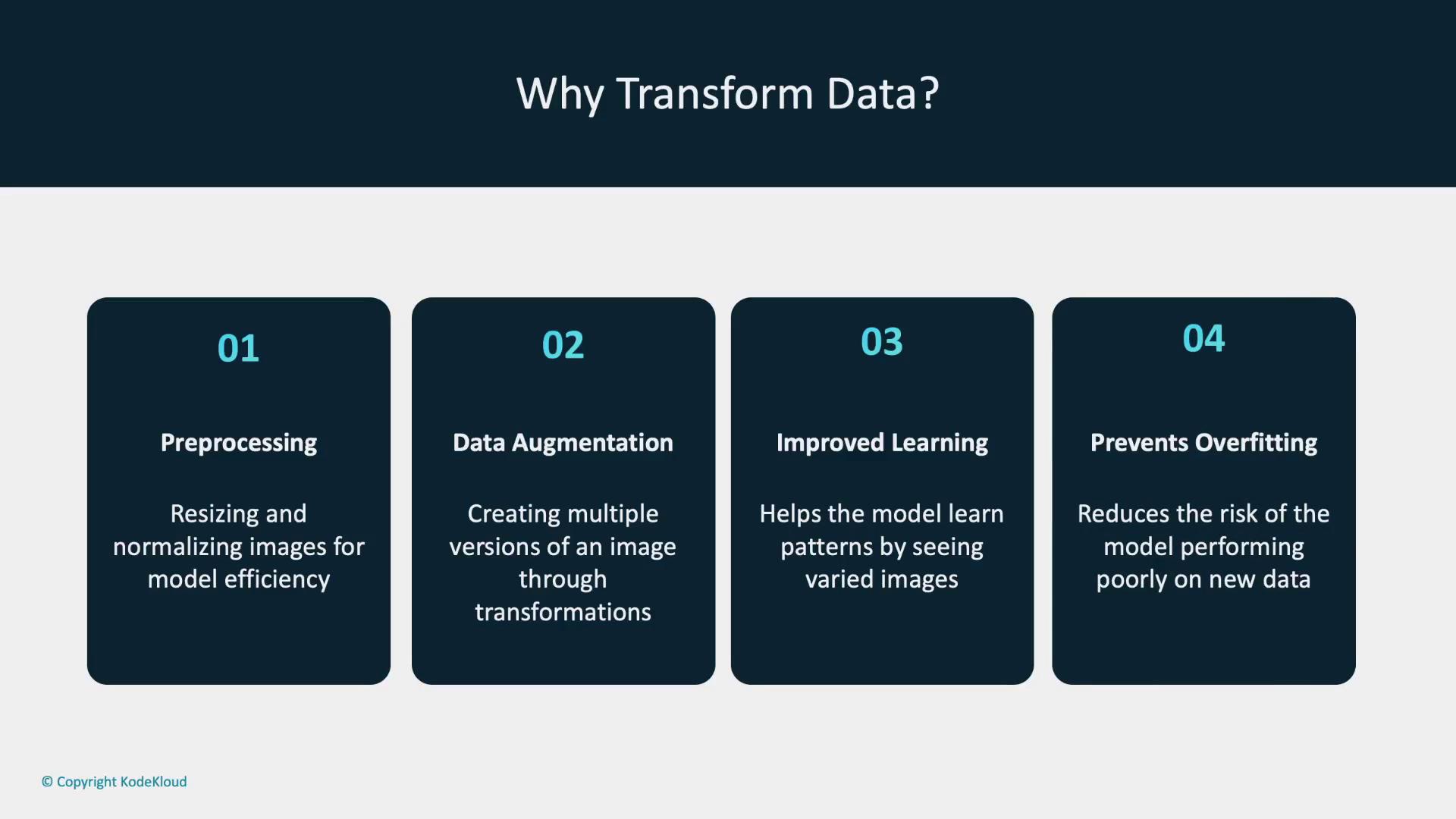
- Preprocessing: Resize images to a uniform dimension and normalize pixel values to ensure consistency across the dataset.
- Data Augmentation: Apply operations such as rotating, flipping, and cropping to generate multiple modified versions of each image. This variation helps the model perform well on unseen data by reducing the risk of overfitting.
Benefits of data transformations include improved preprocessing, effective data augmentation, and enhanced generalization, which collectively reduce overfitting.
- Resize: Adjust the dimensions of an image to a specific size.
- Normalize: Convert pixel intensity values to a standard scale that aids model training.
- ToTensor: Change images into tensors, the primary data structures used in PyTorch for numerical computations.
- RandomHorizontalFlip: Horizontally flip the image with a given probability to simulate different viewing angles.
The diagram below summarizes these common image transformations. The details provided above are typically sufficient for implementation.

Resizing Images
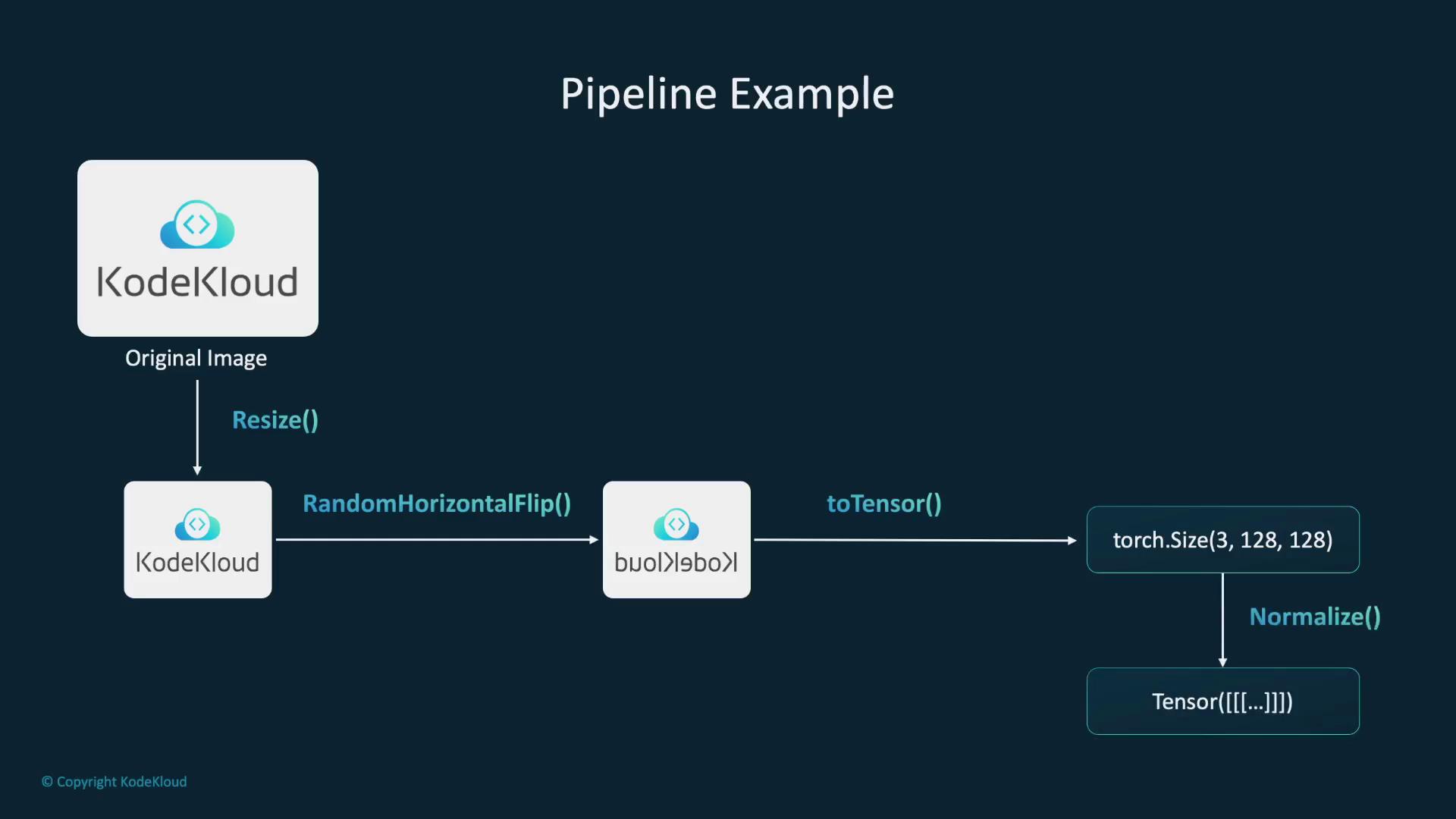
The code below demonstrates how to use the Python Pillow library to load an image and then apply the PyTorch resize transformation to change its dimensions to 128x128 pixels:Normalization and Random Horizontal Flip
Normalization adjusts pixel values, positioning them on a consistent scale, which in turn helps optimize model training. The following example normalizes an image tensor to a mean and standard deviation of 0.5. In addition, applying a random horizontal flip with a 50% probability introduces variation in image perspectives:Creating a Transformation Pipeline
PyTorch allows you to combine multiple transformations into a single pipeline using thetransforms.Compose class. This approach streamlines preprocessing by chaining operations such as resizing, flipping, converting to a tensor, and normalizing pixel values. The diagram below visually outlines this process:
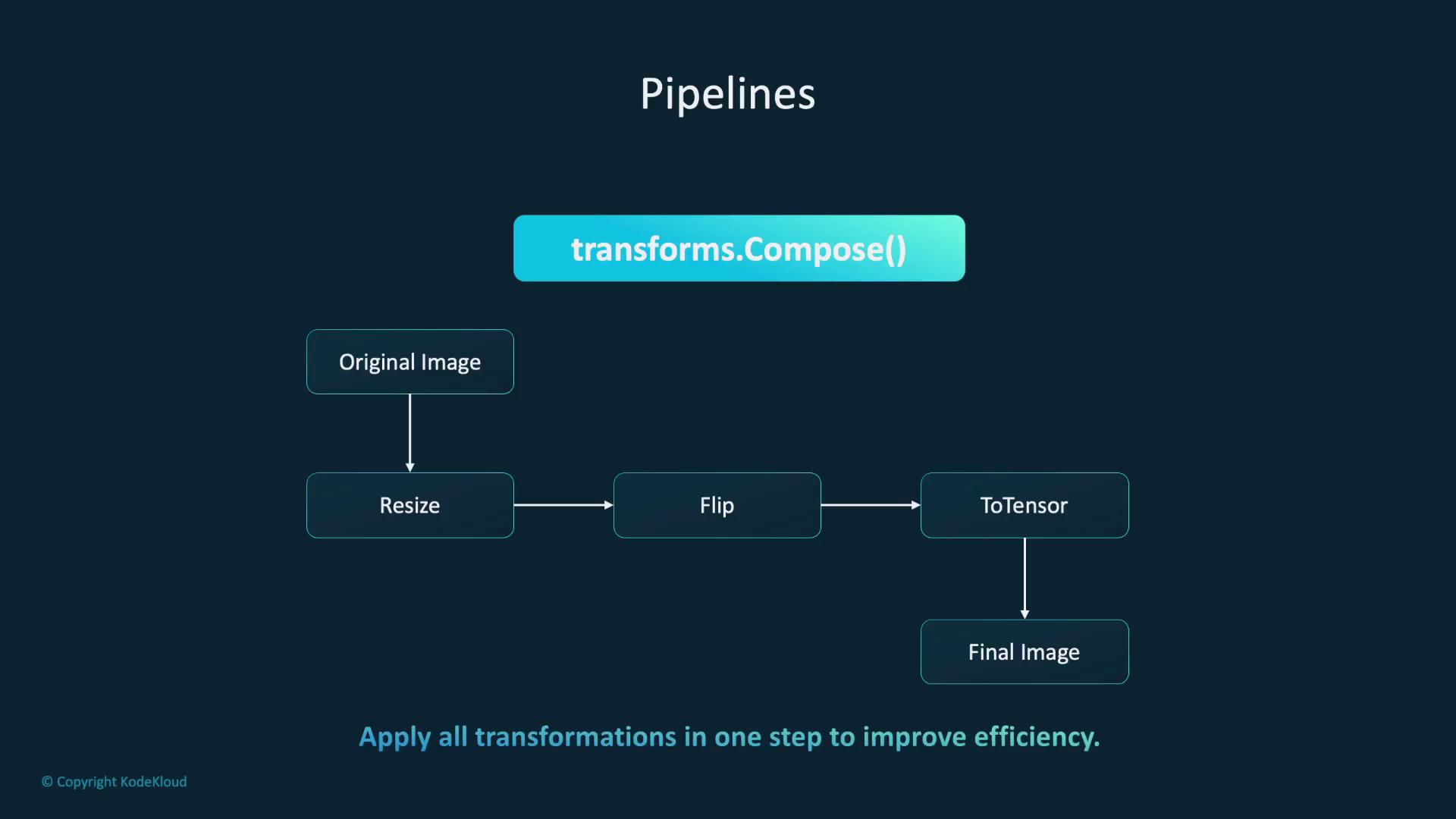
An additional diagram (if available) further clarifies the sequential data processing within this pipeline. The code and explanation above provide a comprehensive overview.
Integrating Transformations with Datasets
Transformations can be directly integrated into dataset objects. For example, when using the preloaded MNIST dataset, you can integrate a transformation pipeline so that each image is preprocessed automatically during data loading:Transitioning to the V2 API
Everything discussed so far is based on version 1 of the transformations API. PyTorch now recommends using the V2 API due to its enhanced features and improved performance. The V2 API is backward compatible with V1 and offers additional functionality and efficiency. Although a diagram may compare the two versions visually, the key takeaway is that V2 provides faster performance and more features while maintaining compatibility.
Summary
Transformations are essential for preparing image data and augmenting it to improve model robustness. Techniques such as flipping and rotating images help prevent overfitting by offering diverse perspectives on the input data. Additionally, combining multiple transformations usingtransforms.Compose creates an efficient and organized preprocessing pipeline.
While a summary diagram could provide a visual recap, the detailed discussion above comprehensively covers the importance and application of data transformations in deep learning workflows.
