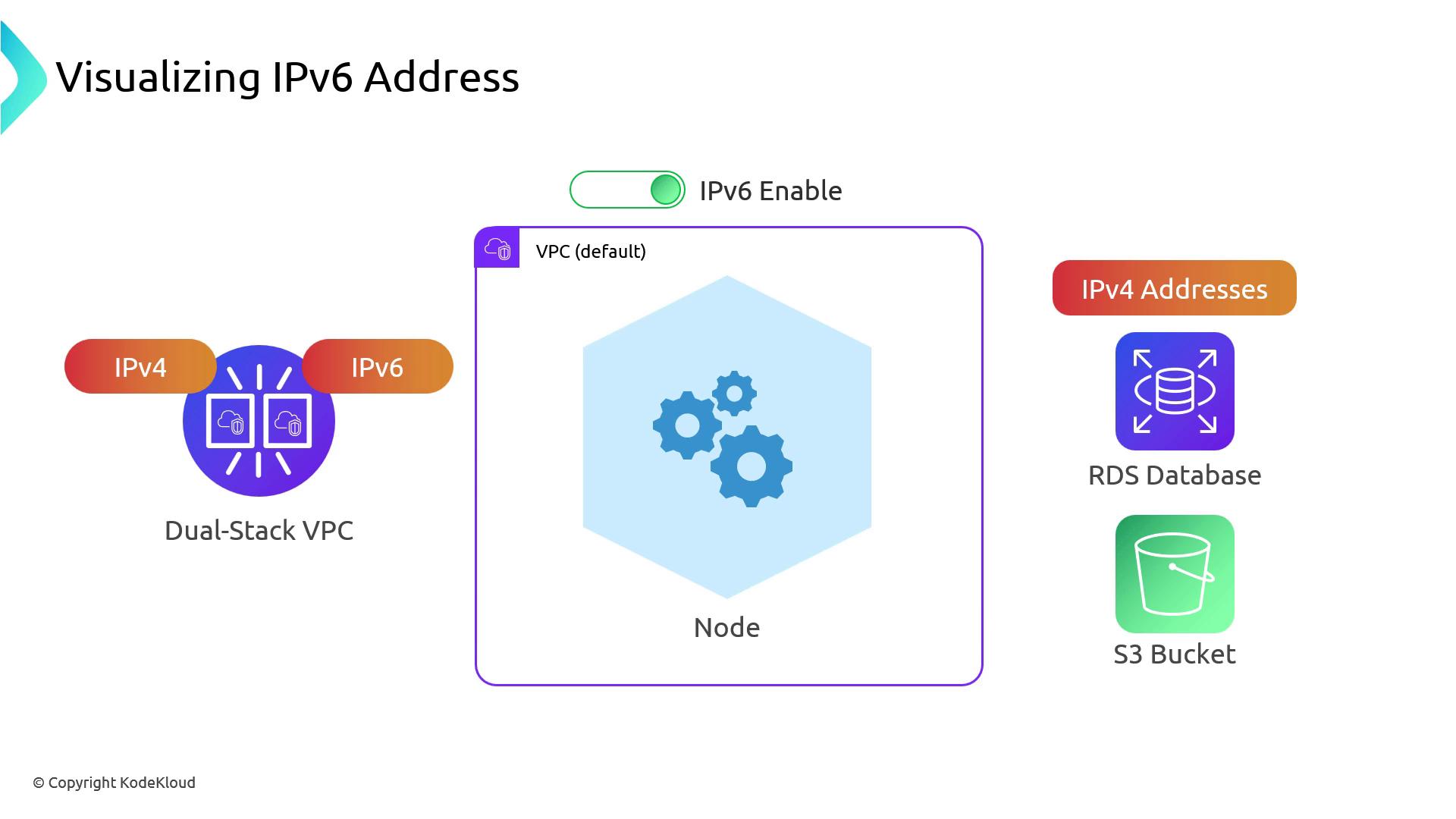
Dual-Stack VPC and Prefix Delegation
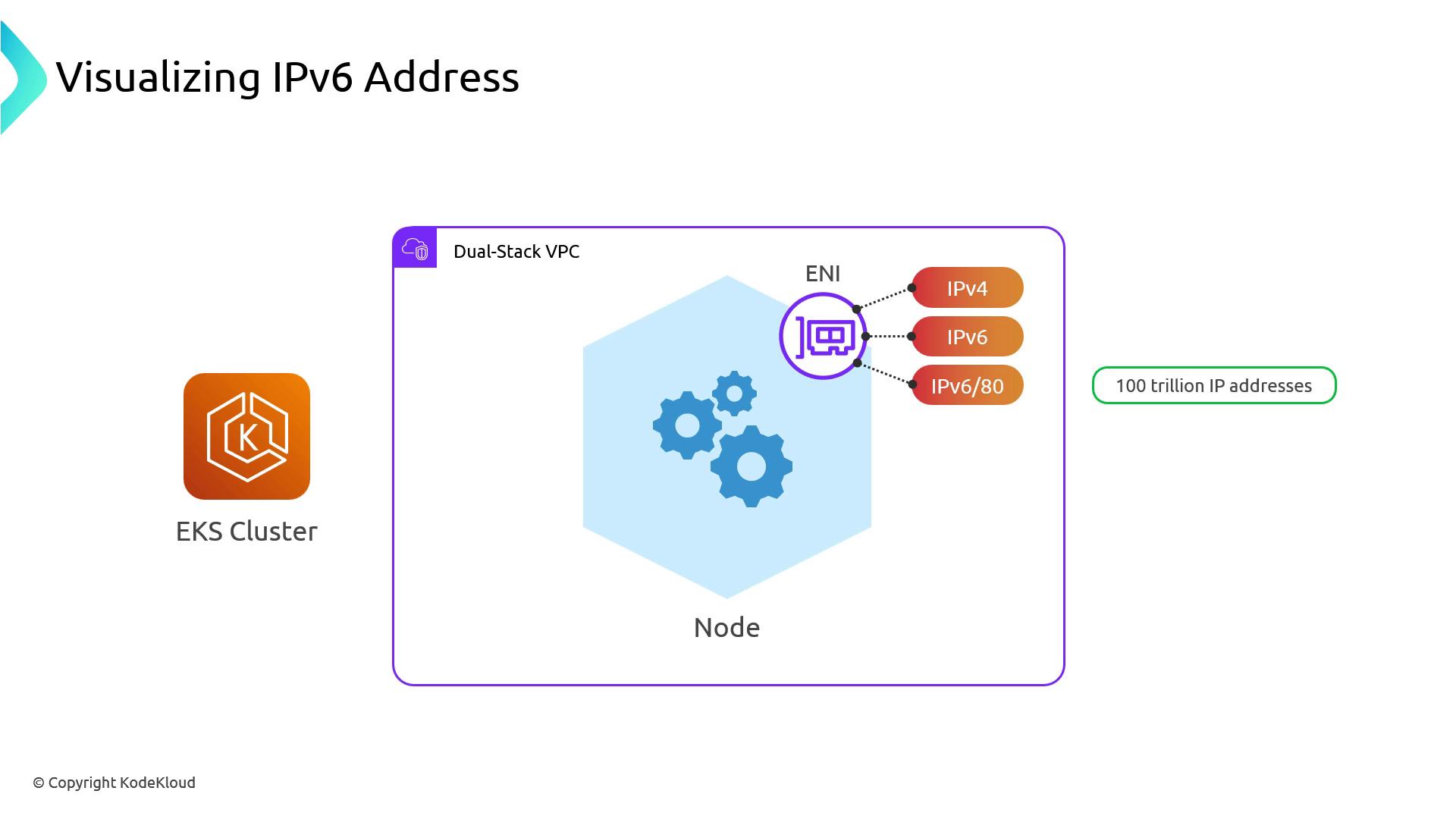
When IPv6 is enabled on your VPC (and on your EKS cluster):- Each worker node’s primary ENI gets one IPv4 and one IPv6 address.
- Kubernetes uses Prefix Delegation to hand out a
/80IPv6 block to each node.
That/80block contains ~2.8 × 10^14 addresses—orders of magnitude more than all IPv4 addresses on the Internet.
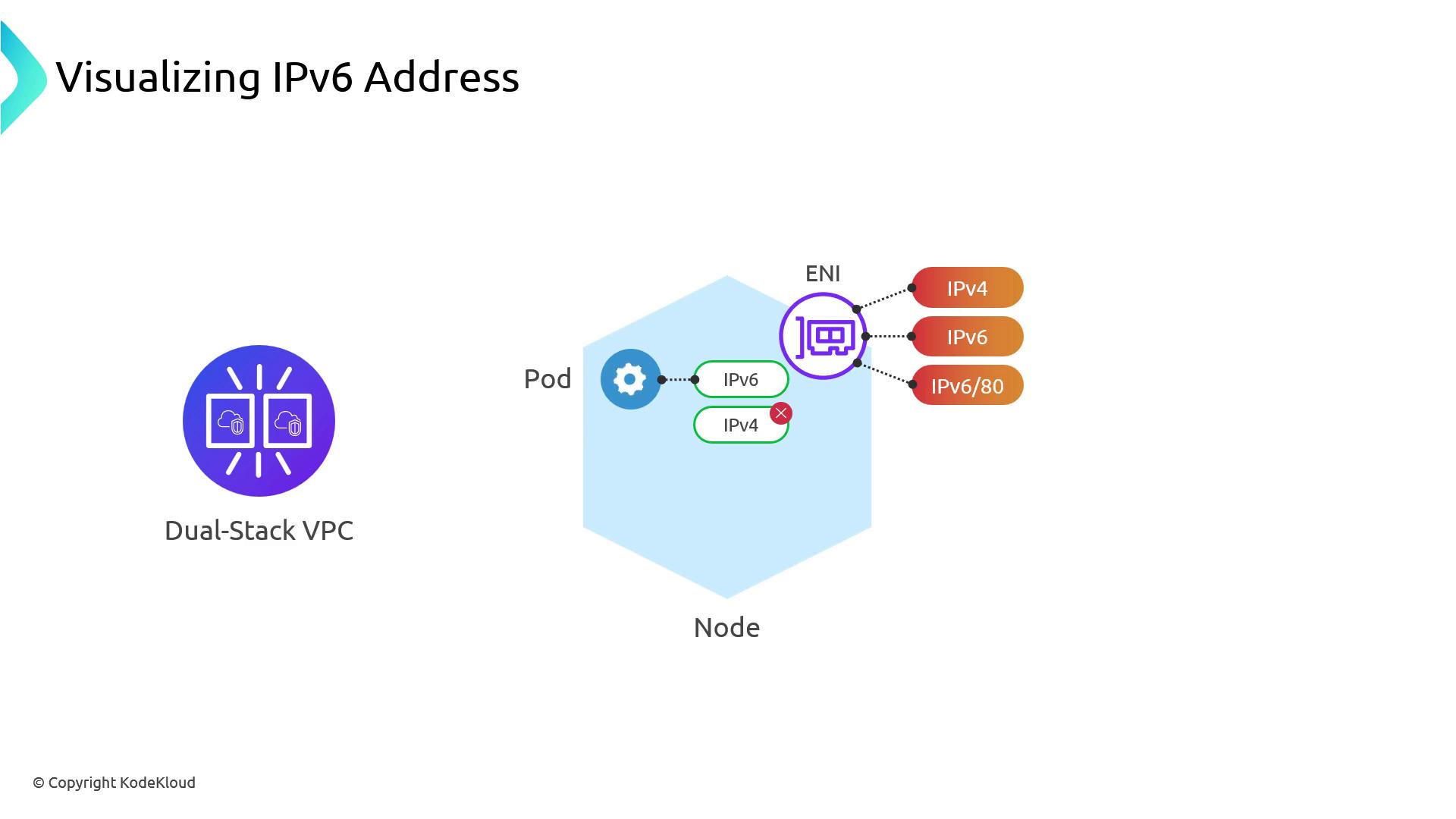
Pod Networking and NAT64 Translation
By design, EKS Pods are single-stack IPv6: they only receive an IPv6 address. To reach IPv4-only endpoints:- Pod sends an IPv6 request.
- Node DNS resolves the target to an IPv4 address.
- The node SNATs the traffic using its IPv4 ENI.
- Responses come back over IPv4 and are mapped to the Pod’s IPv6.
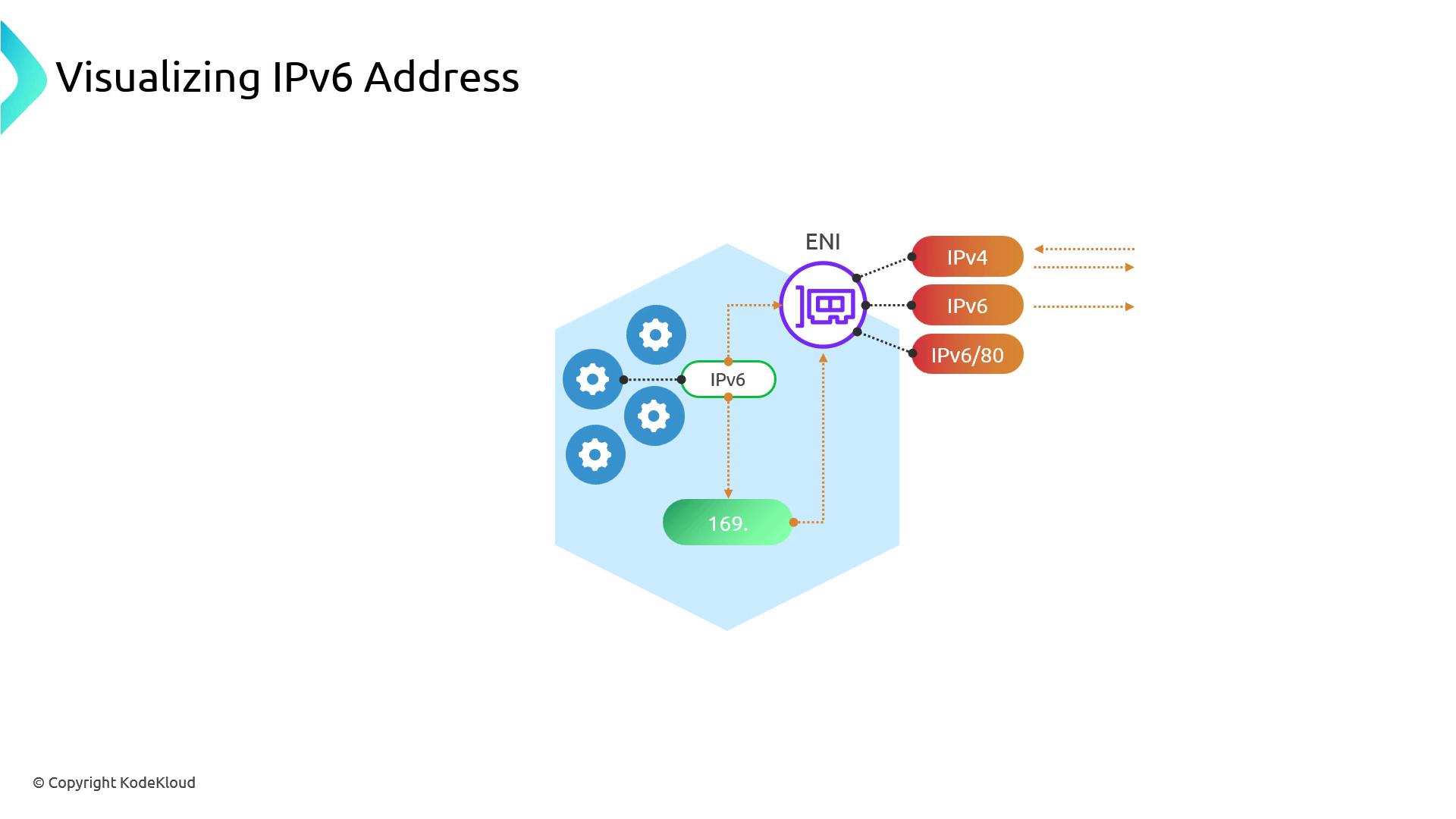
169.254.0.0/16 via veth*). If the destination has native IPv6, traffic flows directly over the IPv6 ENI.
Pods accessing IPv4 services share the same node-level IPv4 address and NAT connections. This can become a throughput bottleneck at scale—plan accordingly.
Egress-Only IPv6 Traffic
Since IPv6 addresses are globally unique, you generally don’t need SNAT or NAT Gateways for Pod-to-Pod or outbound traffic. To control outbound IPv6:| Gateway Type | Direction |
|---|---|
| Egress-only Internet Gateway | IPv6 outbound only |
AWS does not offer an ingress-only IPv6 gateway. Control incoming IPv6 traffic with Security Groups or Network ACLs.
1. Creating a Dual-Stack EKS Cluster
Useeksdemo, eksctl, or the AWS CLI to spin up a dual-stack EKS cluster:
INTERNAL-IP.
Deploy a test Pod and inspect its IP:
IP will be in IPv6 format.
2. Examining Node Interfaces
SSH into a node and list its interfaces:eth0 output:
veth*) will show both 169.254.x.x/32 and fe80::/64.
IPv4 Routes
IPv6 Routes
3. Inspecting IPv6 Prefix Delegation
To view the/80 prefixes assigned to each node, run:
/80 (~280 trillion addresses) for Pod allocation—IP exhaustion is no longer a concern.