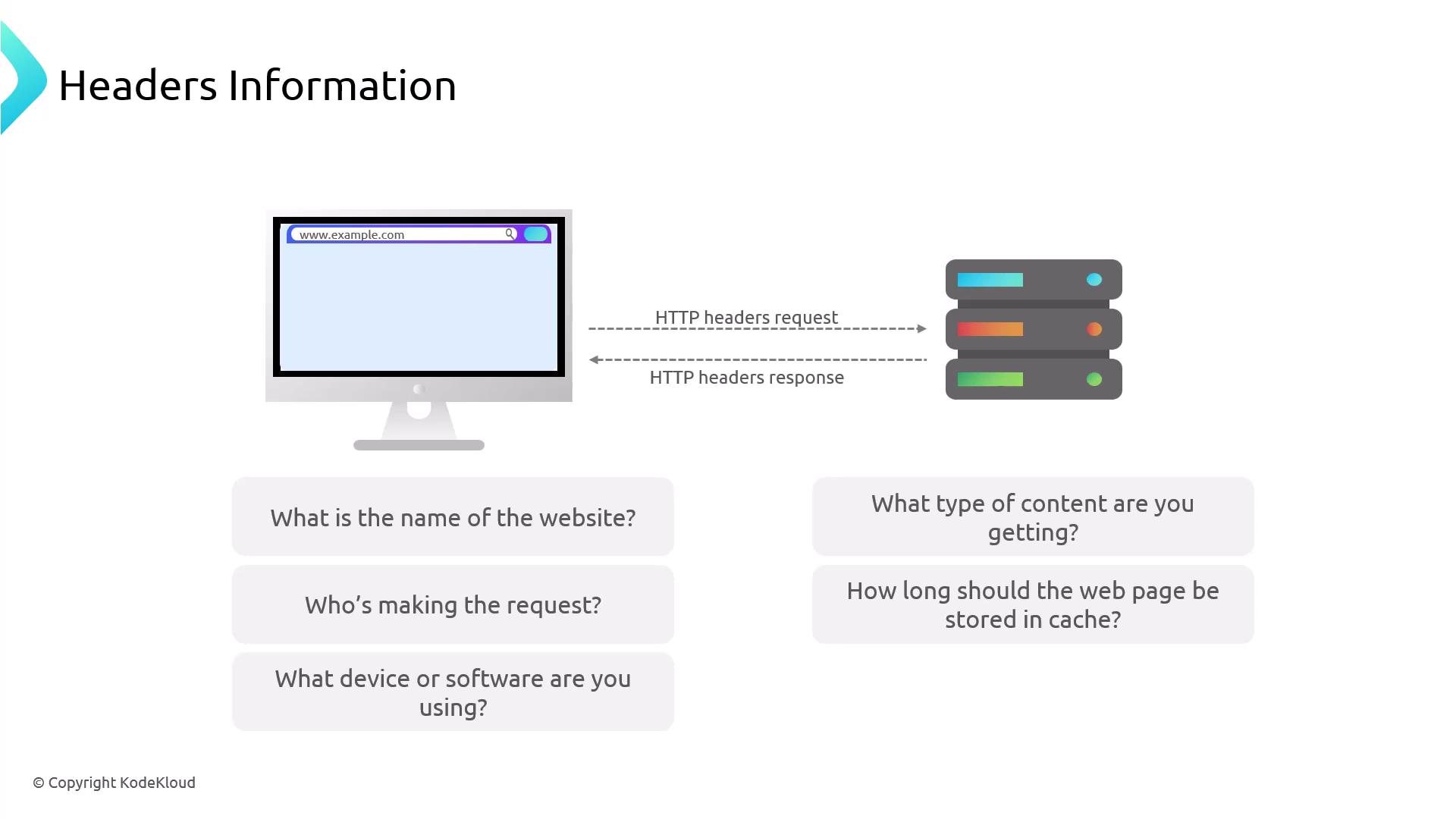
Request–Response Flow
When you navigate to a website:- Your browser sends an HTTP request with request headers describing the desired resource.
- The server processes the request and replies with an HTTP response, including response headers that describe the returned content.
Anatomy of an HTTP Header
Each header line follows the formatKey: Value. For example:
- Host: Specifies the target domain (
example.com). - User-Agent: Provides details about the client software.
- Accept: Indicates which content types the client can process.
- Cache-Control: Instructs caching behavior.
In HTTP/2, pseudo-headers (like
:method, :path) precede regular headers and always start with :.Types of HTTP Headers
HTTP headers are grouped by their roles. Below is a visual overview followed by a summary table.
| Header Category | Purpose | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| General | Used in both requests and responses | Connection, Cache-Control |
| Request | Sent by clients to servers | User-Agent, Accept |
| Response | Sent by servers back to clients | Content-Type, Server |
| Security | Mitigate web vulnerabilities | Content-Security-Policy |
| Authentication | Verify client identity | Authorization |
| Caching | Control resource caching | Expires, ETag |
| CORS | Enable cross-origin resource sharing | Access-Control-Allow-Origin |
| Proxy | Convey client info through proxies | X-Forwarded-For, X-Real-IP |
| Custom | Application-specific metadata | X-Custom-Header |
General Headers
General headers carry metadata applicable to both requests and responses, such as connection management and caching directives.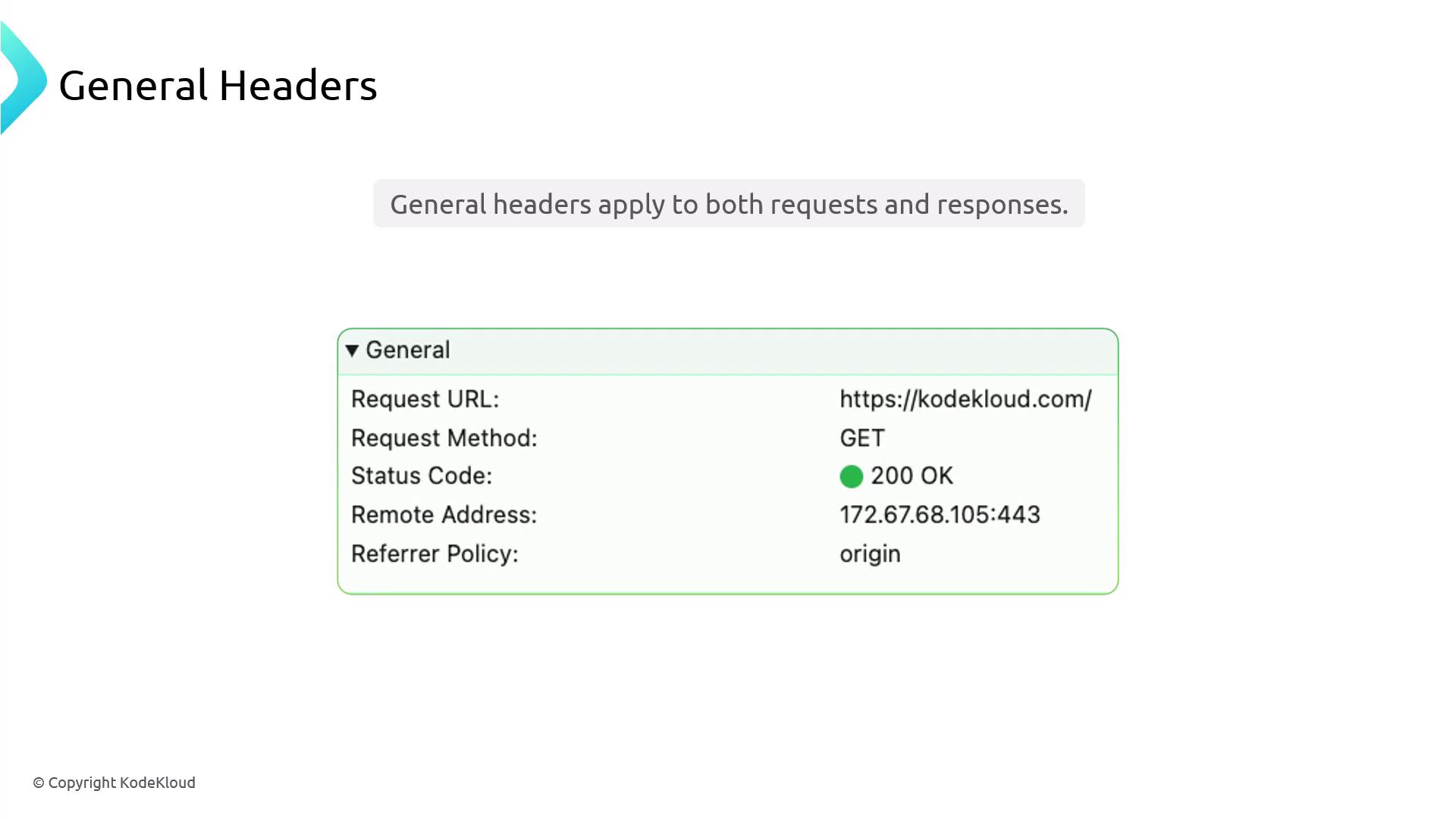
Request Headers
Clients send these headers to the server:- Accept: Media types the client prefers.
- User-Agent: Browser and OS identification.
- Accept-Language: Preferred languages.
- Cookie: Session data stored by the browser.
Response Headers
Servers include these headers in replies:- Content-Type: Media type of the response body.
- Cache-Control: Caching policy instructions.
- Server: Server software identifier.
- X-Cache: Indicates cache hits or misses.
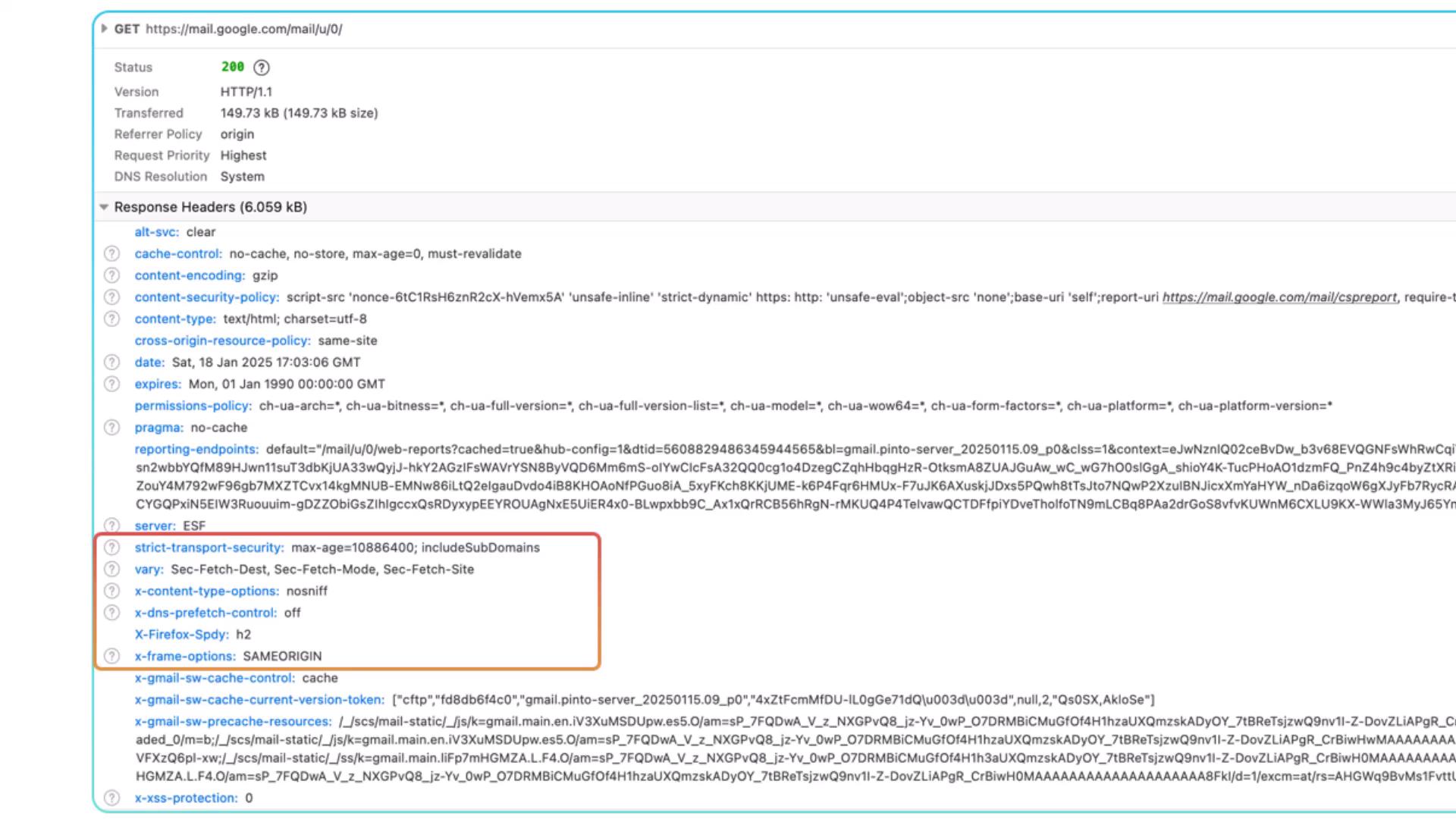
Security Headers
Security headers guard against common web threats like XSS, clickjacking, and mixed-content issues.Improperly configured security headers can break site functionality or leave vulnerabilities. Always test in staging before deploying.
Authentication Headers
Authenticate requests using credentials or tokens:- Basic: Base64-encoded
username:password. - Bearer: Token-based (e.g., OAuth 2.0, JWT).
Caching Headers
Manage how clients and proxies cache responses:- Cache-Control: Fine-grained caching instructions.
- Expires: Absolute expiry date/time.
- ETag: Entity tag for version validation.
CORS Headers
Enable controlled cross-origin requests to protect resources: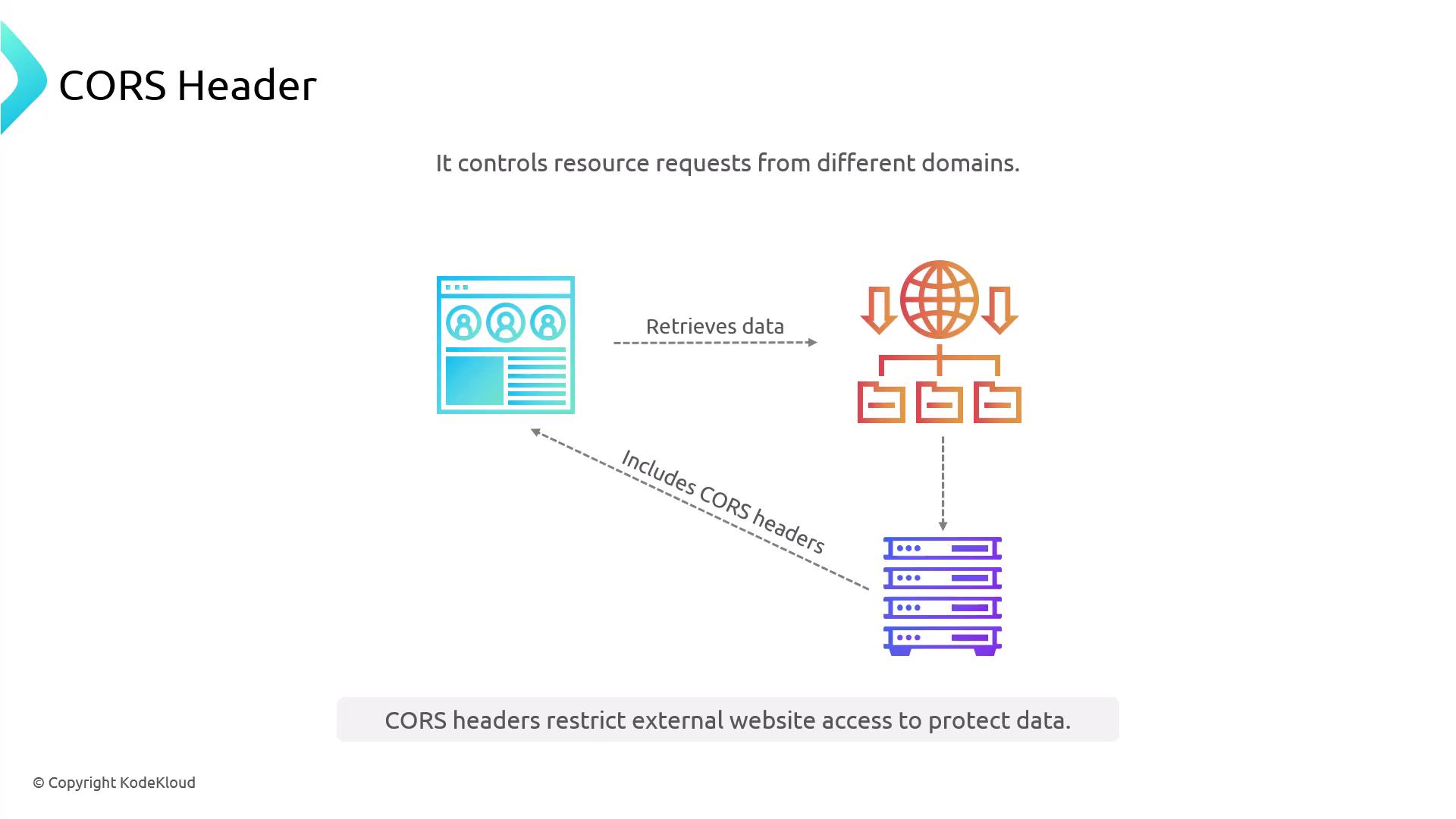
Browsers enforce CORS; servers must explicitly allow desired origins and methods.
Proxy Headers
When requests pass through load balancers or reverse proxies, these headers preserve client information:- X-Forwarded-For: Original client IP through multiple proxies.
- X-Forwarded-Host: Original
Hostheader. - X-Forwarded-Proto: Protocol used by the client.
- X-Real-IP: Direct client IP (single proxy scenario).
Custom Headers
Define your own headers for feature flags, tracing, or legacy integrations:X- (for legacy) or a vendor namespace.
Nginx Built-in Variables
Nginx uses$-prefixed variables to access request and server data dynamically.

$remote_addr: Client IP address$host: Host header value$scheme: Protocol (httporhttps)$request_uri: Full request URI including query string

Example Nginx Configuration
Below is a sample Nginxserver block that sets security headers and proxies traffic to an upstream backend:
- add_header: Appends headers to outbound responses.
- proxy_set_header: Customizes headers sent to upstream servers.