| Permission Type | Event Source | Managed By | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invocation Permission | Push (e.g., SNS) | IAM Resource Policy | Allow an external service or account to invoke your function |
| Execution Role | Pull or AWS actions | IAM Role (AssumeRole) | Grant your function permissions to use other AWS services |
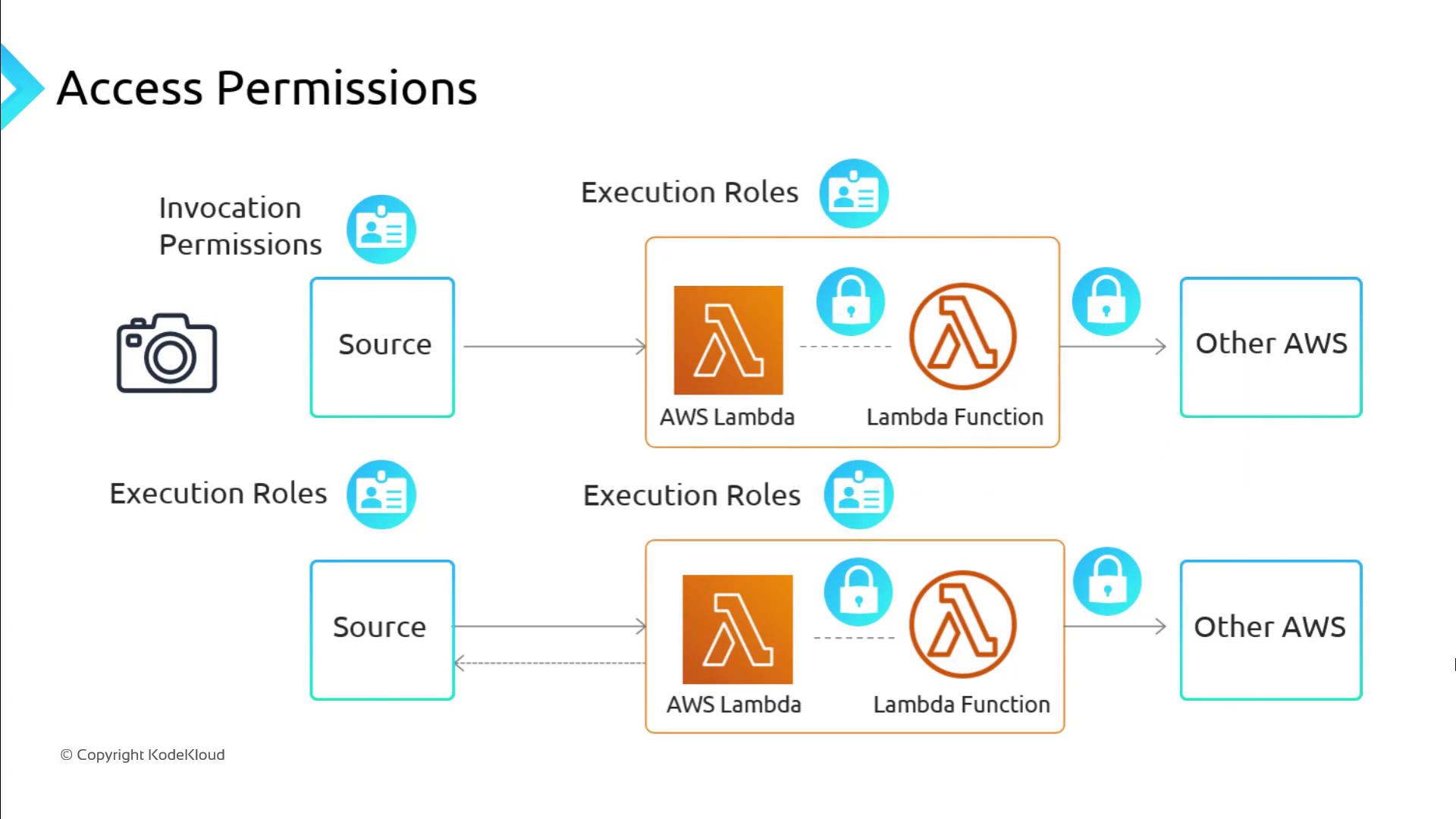
Invocation Permissions
Invocation permissions are required only when a push event source directly triggers your Lambda function (for example, Amazon SNS, Amazon API Gateway, or CloudWatch Events). You grant these permissions by attaching an IAM resource policy to your function.When you configure a push-based event source in the AWS Management Console, AWS Lambda automatically creates the necessary invocation policy.
Execution Role
The execution role is an IAM role that your Lambda function assumes when it runs. It must include:- Permissions policy: Defines the AWS service actions your function can perform.
- Trust policy: Specifies that the Lambda service (
lambda.amazonaws.com) is allowed to assume the role.
Avoid overly broad permissions (e.g.,
Action": "*") in your execution role. Grant only the minimum privileges your function requires.Example Permissions Policy
- Action:
s3:PutObjectgrants write access to the specified S3 bucket. - Condition: Restricts this permission to invocations originating from a particular Lambda function.
Example Trust Policy
- Principal: Specifies
lambda.amazonaws.comas the trusted entity. - Action:
sts:AssumeRoleallows Lambda to assume this role at runtime.