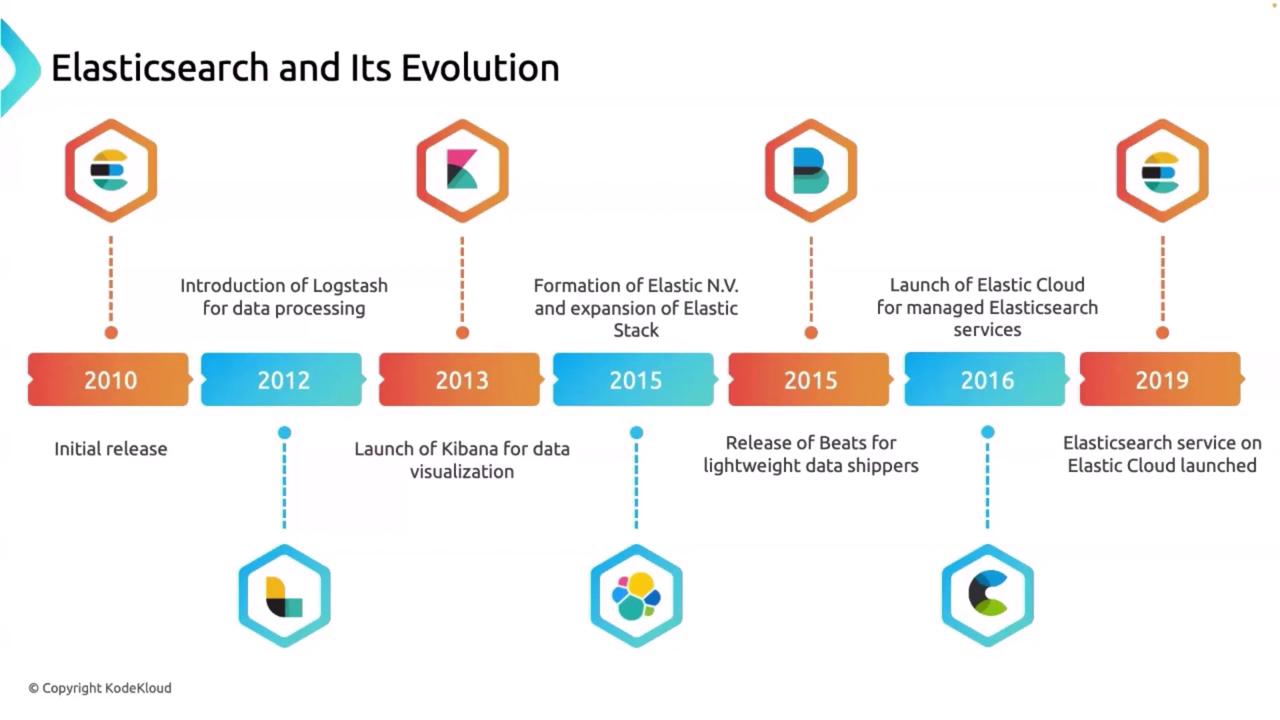
The Early Days: 2010 to 2013
In 2010, Shay Banon released Elasticsearch, a powerful search engine engineered for real-time search and analytics. Its innovative design enabled organizations to efficiently sift through and analyze vast amounts of data. By 2012, the capabilities of Elasticsearch expanded significantly with the introduction of Logstash—a server-side data processing pipeline. Logstash ingests data from various sources, transforms it, and then outputs it to the desired storage system. This enhancement allowed users to pre-process and structure their data, ultimately making it more searchable and analyzable. A year later, in 2013, the launch of Kibana marked another major milestone. Kibana is an open-source dashboard that provides intuitive data visualization by presenting data stored in Elasticsearch. With Kibana, users can create dynamic, shareable dashboards to interpret even the most complex datasets. Together, Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana form what is famously known as the ELK stack.Expansion and Integration: 2015 to 2016
The evolution of the Elastic ecosystem continued in 2015 with the formation of Elasticsearch NV—the company behind Elasticsearch. This period saw significant expansion of the Elastic Stack as Elastic NV integrated additional tools into a comprehensive data analysis suite. In the same year, Beats was introduced as lightweight data shippers designed to send data directly from edge machines to Elasticsearch. Beats play a pivotal role in streamlining data collection, reducing the load on central processing systems, and enhancing overall performance. In 2016, the launch of Elastic Cloud offered fully managed Elasticsearch services in the cloud. This service simplified the deployment, management, and scaling of Elasticsearch clusters, making it easier for organizations to embrace cloud solutions without the complexities of maintaining underlying infrastructure.The integration of these components into the Elastic Stack revolutionized data analysis by offering a seamless flow from data collection through visualization.
A Unified Cloud Experience: 2019 and Beyond
By 2019, Elastic Cloud had successfully integrated Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats into a single, cohesive cloud offering. This unified platform provided a scalable, accessible solution that empowered organizations to leverage the full capabilities of the Elastic Stack. The timeline below visually summarizes this evolution: