- Value: Which results matter most?
- Effort / Time: How long will it take?
- Urgency: Are deadlines looming?
1. Weighted Shortest Job First (WSJF)
WSJF calculates a priority score by dividing the sum of business value and time criticality by job size (effort). A higher score signals a higher priority.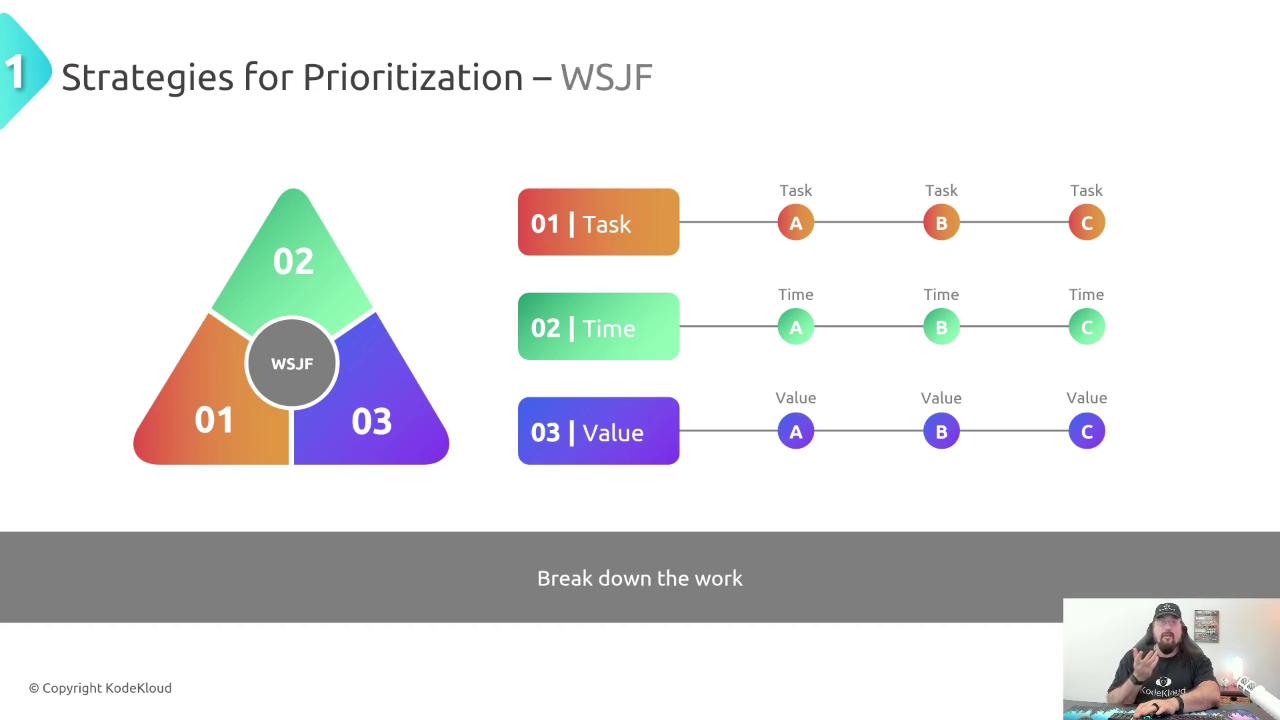
WSJF Prioritization Matrix
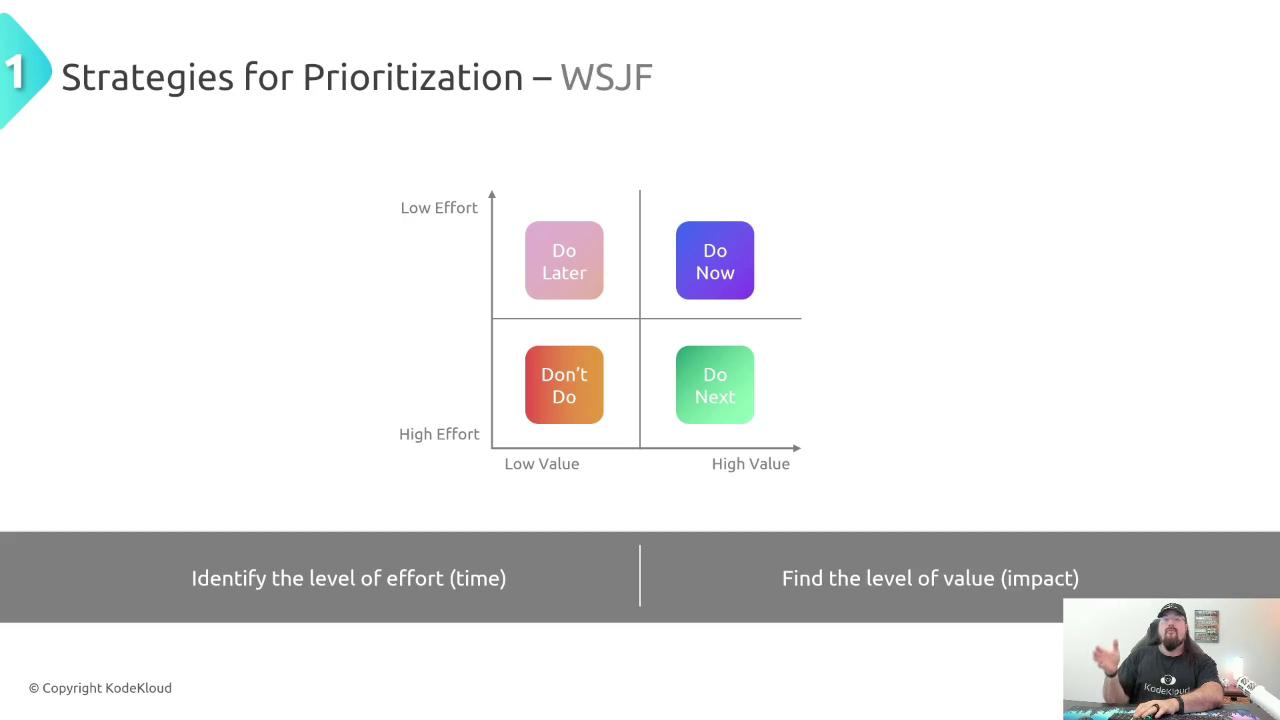
Map tasks into four quadrants based on value versus effort:| Quadrant | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Do Now | High value, low effort | Tackle immediately for maximum ROI. |
| Do Next | High value, high effort | Schedule soon but allocate proper resources. |
| Do Later | Low value, low effort | Slot into backlog; may revisit. |
| Don’t Do | Low value, high effort | De-prioritize or drop entirely. |
Compute each task’s WSJF score:
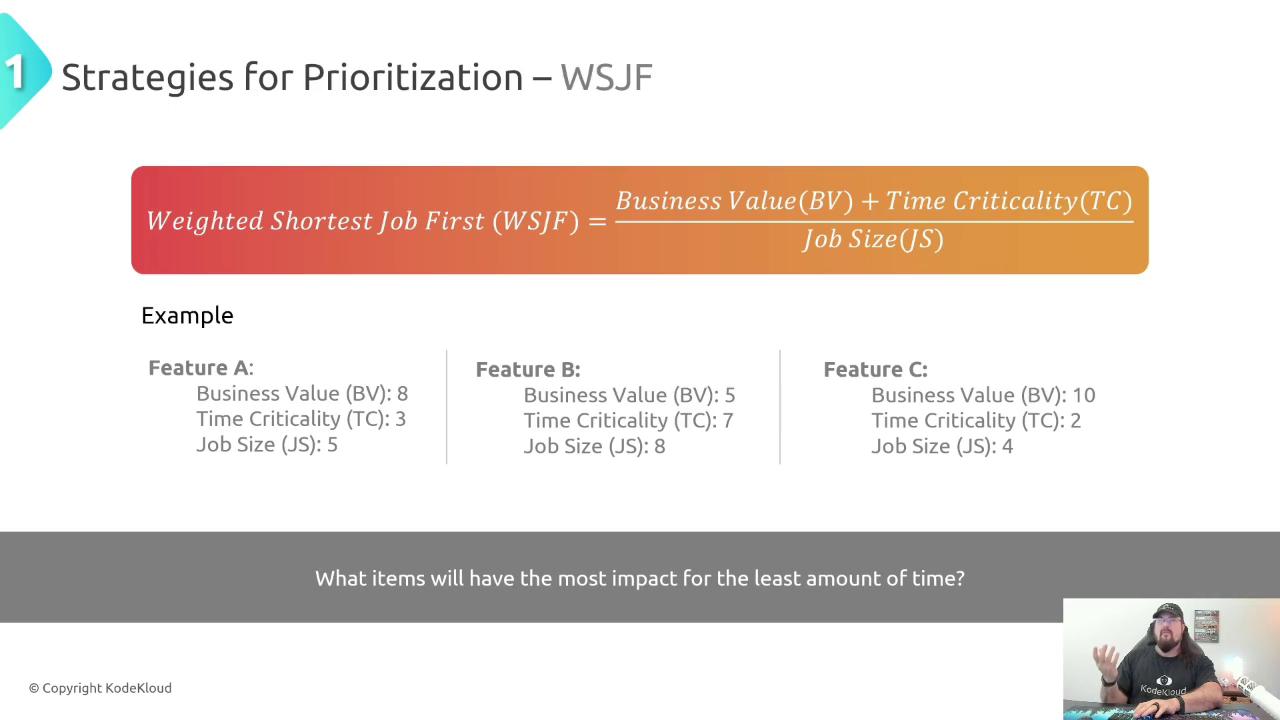
Example Comparison
Feature C (highest value, low effort) outranks A and B. Always recalculate if value or deadlines change.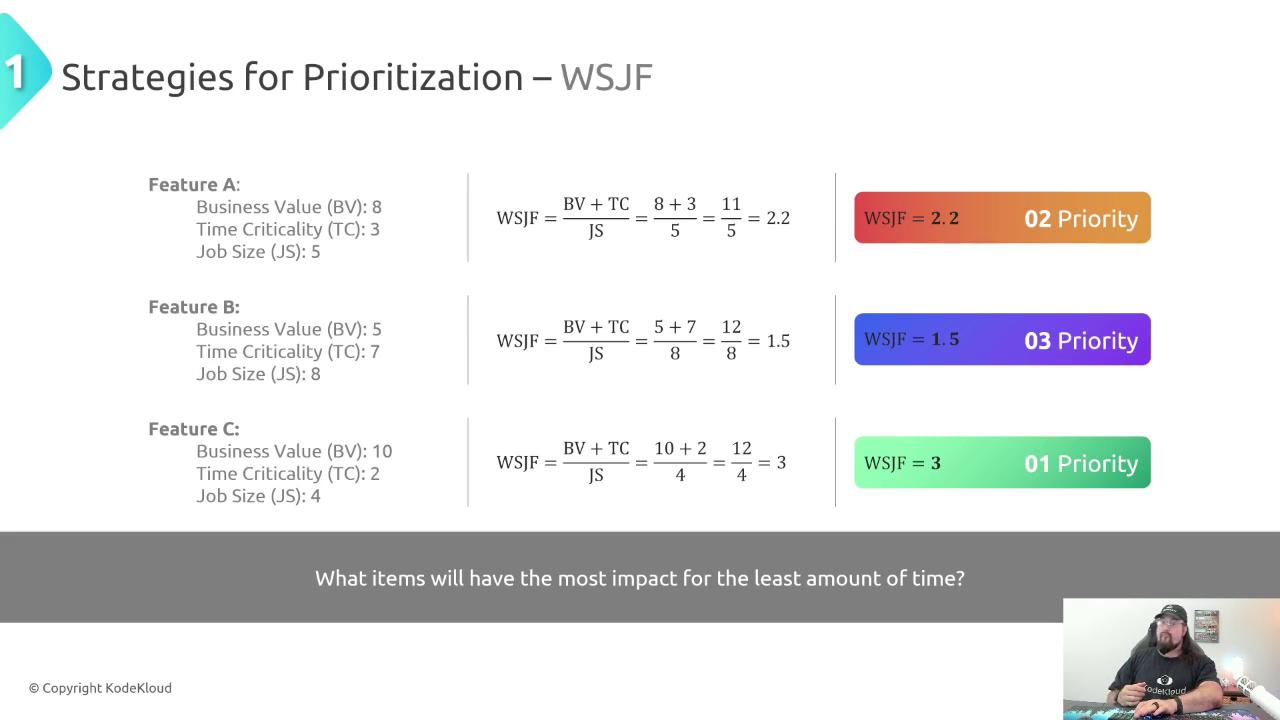
2. Pareto Principle (80/20 Rule)
Often, 20% of tasks yield 80% of your results. Identify that critical 20%—whether it’s revenue-driving features, customer-impacting fixes, or reputation boosters—and focus on them first.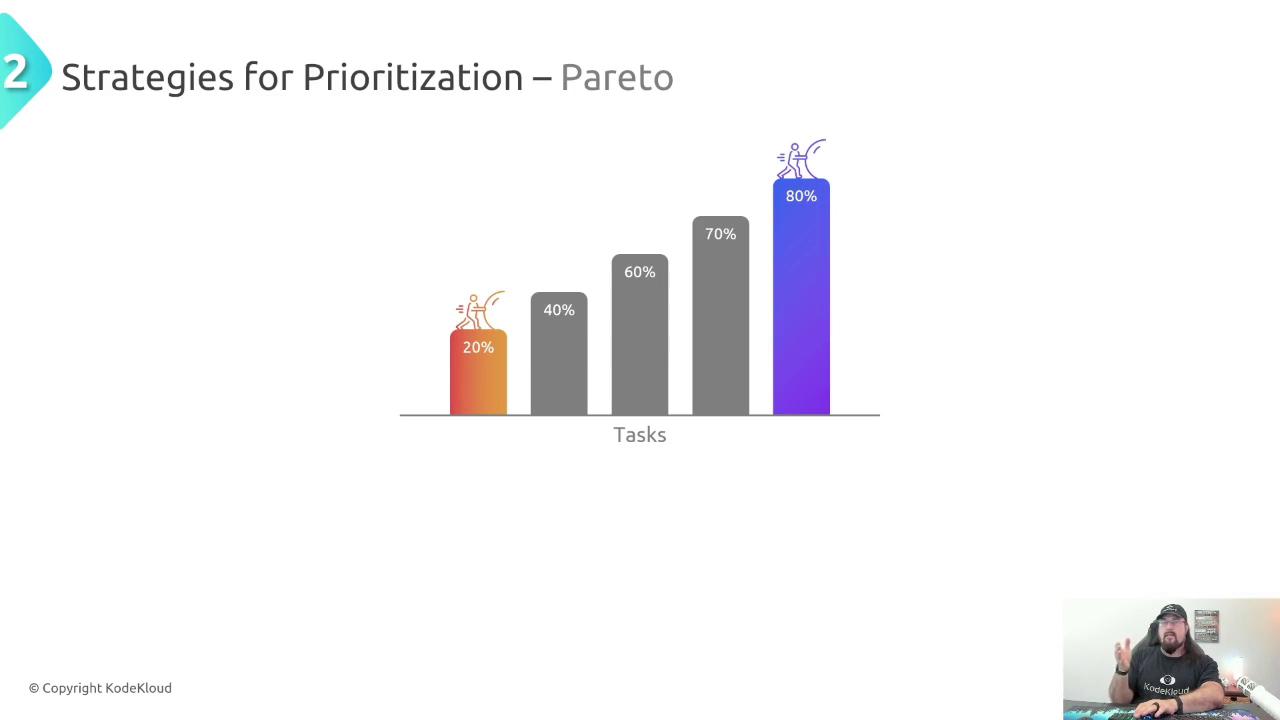
Adapting to Rapidly Changing Inputs
Even the best-laid plans must flex when emergencies occur. Keep your priorities visible, but stay ready to re-evaluate based on new stakeholder requests or shifting deadlines.
Communicate Priority Changes
Whenever you bump or reorder tasks, inform everyone affected—team members and stakeholders alike. Transparency prevents confusion and broken agreements.
Project Work vs Interrupt-Driven Work
Context switches erode focus. If you juggle support tickets and project tasks, timebox each segment—for example, 90 minutes on firefighting and 90 minutes on project deliverables.
Visualize Your Workflow
A Kanban-style board (To Do → Doing → Done) makes priorities crystal clear. Pull one task at a time, finish it, then move on.
Integrating Prioritization, Time Management & Capacity Planning
These three disciplines overlap and reinforce each other:- Prioritization: Which tasks come first?
- Time Management: When will you work on them?
- Capacity Planning: Who will do the work?
Summary
- Break large tasks into day-sized chunks.
- Use WSJF or the Pareto Principle (80/20) to rank work.
- Communicate any shifts in priority immediately.
- Timebox interruptions vs. project work.
- Visualize progress with a Kanban board.
- Align tasks with team capacity and deadlines.
