Understanding Data Privacy
Data privacy is all about protecting individuals’ rights to control their personal information. This involves how data is collected, used, and shared, ensuring that organizations handle personal details ethically and legally.Data Collection
Organizations collect personal information from a variety of sources, making it imperative to secure this data right from the start. Preventing misuse at the moment of collection sets the groundwork for sound privacy practices.
Data Usage
When it comes to data usage, the focus is on the responsible processing of collected data. It is vital that data is used strictly in accordance with user consents and agreed terms.Data Sharing
Data sharing refers to the distribution of personal information to external entities. Unauthorized sharing or misuse of this data can lead to serious privacy breaches.Data privacy is governed by regulations and legal frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA. These laws ensure the protection of personal information including names, contact details, and biometric data.
Exploring Data Security
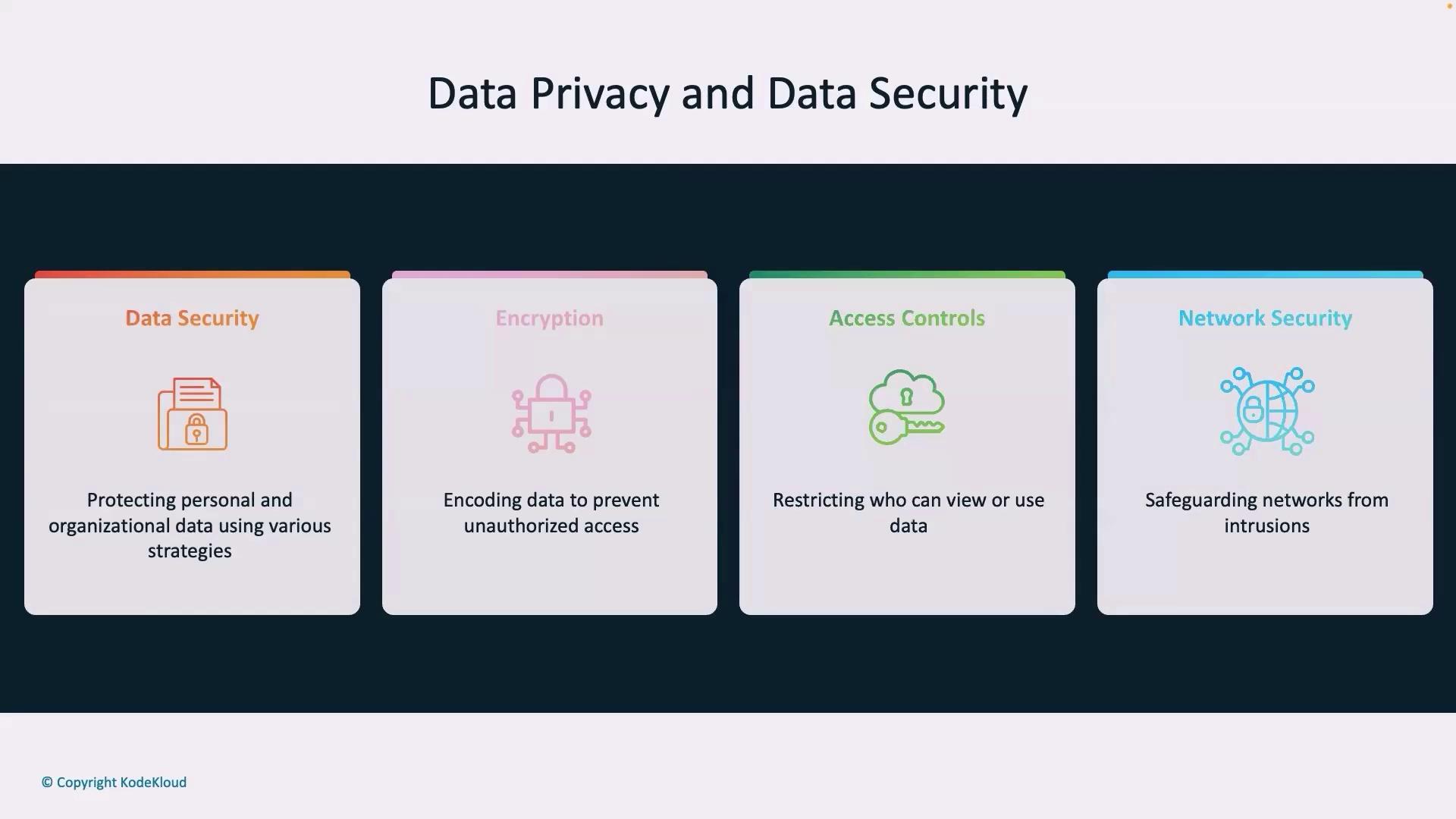
Data security is the shield that protects data from unauthorized access and breaches. It complements data privacy by focusing on the technical aspects required to secure both personal and organizational data.Technical Measures
Data security relies on a variety of technical measures. These include encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, all designed to block unauthorized access and minimize risks of breaches.Protocols
Security protocols define the rules for data storage and transmission. They ensure that organizational data remains under strict control throughout its lifecycle.
Real-World Data Breach Examples
Examining data breaches from prominent cases provides insight into the effectiveness of security measures:Yahoo Data Breach (August 2013)
The Yahoo breach compromised approximately 3 billion accounts. Although no payment data was stolen, personal account details were exposed, emphasizing the importance of proactive data security measures.
Aadhaar Breach (January 2018)
In this incident, the personal identity and biometric data of over 1.1 billion Indian citizens was exposed due to weak API security. This breach underlines the need for robust encryption and strict access control policies.Facebook Data Exposure (April 2019)
A data exposure incident at Facebook affected 533 million users. Publicly accessible phone numbers and account IDs were among the compromised data, emphasizing the necessity of regular security audits.
Compliance, Legal Frameworks, and Best Practices
Adhering to legal frameworks and industry standards is crucial for safeguarding data. Consent is the cornerstone of data privacy, and policies such as GDPR and CCPA help maintain high protection standards.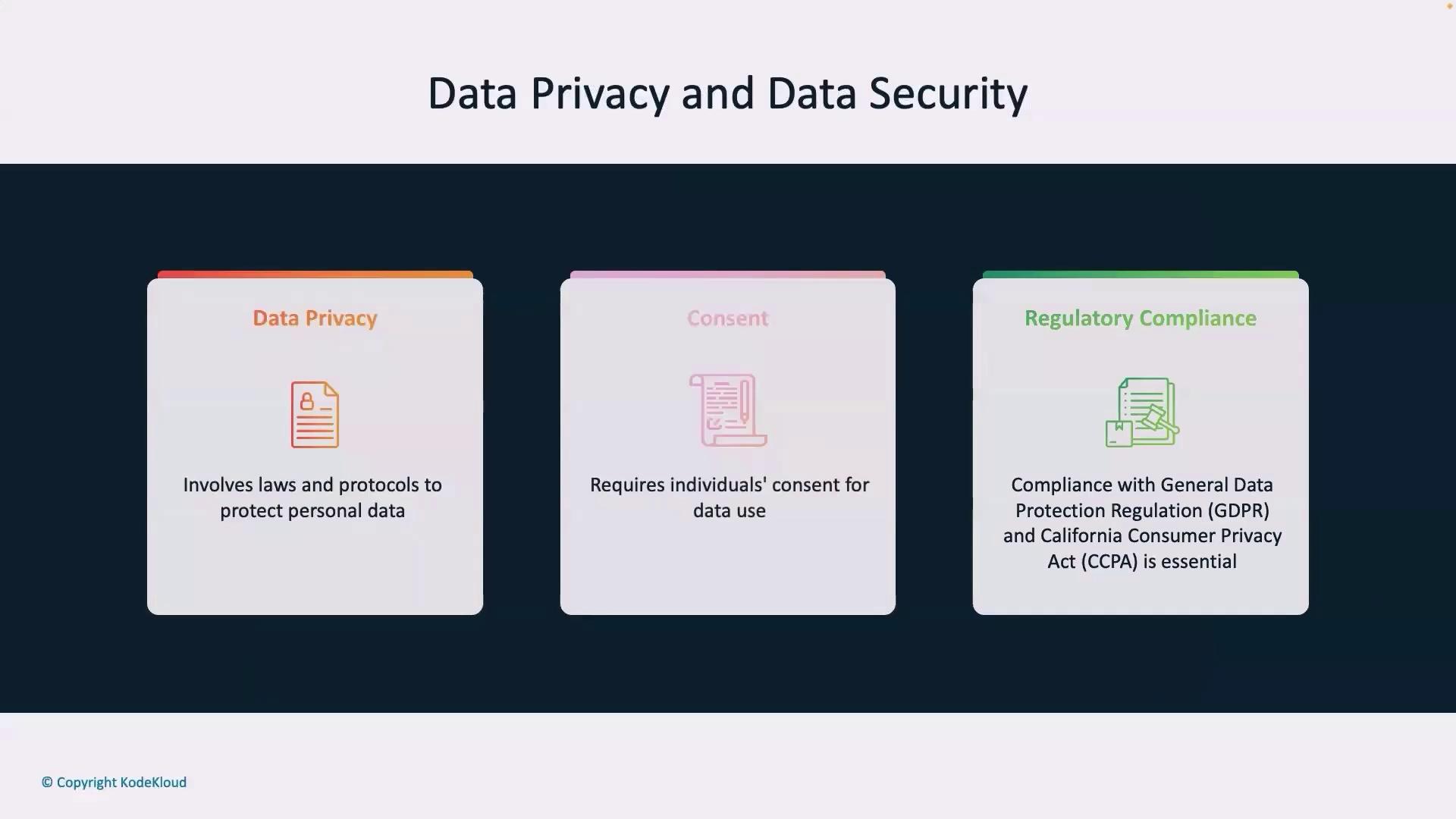
- Encryption: Encodes sensitive data, making it unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
- Access Control: Restricts data manipulation and viewing to authorized personnel.
- Network Security: Protects systems from cyberattacks, ensuring uninterrupted and secure access.
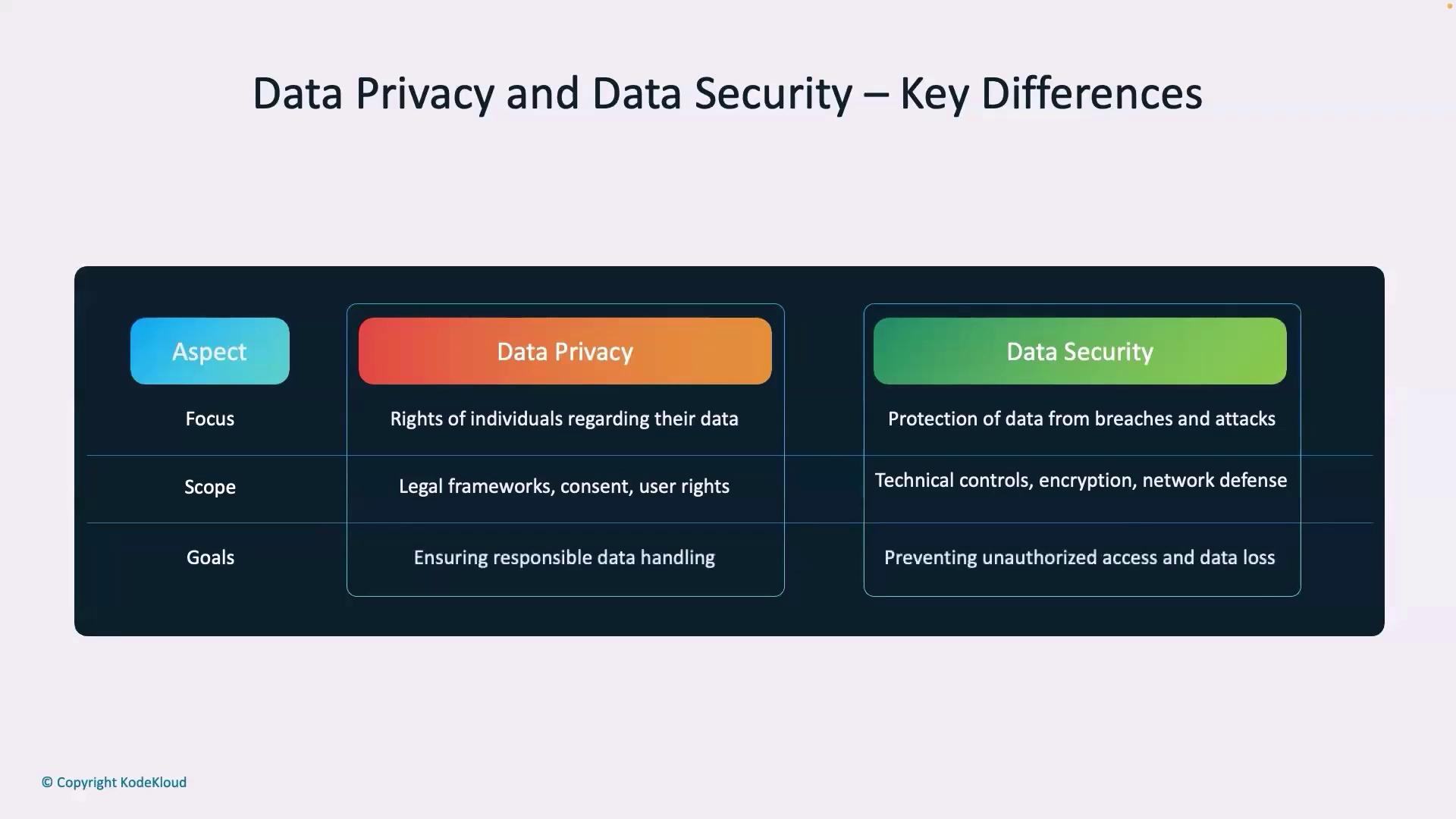
Comparing Data Privacy and Data Security
Understanding the difference between data privacy and data security is essential:- Data Privacy: Focuses on legal rights and ethical handling of personal data, emphasizing collection, sharing, and usage in line with regulations.
- Data Security: Concentrates on safeguarding data through physical and digital protection measures such as firewalls, encryption, and secure protocols.
The Interrelationship Between Data Privacy and Data Security
Data privacy and security are intertwined. Effective data security measures—like regular audits, strong encryption, and controlled access—are necessary to enforce privacy practices. Without these safeguards, efforts to protect personal data can fall short.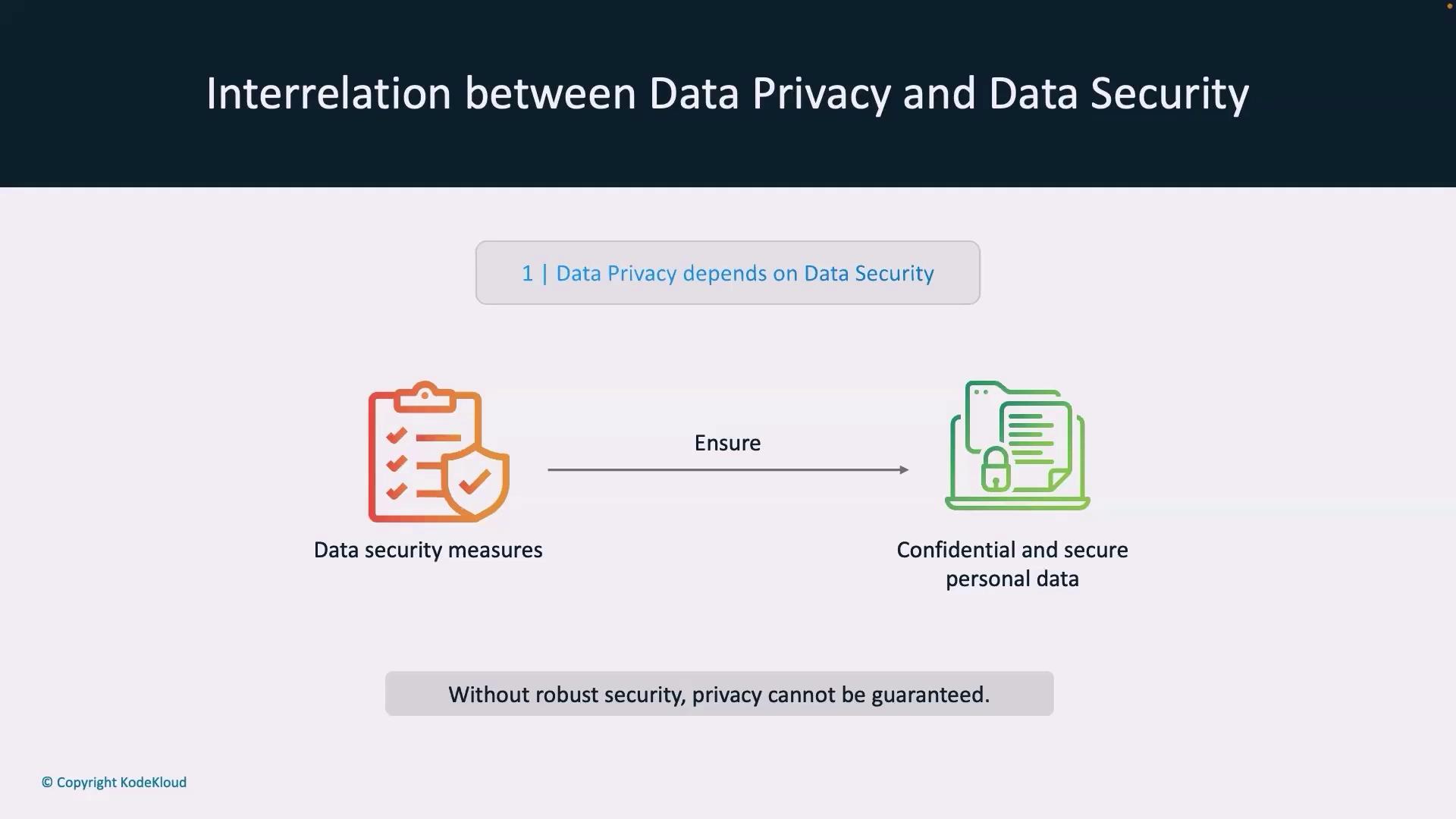
Best Practices to Enhance Data Protection
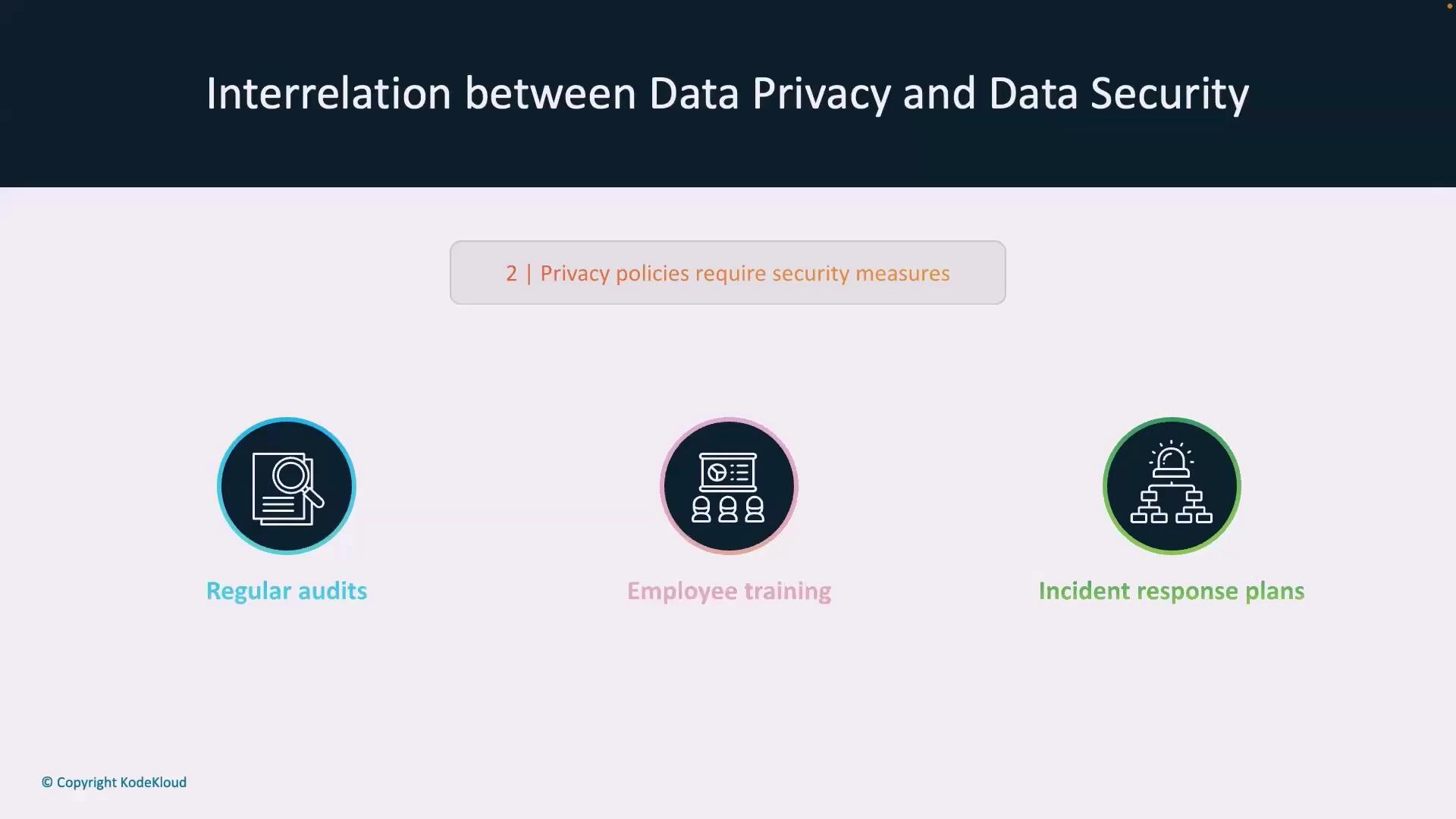
Implementing comprehensive strategies to manage both data privacy and data security is crucial. Here are some best practices:- Regular Audits: Continuously evaluate systems to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Employee Training: Provide training on data handling best practices and the importance of security protocols.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop and update detailed response plans to quickly address any data breaches. Knowing where data is stored, who has access, and having clear logs is essential if a breach occurs.
Ensure your incident response plan is up-to-date and that all staff are familiar with their roles in the event of a data breach.