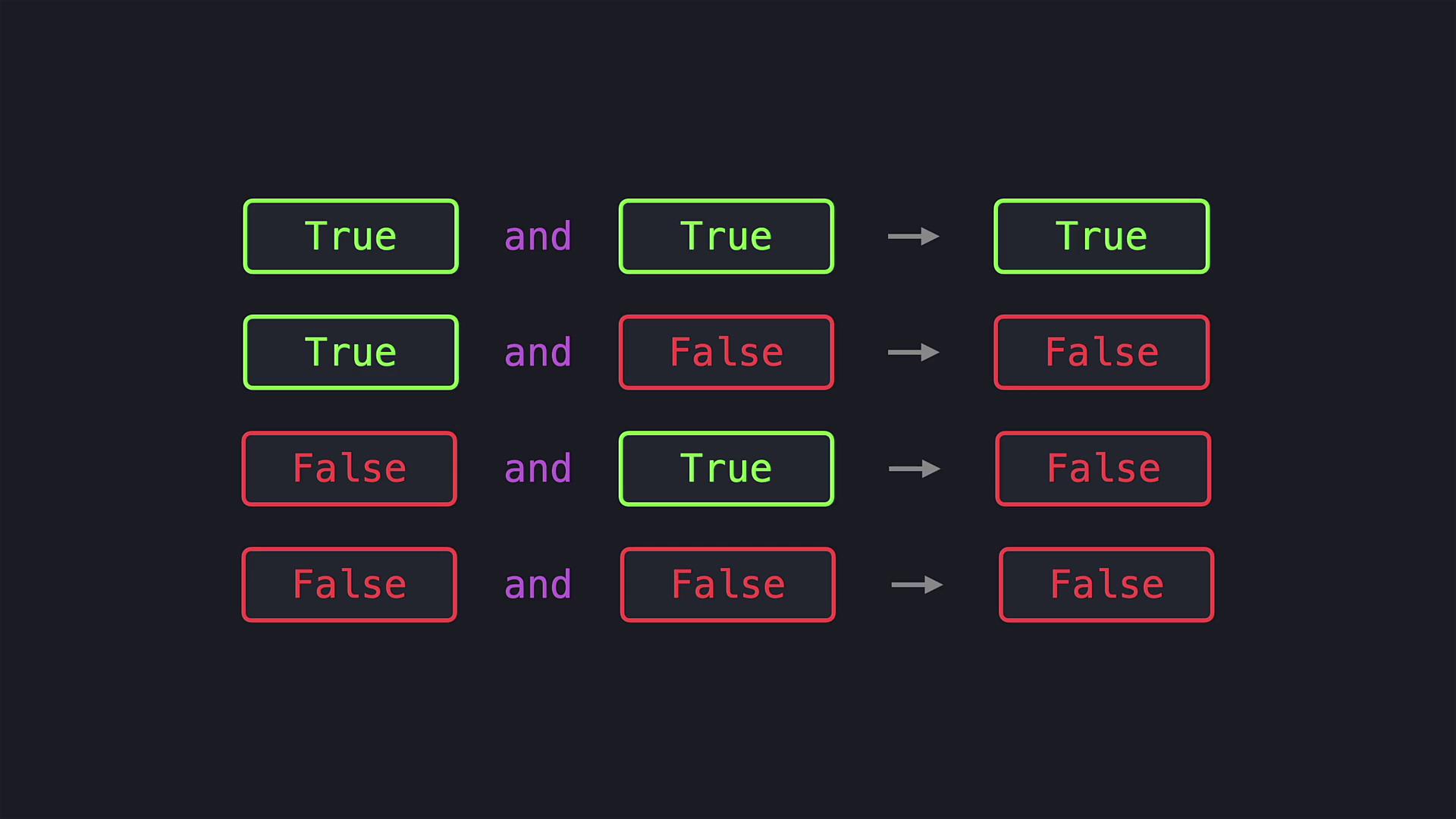
and operator to determine if both age1 and age2 are greater than or equal to 18. The and operator returns True only when both conditions are met; otherwise, it yields False, and the following code blocks are evaluated accordingly.
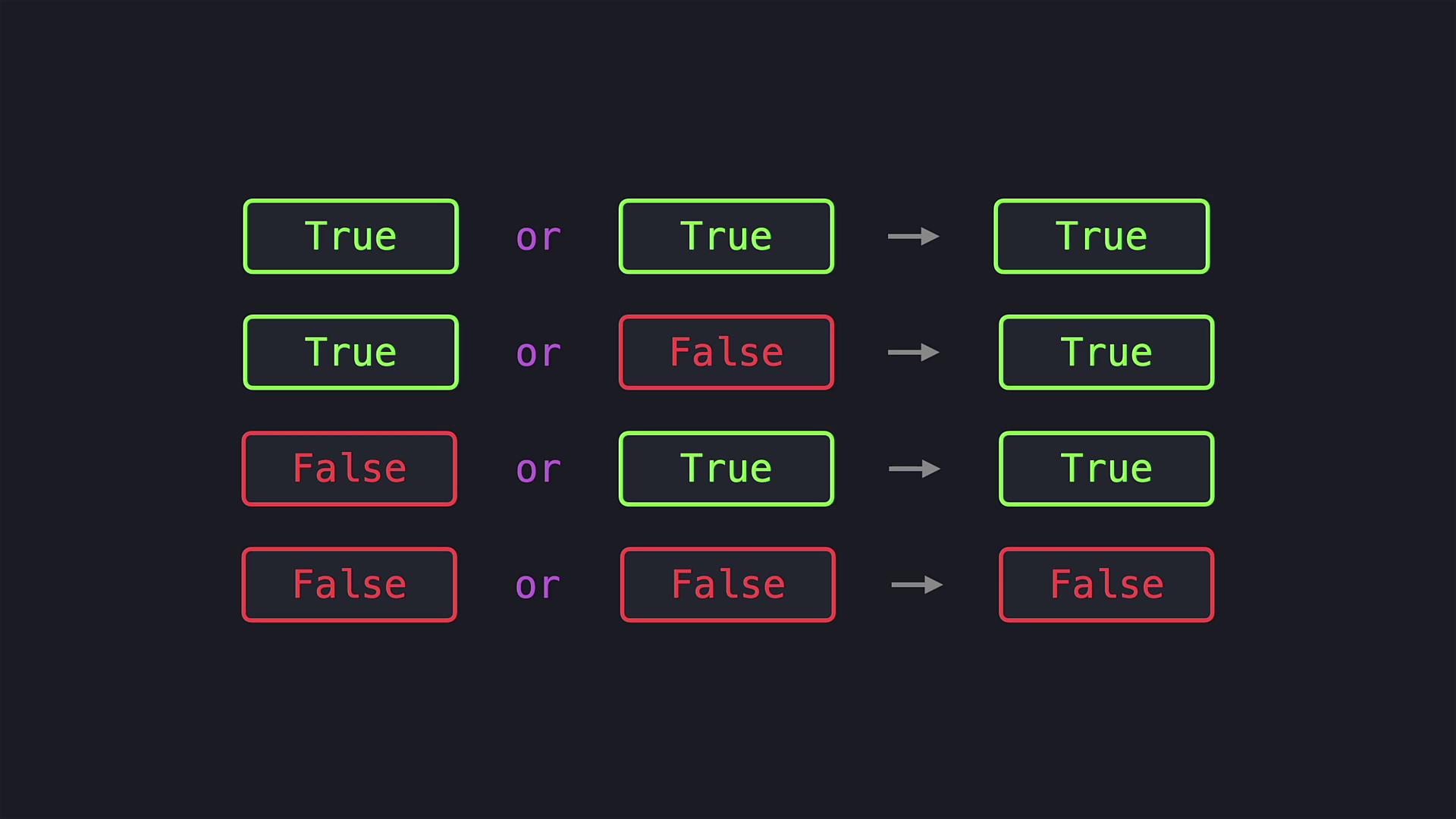
or operator. This operator returns True if at least one of the conditions is True. In this scenario, if either age1 or age2 is 18 or older, the program will execute the corresponding code block. Only when both conditions are False does the program fall through to the final block.
Logical operators like
and, or, and not are fundamental in programming. They help you combine or invert conditions to build complex decision-making logic in your code.not. This operator reverses the truth value of a boolean expression. For example, if we want to display “You are not hungry” when the variable is_hungry is False, we can check this condition as follows:
is_hungry is False, the expression not is_hungry evaluates to True, and the message is printed.
That’s all for this lesson. Happy coding, and see you in the next article!