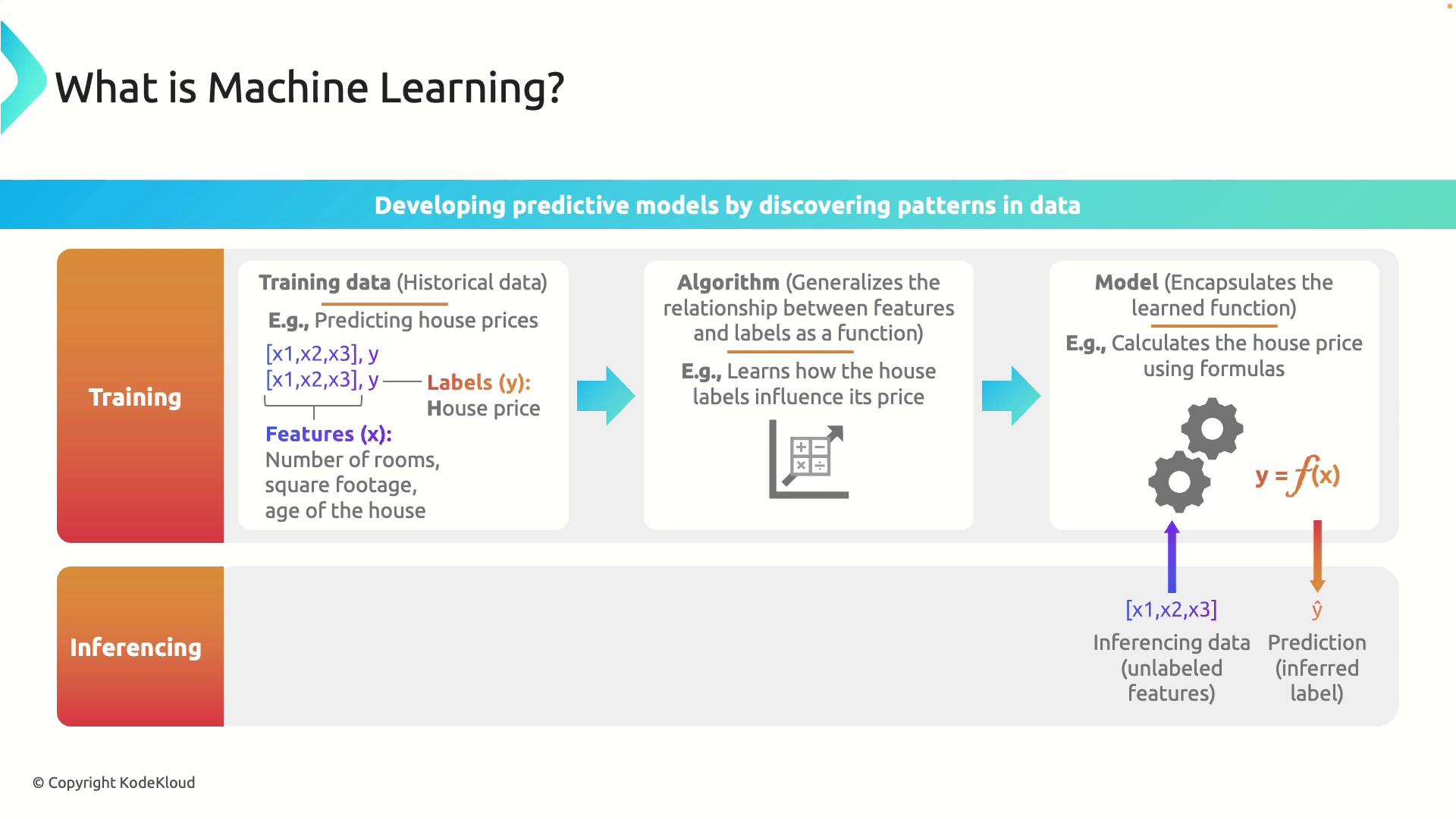
Training Phase
During the training phase, the model learns from historical data. The training dataset includes observations where each observation contains input features and a corresponding label. In this context:- Features: Attributes or variables (e.g., number of rooms, square footage, age).
- Label: The target outcome to predict, such as the house price.
- 3 bedrooms
- 1,500 square feet
- 20 years of age
- Priced at $300,000
This sample function is a simplified representation for educational purposes. In real-world applications, models are often more complex and consider additional factors.
Inferencing Phase
Once trained, the model enters the inferencing phase, where it uses the learned function to predict outcomes for new data that includes features without labels. Consider predicting the price of a new house with the following features:- 4 bedrooms
- 2,000 square feet
- 10 years of age
- 50,000 × 4 (for the number of rooms)
- 200 × 2,000 (for the square footage)
- Minus 1,000 × 10 (for the age)
The inferencing phase applies the model’s learned patterns to new data, enabling reliable predictions even when the label is not provided.
Summary
Machine learning involves three key steps:- Training: Learning patterns from historical data by mapping input features to labels.
- Algorithm Processing: Generalizing these relationships into a function or formula.
- Inferencing: Applying the trained model to predict outcomes on new data.