Prerequisites
- An AWS account with permissions to create Lambda functions
- Basic knowledge of Python
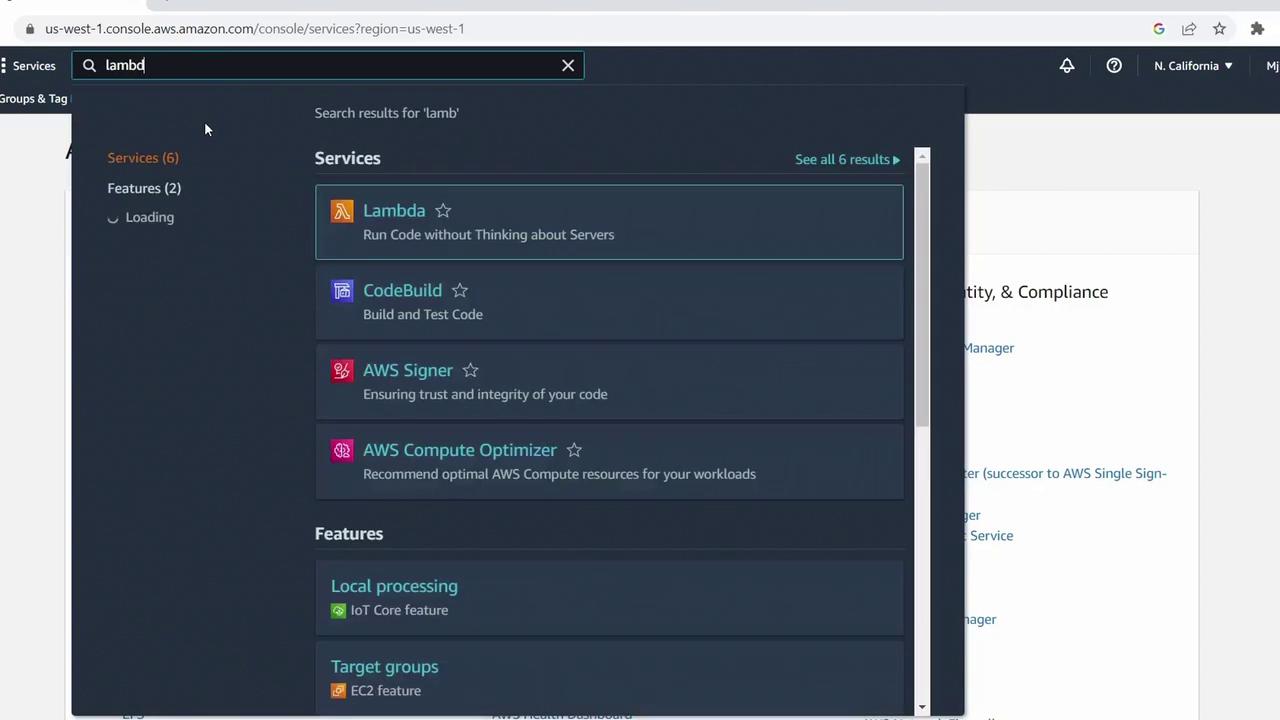
1. Navigate to the AWS Lambda Console
- Sign in to the AWS Management Console.
- In the search bar, type Lambda and select AWS Lambda.
2. Create a New Function
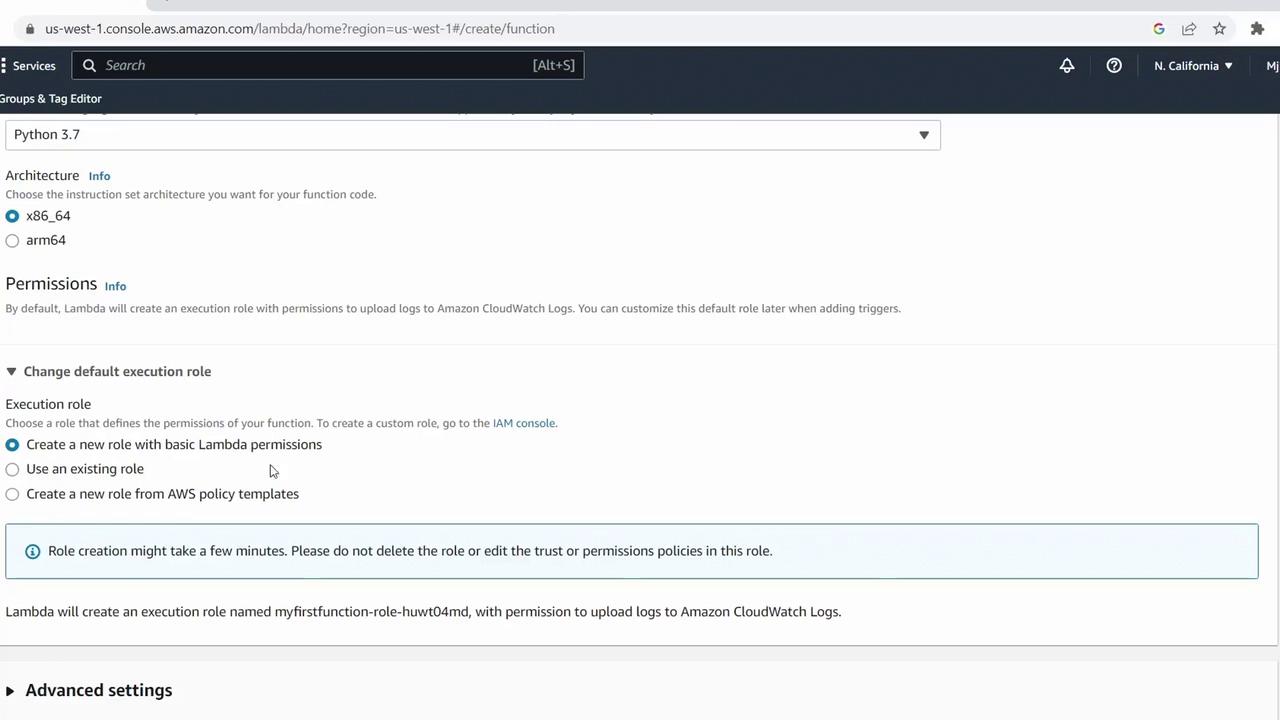
- Click Create function.
- Select Author from scratch.
- Enter a name, e.g.,
MyFirstFunction. - Choose Python 3.7 for the runtime.
- Under Permissions, leave the default to let AWS create a new IAM role with basic Lambda permissions.
- Click Create function.
3. Add and Deploy Your Code
Scroll to the Code source section, remove the default boilerplate, and paste the following handler:The function returns a simple string based on the
name parameter. You can expand this logic to handle more complex business rules.4. Test Your Lambda Function
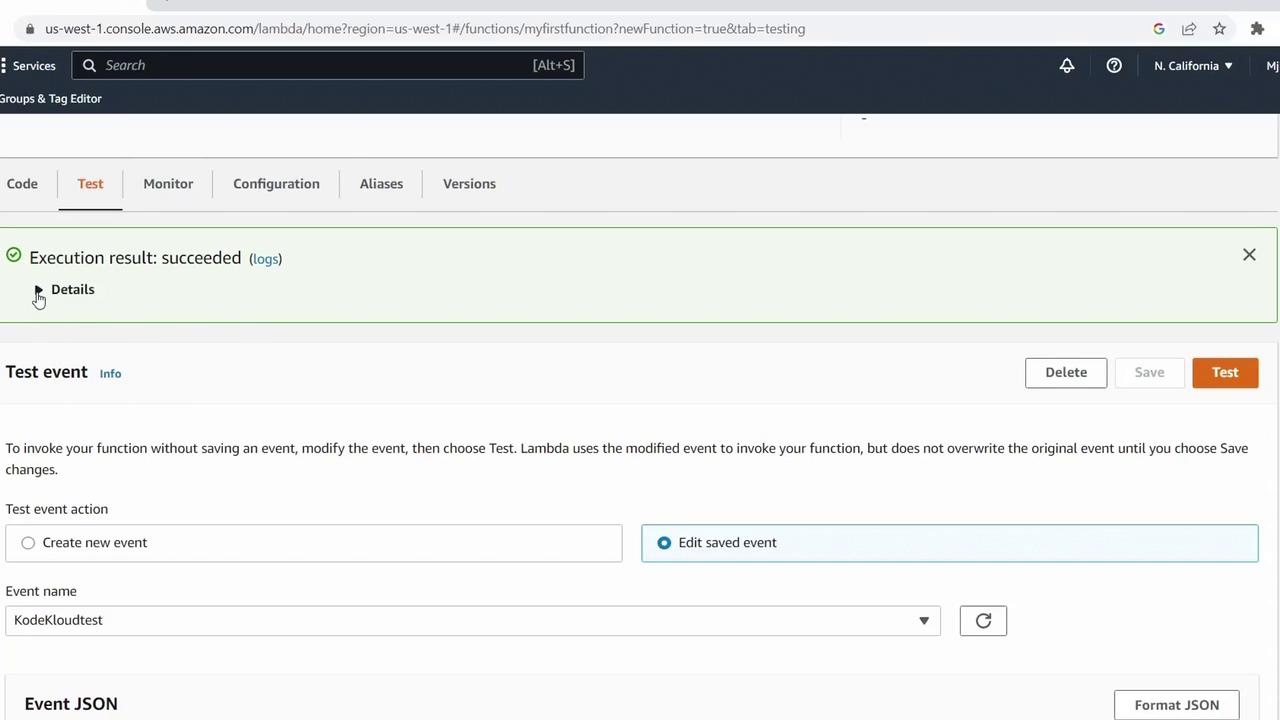
- Switch to the Test tab.
- Click Create new test event.
- Configure the event:
- Event name:
ColdStartTest - Template: Hello World
- Event JSON:
- Event name:
- Click Create and then Test.
"Success" and execution details:
Review CloudWatch Logs
Under Monitor, click View logs in CloudWatch to inspect log entries similar to:5. Test the Else Branch
Create a second test event:- Event name:
OtherTest
"No".
6. Summary of Test Events
| Event Name | Input JSON | Expected Output |
|---|---|---|
| ColdStartTest | {"name": "KodeKloud"} | ”Success” |
| OtherTest | {"name": "Other"} | ”No” |
Next Steps
You’ve successfully created, configured, and tested a Python-based AWS Lambda function. In upcoming lessons, we’ll explore:- Advanced Lambda configurations
- Integrating event source triggers (S3, SNS, API Gateway)
- Environment variables and layers