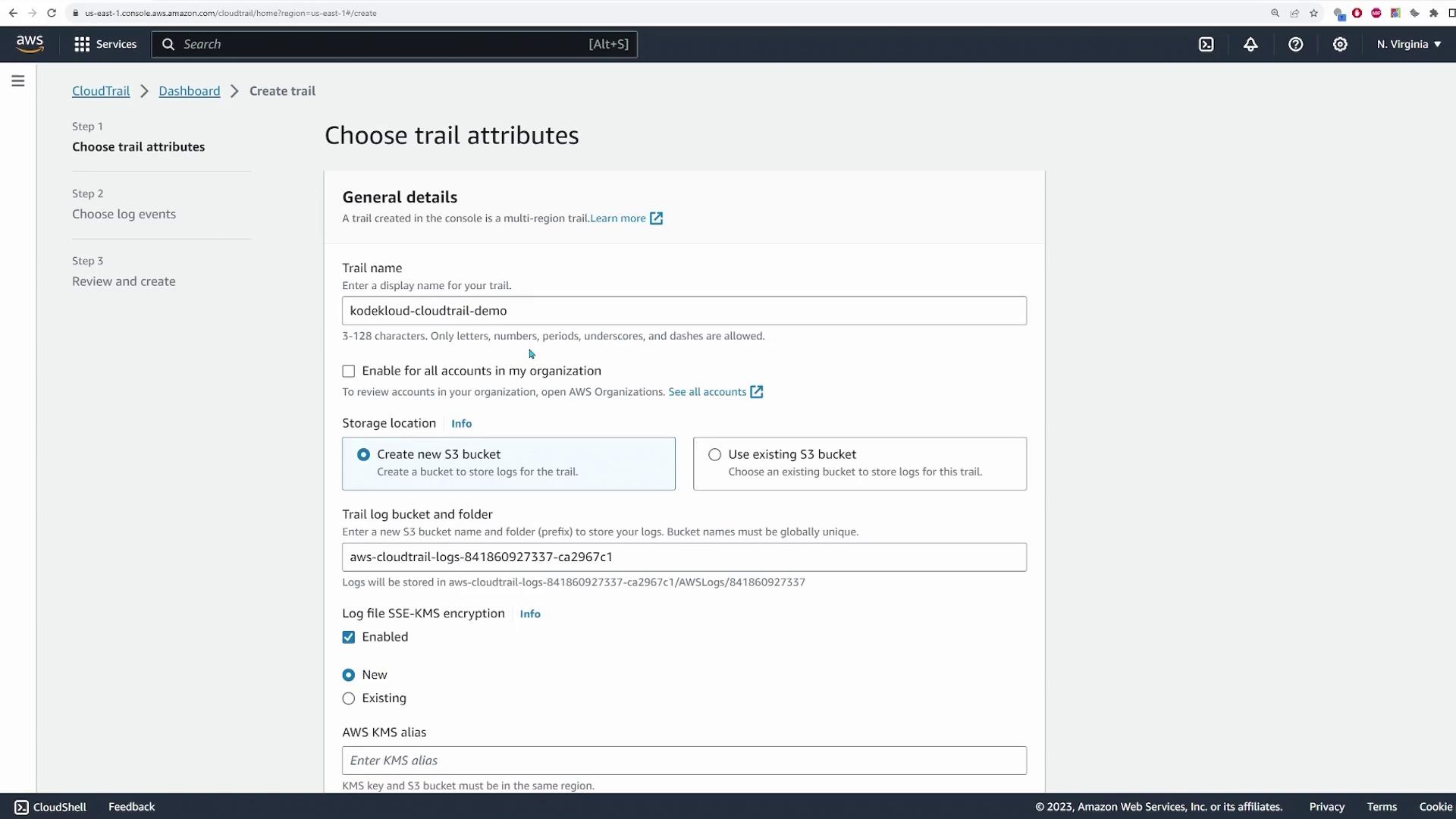
To extend the log retention period and enable additional integrations, follow these steps to set up a CloudTrail trail:
Create a New Trail:
Click on Create trail in the CloudTrail dashboard.Name Your Trail:
Enter a trail name (for example, "KodeKloud CloudTrail demo").Select Event Sources:
By default, the trail captures events from all regions in your account.
(If you wish to capture events from all accounts or your organization, select the appropriate option. In this demo, the organization option is not configured.)Configure Storage Settings:
Choose a storage location by either creating a new S3 bucket or selecting an existing one. A new bucket will be created with the suggested name unless renamed.Optional Encryption:
Enable encryption for your log files if required. In this demo, encryption remains disabled.Enable Log File Validation:
Decide whether to enable this feature to detect any modifications or deletions of log files.SNS Notifications (Optional):
Optionally, set up SNS notifications for new CloudTrail events or log file deliveries. This is disabled in the demo.Forward Logs to CloudWatch:
Enable the CloudWatch logs option. You can create a new log group or select an existing one. In this demonstration, the option "Create new log group" is selected with default configurations.Configure IAM Role for CloudWatch:
Set up a role to grant CloudTrail permissions to forward logs to CloudWatch. Choose New and leave the default configuration. When prompted, assign a role name (e.g., "CloudTrail CloudWatch role").Specify Event Types:
By default, management events are selected. Although you have the option to log data and insight events, these are left unchecked in this demo.
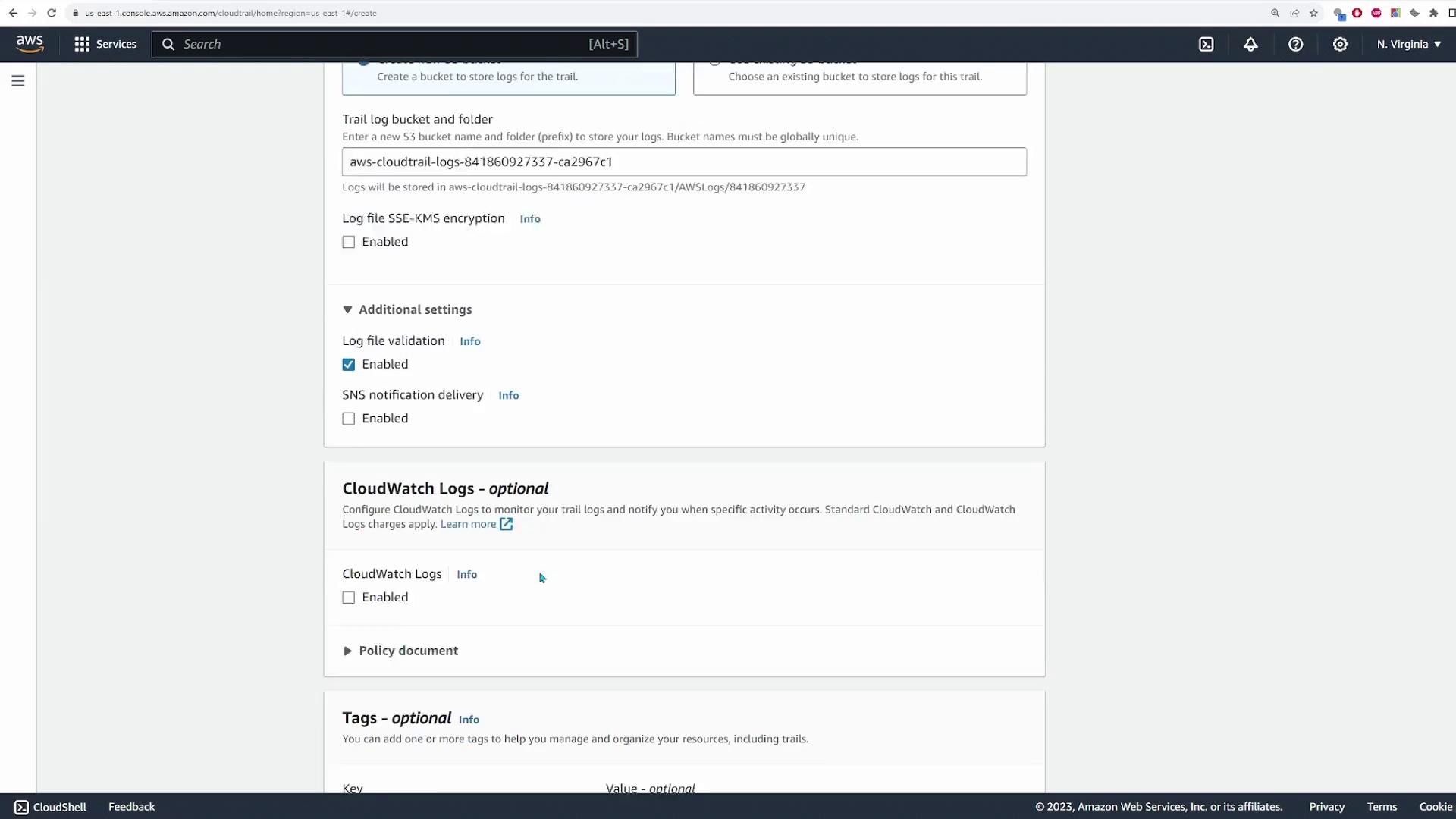
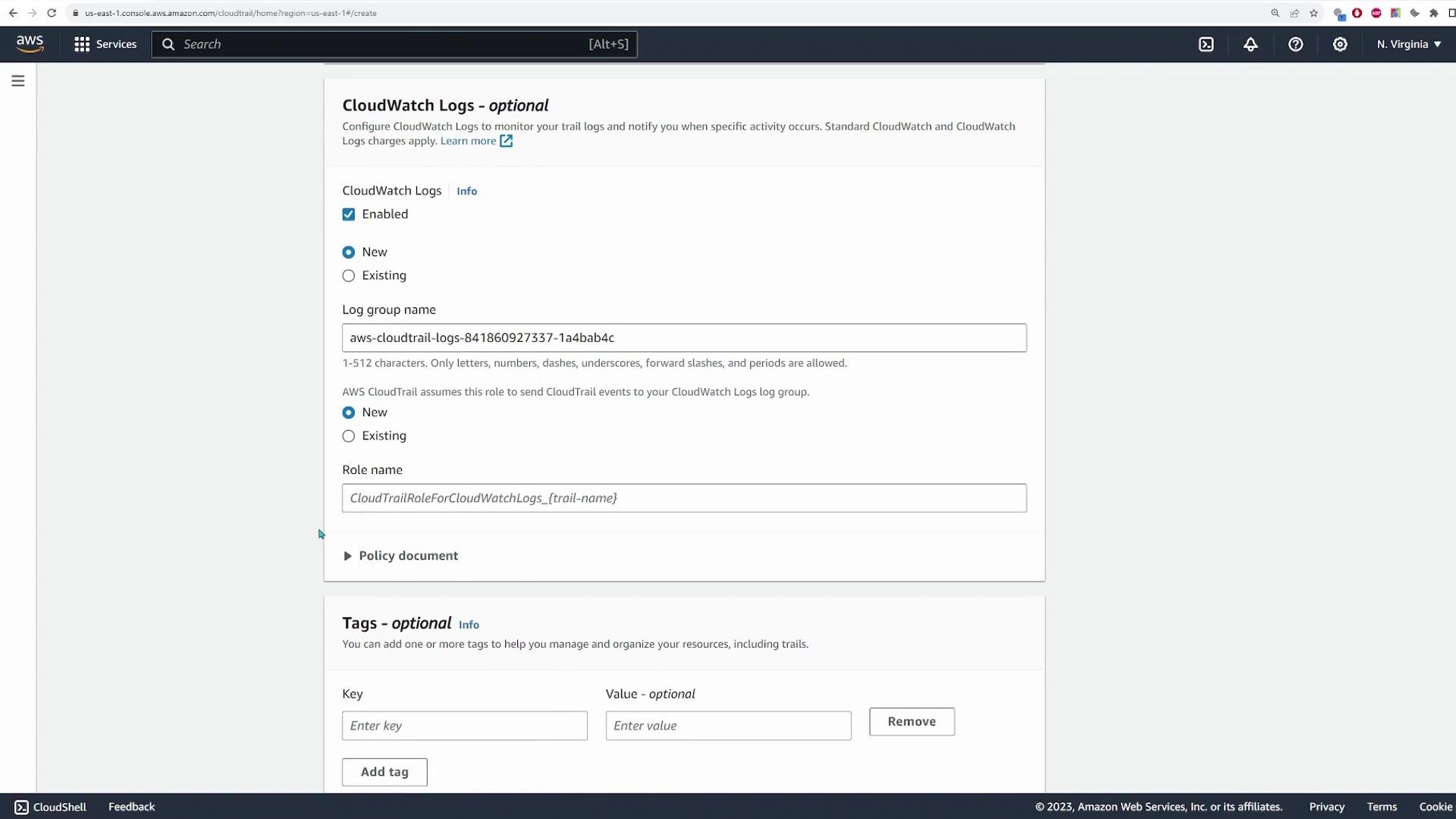
After reviewing your configuration, create the trail. Once the trail is active, navigate to your selected S3 bucket to view the stored log files.
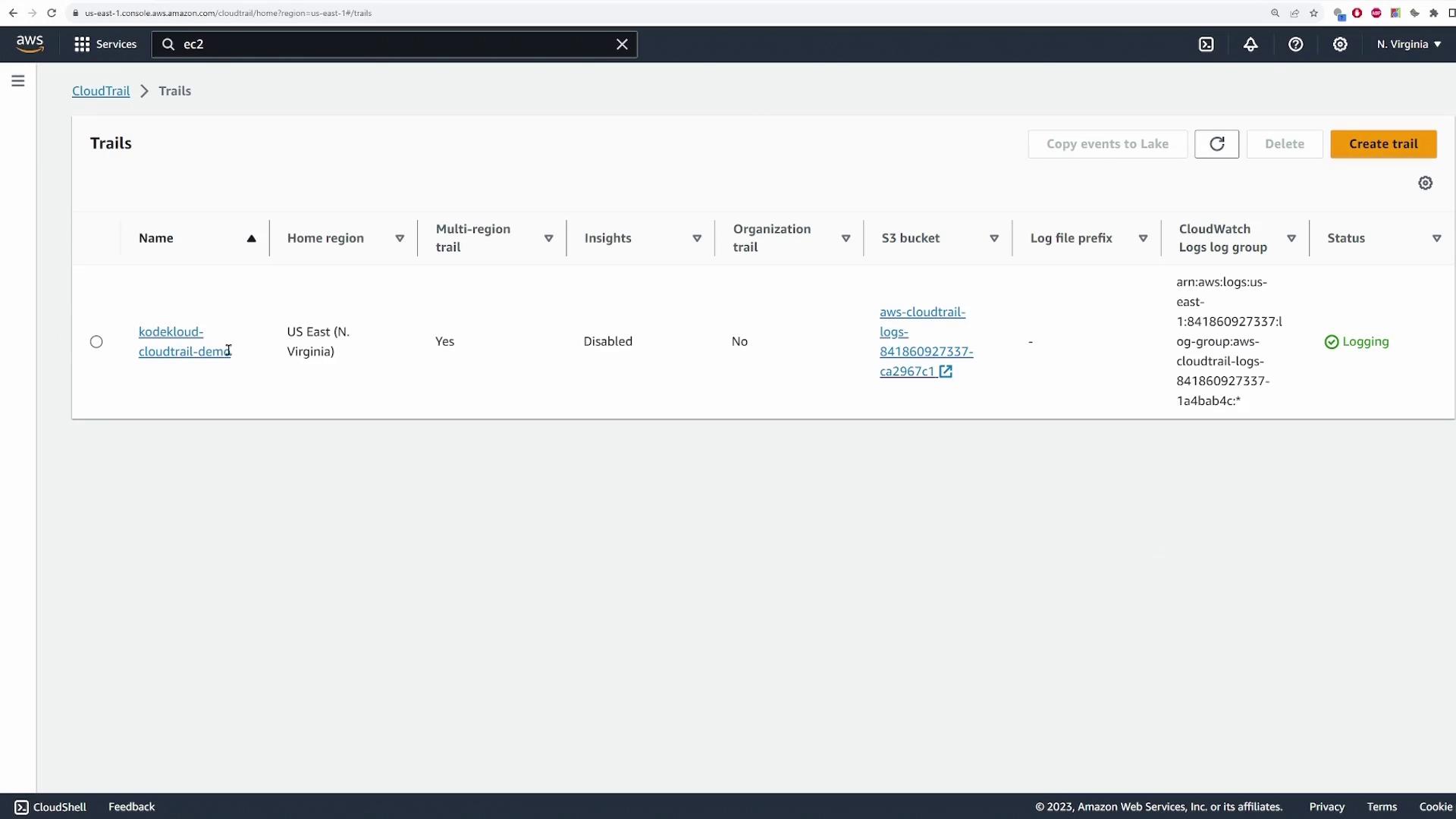
Exploring Logs in Amazon S3
When you follow the link provided in the CloudTrail console, you will be directed to the corresponding path within your S3 bucket. Inside the bucket:
- You will see an "AWSLogs" folder.
- Inside "AWSLogs", there is a folder corresponding to your account ID (for example, "841860927337").
- Within your account ID folder, open the "CloudTrail" folder.
- Logs are organized into sub-folders by region (in this demo, only "us-east-1" is present), then by year, month, and date.
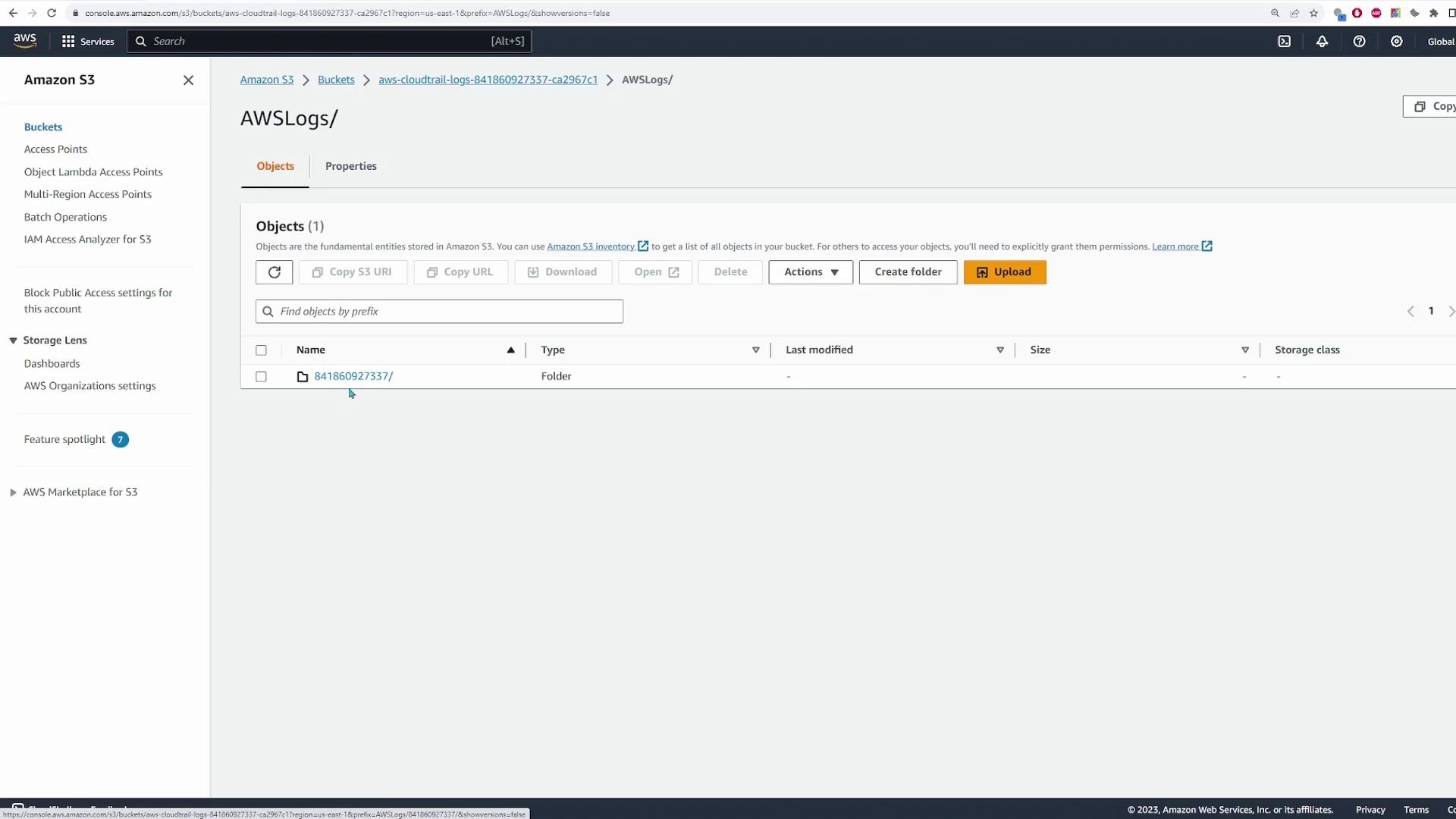
Inside the appropriate date folder, you will find JSON log files. Opening a JSON file in a new browser tab displays the raw log data. Since JSON may appear unformatted, you can copy and paste the data into a JSON viewer tool (e.g., JSON Viewer) to enhance readability.

For instance, the following JSON snippet is an event record for a "CreateRole" action stored in the S3 bucket:
{
"eventVersion": "1.08",
"userIdentity": {
"type": "Root",
"principalId": "841860927337",
"arn": "arn:aws:iam::841860927337:root",
"accountId": "841860927337",
"accessKeyId": "ASIAIAJW5J5USLDMR7RZ",
"sessionContext": {},
"sessionIssuer": {},
"webIdFederationData": {},
"attributes": {
"creationDate": "2023-10-21T17:04:29Z",
"mfaAuthenticated": "true"
}
},
"eventTime": "2023-10-21T17:13:23Z",
"eventSource": "iam.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "CreateRole",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"sourceIPAddress": "173.73.184.248",
"userAgent": "Coral/Jakarta",
"requestParameters": {
"path": "/service-role/",
"roleName": "Cloudtrail-cloudwatch-role",
"assumeRolePolicyDocument": "{\n \"Version\": \"2012-10-17\",\n \"Statement\": [\n {\n \"Effect\": \"Allow\",\n \"Principal\": {\n \"Service\": \"cloudtrail.amazonaws.com\"\n },\n \"Action\": \"sts:AssumeRole\"\n }\n ]\n}"
}
}
Storing logs in an S3 bucket guarantees that your logs are retained beyond the default 90-day retention period.
Monitoring with CloudWatch
Next, let’s review how CloudTrail logs are forwarded to CloudWatch for real-time monitoring. To access CloudWatch logs:
- Search for the CloudWatch service in the AWS Console.
- Navigate to Log Groups.
Here, you will find a log group that contains all the forwarded CloudTrail logs. - Click on a log stream within the group to see the events in a structured JSON format.
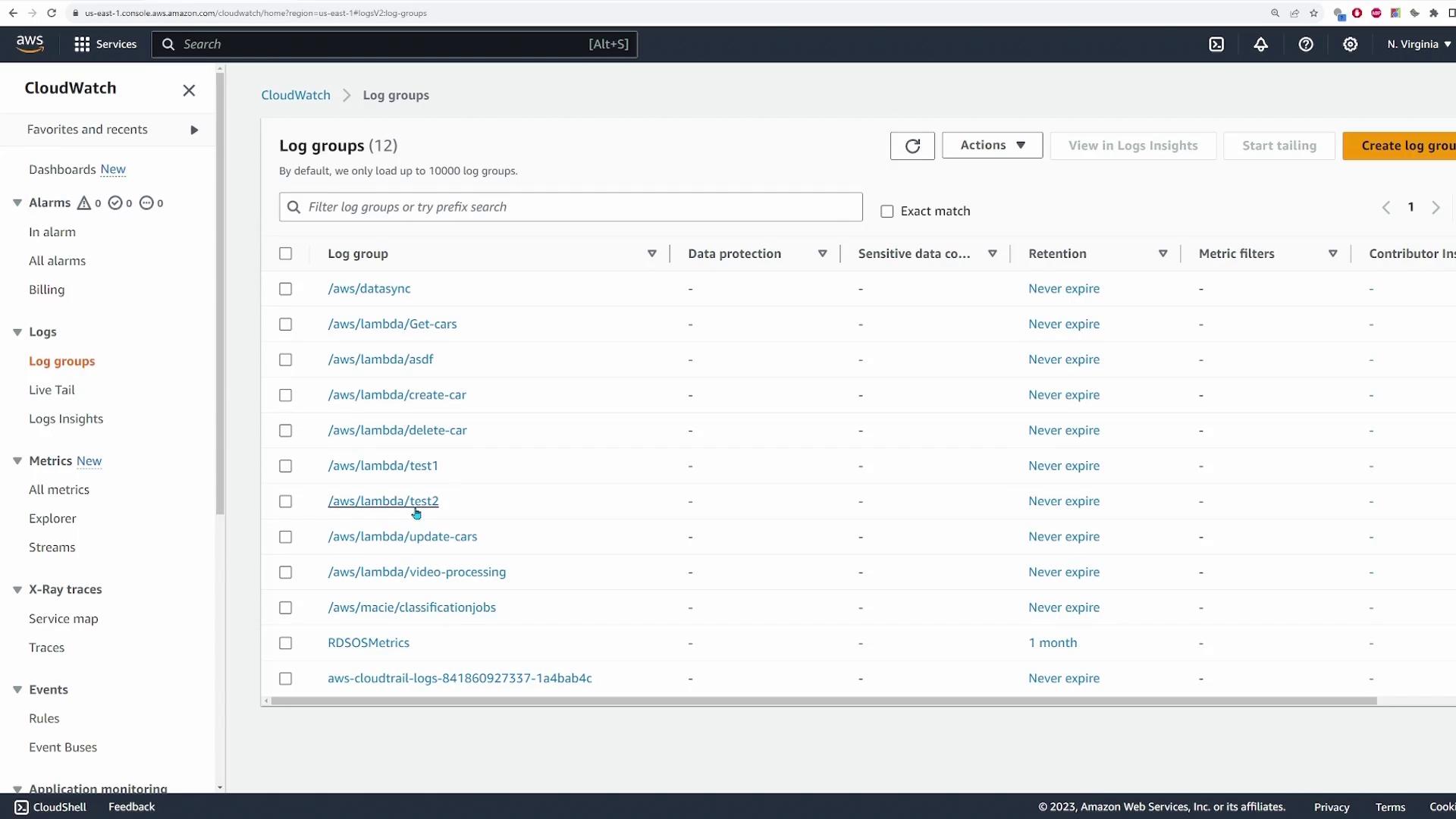
Below is an example of a CloudTrail event forwarded to CloudWatch:
{
"eventVersion": "1.08",
"userIdentity": {
"type": "Root",
"principalId": "841869297337",
"arn": "arn:aws:iam::841869297337:root",
"accountId": "841869297337",
"accessKeyId": "ASIA...",
"sessionContext": {
"sessionIssuer": {},
"webIdFederationData": {},
"attributes": {
"creationDate": "2023-10-21T17:04:29Z",
"mfaAuthenticated": "true"
}
}
},
"eventTime": "2023-10-21T17:19:44Z",
"eventSource": "notifications.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "ListNotificationHubs",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"sourceIPAddress": "173.73.184.248",
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/118.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"requestParameters": null,
"responseElements": null,
"eventID": "7dcad2c4-c99a-42c2-3c2e3c1f81a",
"readOnly": true,
"eventType": "AwsApiCall",
"managementEvent": true,
"recipientAccountId": "841869297337",
"eventCategory": "Management"
}
With CloudTrail integrated to store logs in Amazon S3 and forward them to CloudWatch, you gain both the long-term data retention you need and the ability to monitor changes in real time.
Conclusion
In this demonstration, you learned how to:
- View recent CloudTrail events in the AWS Console,
- Set up a CloudTrail trail to extend log retention and enable integration with S3 and CloudWatch,
- Navigate the S3 bucket structure to locate JSON log files,
- Use CloudWatch to monitor real-time events.
Pro Tip:
For further reading on AWS CloudTrail and its integration with other AWS services, visit the AWS CloudTrail Documentation and explore related tutorials on AWS Blogs.
Enjoy exploring AWS CloudTrail to enhance the security and monitoring of your AWS account!
Watch Video
Watch video content