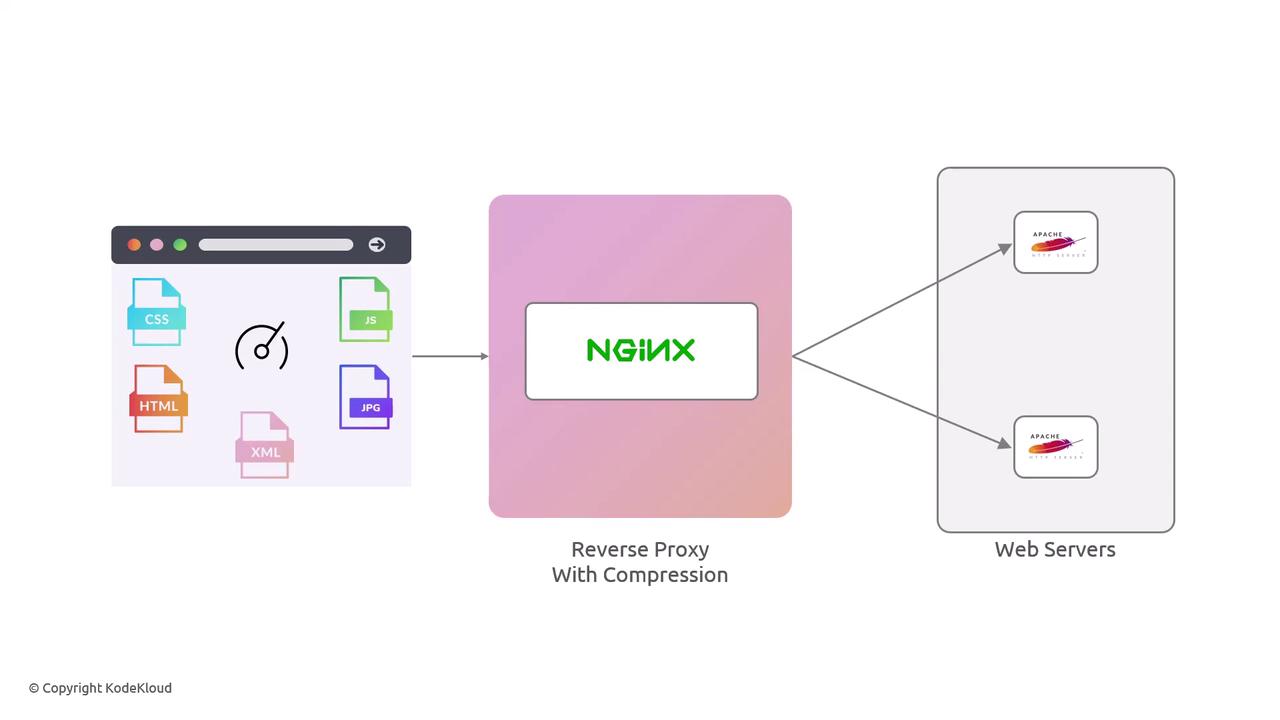
Learn how to optimize your Nginx reverse proxy by enabling gzip compression. We’ll demonstrate loading large JPEG files before and after gzip, measure performance gains, and configure a complete server block with SSL, caching, rate limiting, and security headers.
1. Prepare Large JPEG Files By default, JPEGs are already compressed and benefit little from gzip. For demo purposes, inflate them to 20 MB:
Inflating JPEGs simulates slow-loading assets. In production, you typically gzip text-based resources only.
# Move into the images directory cd /var/www/html/images/ # Check original file sizes ls -lh * .jpg # Inflate each file to 20 MB for file in *.jpg ; do fallocate -l 20M " $file " done # Confirm new sizes ls -lh * .jpg
2. Monitor Apache Access Logs Keep an eye on incoming requests while you load resources:
tail -F /var/log/apache2/access.log
Load the site in your browser or via curl to see entries in real time.
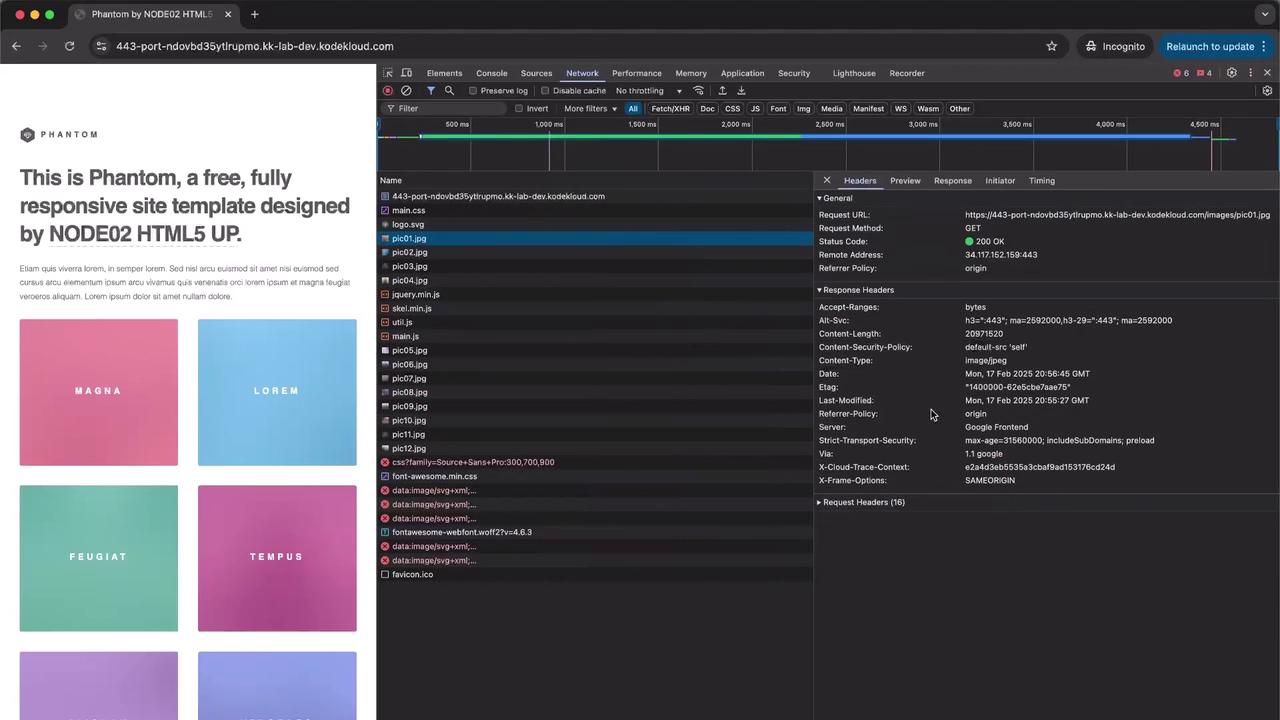
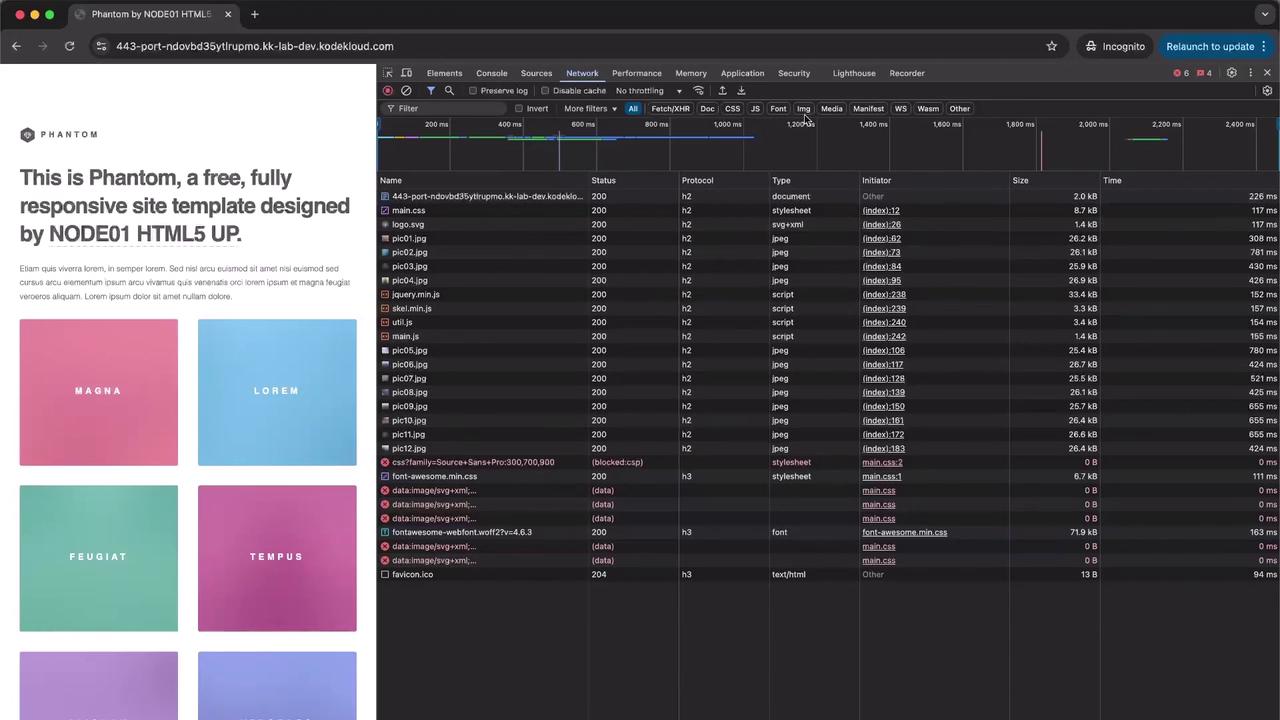
3. Test Without gzip Compression Open your web page in Incognito or Private mode. In Chrome DevTools:
Switch to the Network tab.
Reload the page.
Observe image requests taking 4–5 seconds each.
In Firefox’s network panel, note that the Transfer Size equals the full ~20 MB:
4. Enable gzip in Nginx Edit /etc/nginx/nginx.conf (or your include file) to add gzip settings under the http block:
http { # --------------------------- # Gzip Compression Settings # --------------------------- gzip on ; gzip_vary on ; gzip_proxied any; gzip_comp_level 6 ; gzip_buffers 16 8k ; gzip_http_version 1.1 ; gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript image/jpg image/jpeg font/ttf font/eot; # ... other HTTP-level settings ... }
Test and apply the configuration:
nginx -t systemctl restart nginx
Always test your configuration (nginx -t) before reloading Nginx to avoid downtime.
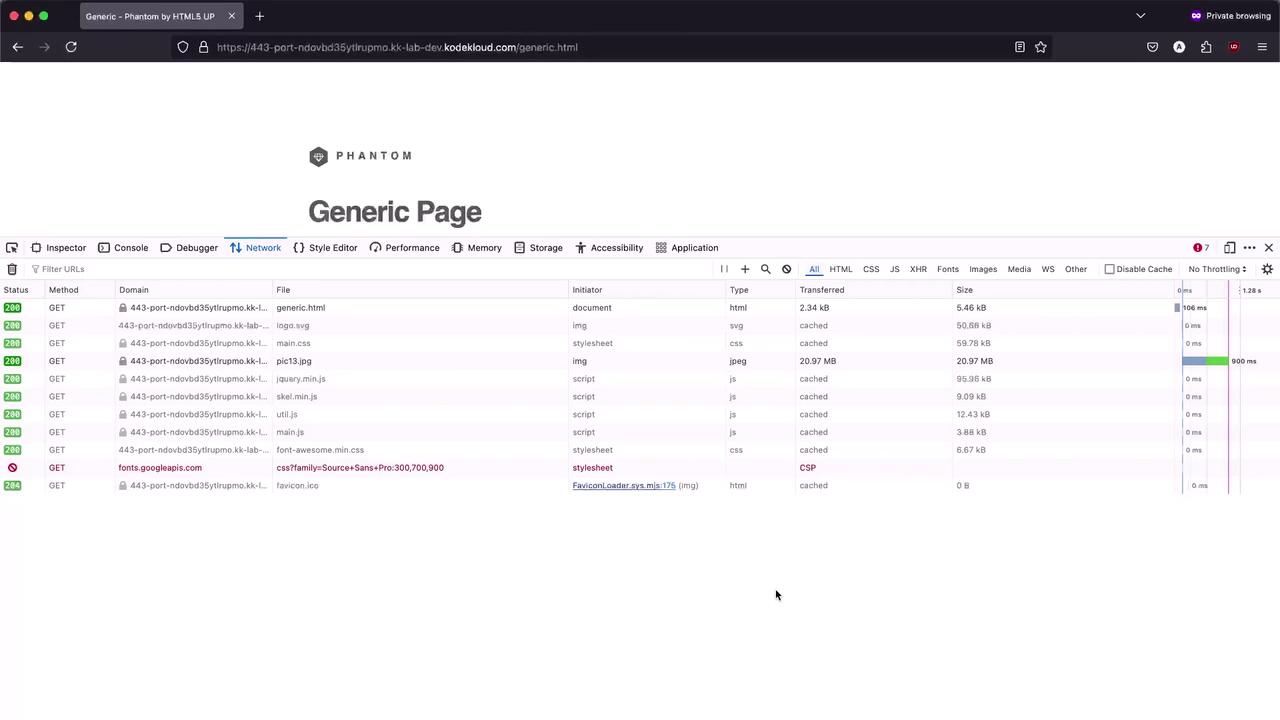
Reload the page in Chrome DevTools → Network → All . You should see image loads in milliseconds:
Click any resource and inspect the Response Headers for:
In Firefox, confirm that Transfer Size is significantly lower and load times drop to the low hundreds of milliseconds.
6. Complete Example: Nginx Server Block Below is a full Nginx configuration combining upstream proxy, SSL, security headers, gzip, caching, and rate limiting:
# Define backend servers upstream example { server node01:443; server node02:443; } # Redirect HTTP to HTTPS server { listen 80 ; server_name example.com; return 301 https://$ host $ request_uri ; } # Main HTTPS server server { listen 443 ssl; server_name example.com; ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/example.com.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/certs/example.com-key.pem; root /var/www/html; index index.html index.htm; # Security headers add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" ; add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" ; add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src 'self'" ; add_header Referrer-Policy "origin" ; add_header Cache-Control "public, max-age=3600" ; # Rate limiting limit_req_zone $ binary_remote_addr zone=req_limit_per_ip:10m rate=1000r/m; limit_req_status 429 ; # Proxy cache configuration proxy_cache_path /var/lib/nginx/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=app_cache:10m; proxy_cache_key "$ scheme $ request_method $ host $ request_uri " ; proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m ; proxy_cache_valid 404 1m ; # Gzip settings (same as above) gzip on ; gzip_vary on ; gzip_proxied any; gzip_comp_level 6 ; gzip_buffers 16 8k ; gzip_http_version 1.1 ; gzip_types text/plain text/css application/json application/javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript image/jpg image/jpeg font/ttf font/eot; location / { proxy_set_header Host $ host ; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $ proxy_add_x_forwarded_for ; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $ scheme ; proxy_cache app_cache; proxy_pass https://example; } location /admin { auth_basic "Restricted Access" ; auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/conf.d/.htpasswd; } }
Deep dive into HTTP headers for security, caching, CORS, and more. Useful references: