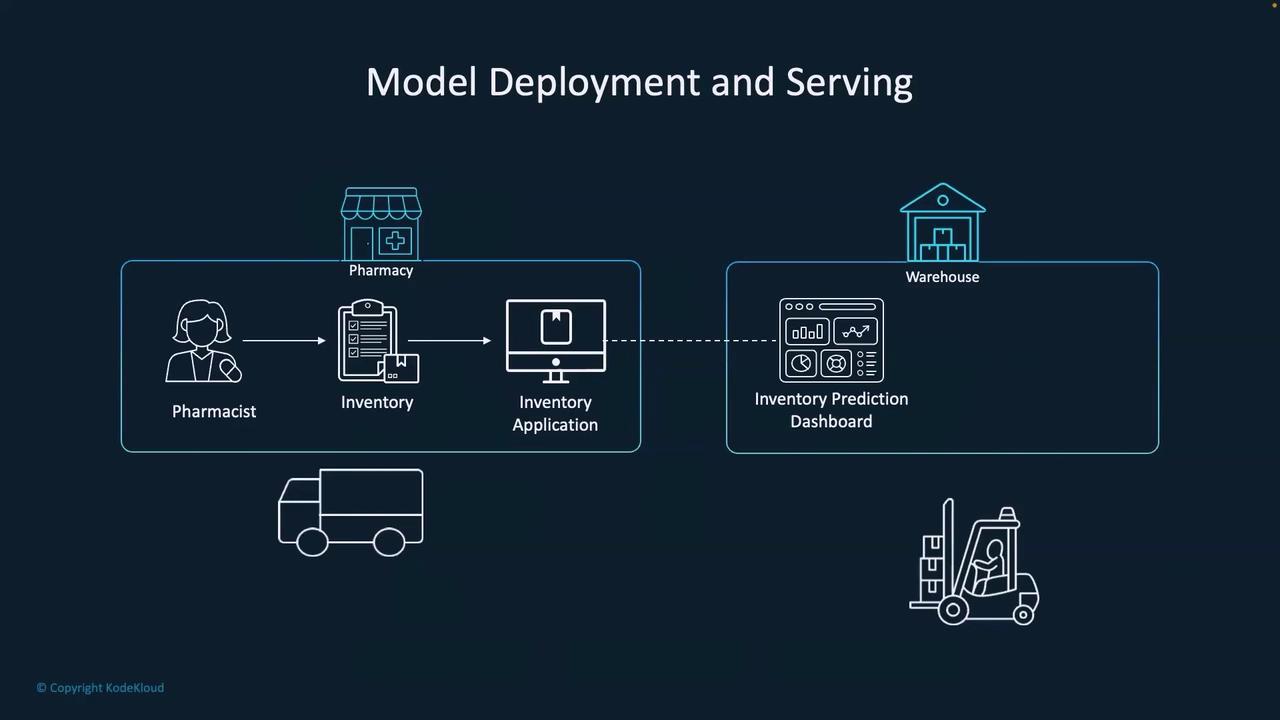
How the Inventory Prediction Dashboard Works
Within our inventory prediction dashboard, users select a branch and a month before clicking the green “Go” button. This action triggers a call from the frontend to a dedicated API endpoint—/predict—which hosts our ML model configured for inventory prediction. For instance, the dashboard might predict that a pharmacy at Dubai Mall in December 2025 will require four units of a specific medicine.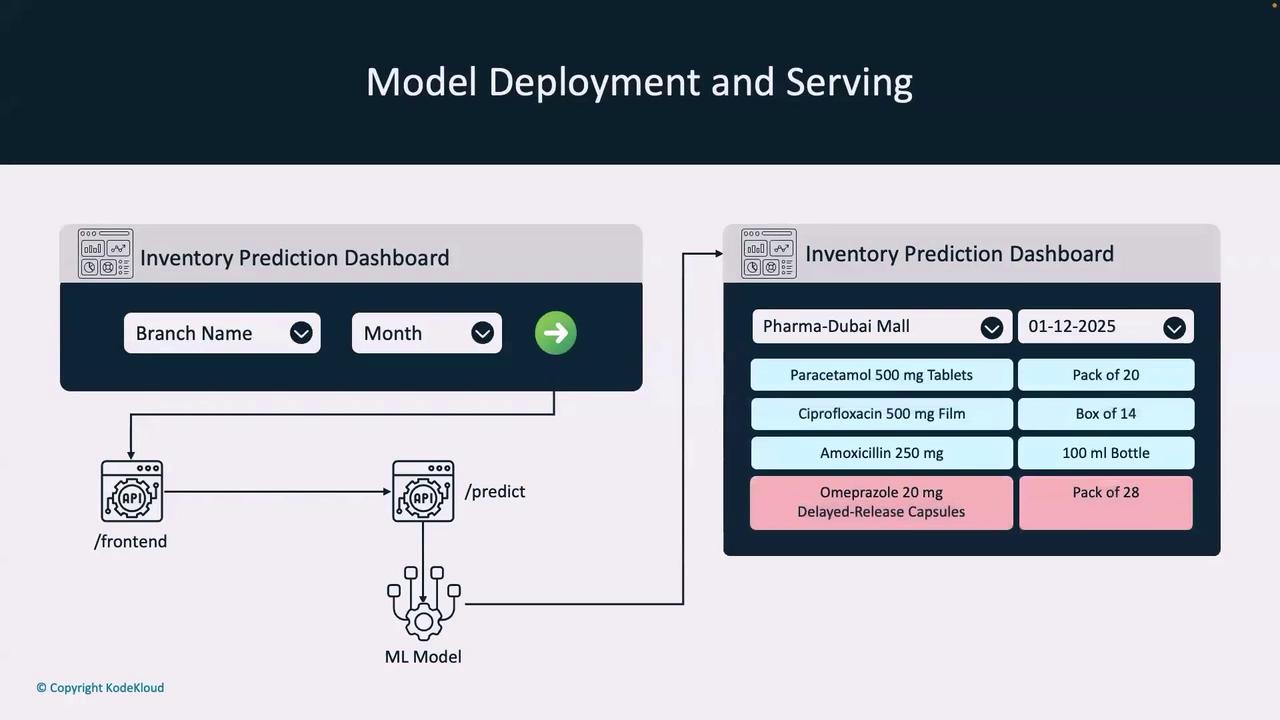
- It supports proactive inventory planning by allowing purchase orders to be placed well in advance.
- It enhances cost efficiency through reliable forecasts, paving the way for better vendor negotiations.
Transitioning to a Microservices Architecture
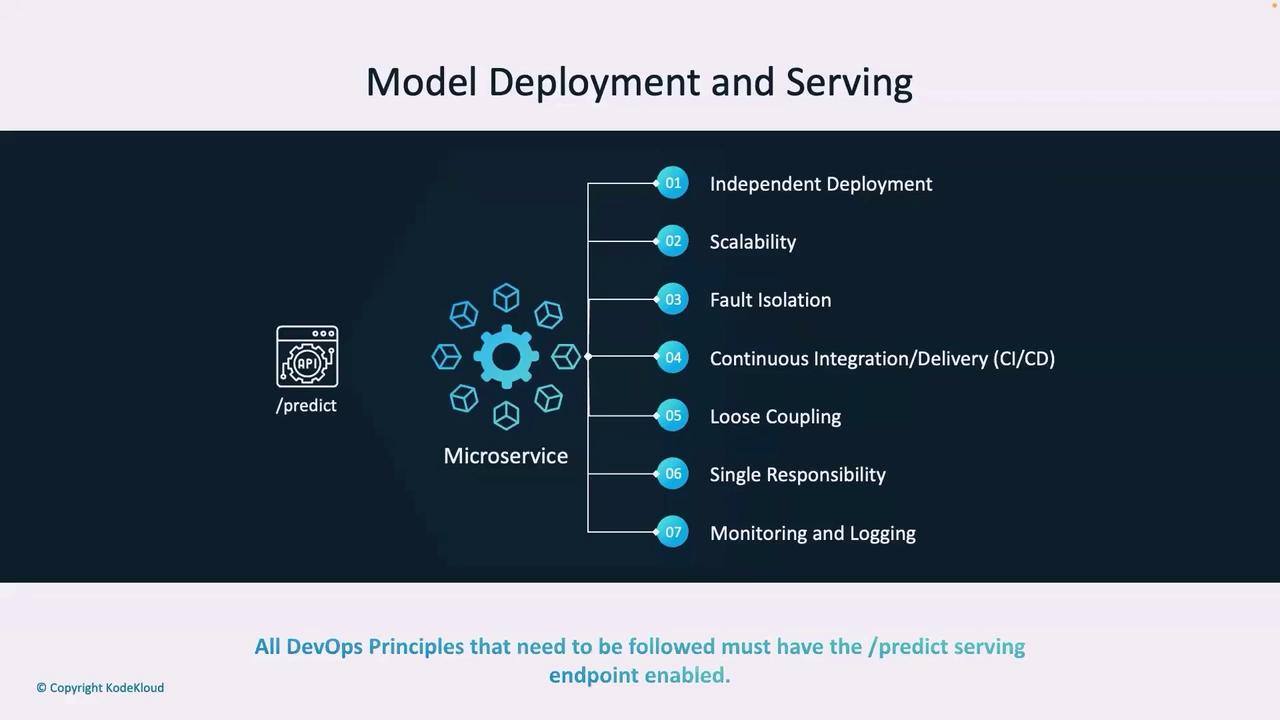
Once the ML model is ready, integrating it into an API shifts the deployment strategy towards a microservices architecture. The /predict endpoint is deployed as a microservice with the following core properties:- Independent deployability
- Scalability
- Fault tolerance
- Dedicated CI/CD process
- Loose coupling (single responsibility—inventory prediction)
- Comprehensive monitoring and logging
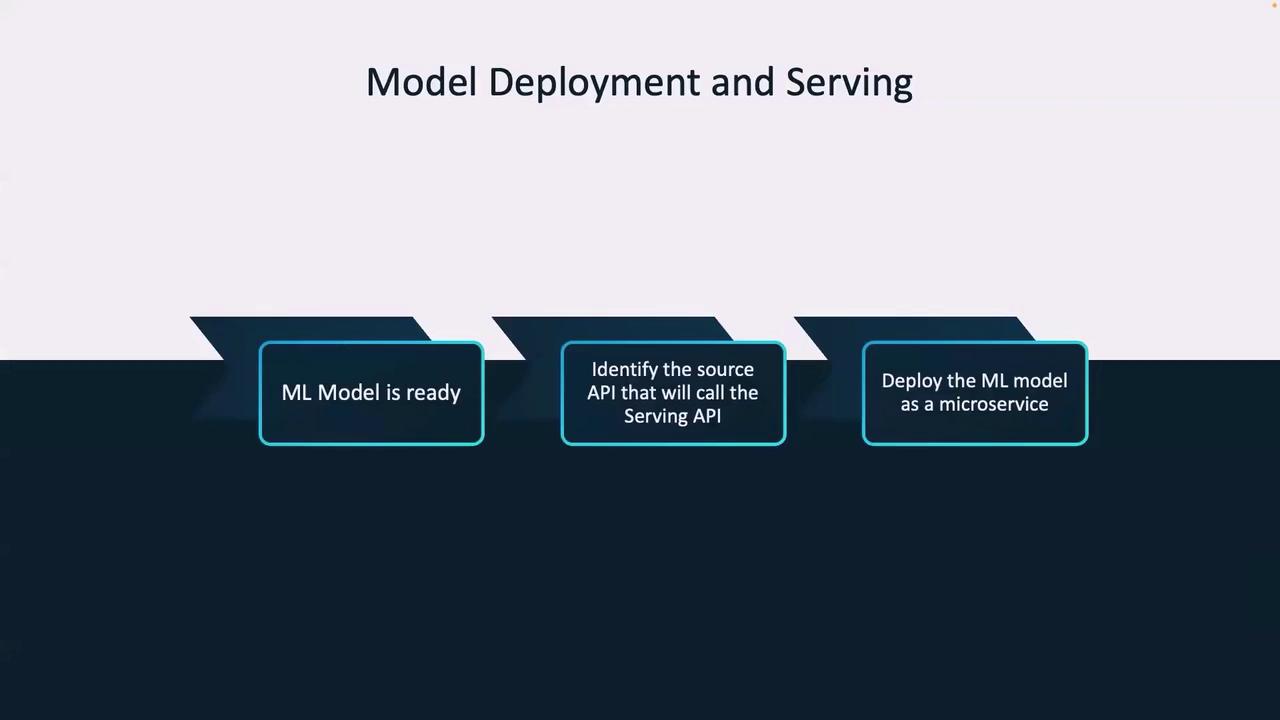
High-Level Deployment Process
Follow these high-level steps for successful model deployment and serving:- Ensure the ML model is production-ready.
- Identify the source API calling the serving API, typically the frontend endpoint.
- Deploy the ML model as a microservice accessible via the /predict endpoint.
Operational Workflow and Team Collaboration
In an operational context, the MLOps engineer queries, “Which backend service will call the ML model API?” The frontend engineer responds that their API is responsible for calling the /predict endpoint, passing two parameters: branch name and date. The endpoint then uses these inputs to generate an inventory prediction.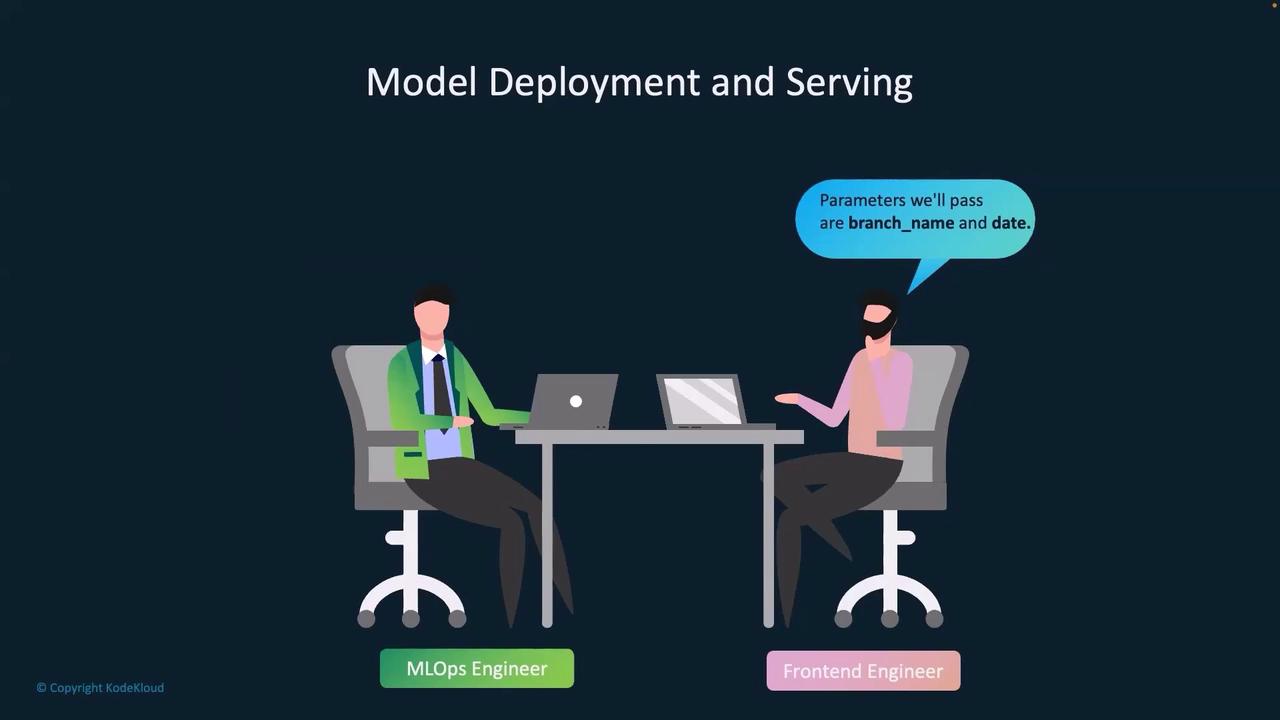
- Deploy the API in a staging environment.
- Frontend engineers update their code to call the /predict endpoint.
- Conduct staging tests.
- Transition to production by initially routing 10% of frontend traffic to the /predict endpoint.
- Monitor the service and infrastructure.
- Upon validation, route 100% of traffic through the /predict endpoint.
Jointly agreeing on API parameters and communication protocols is essential for a smooth deployment process.
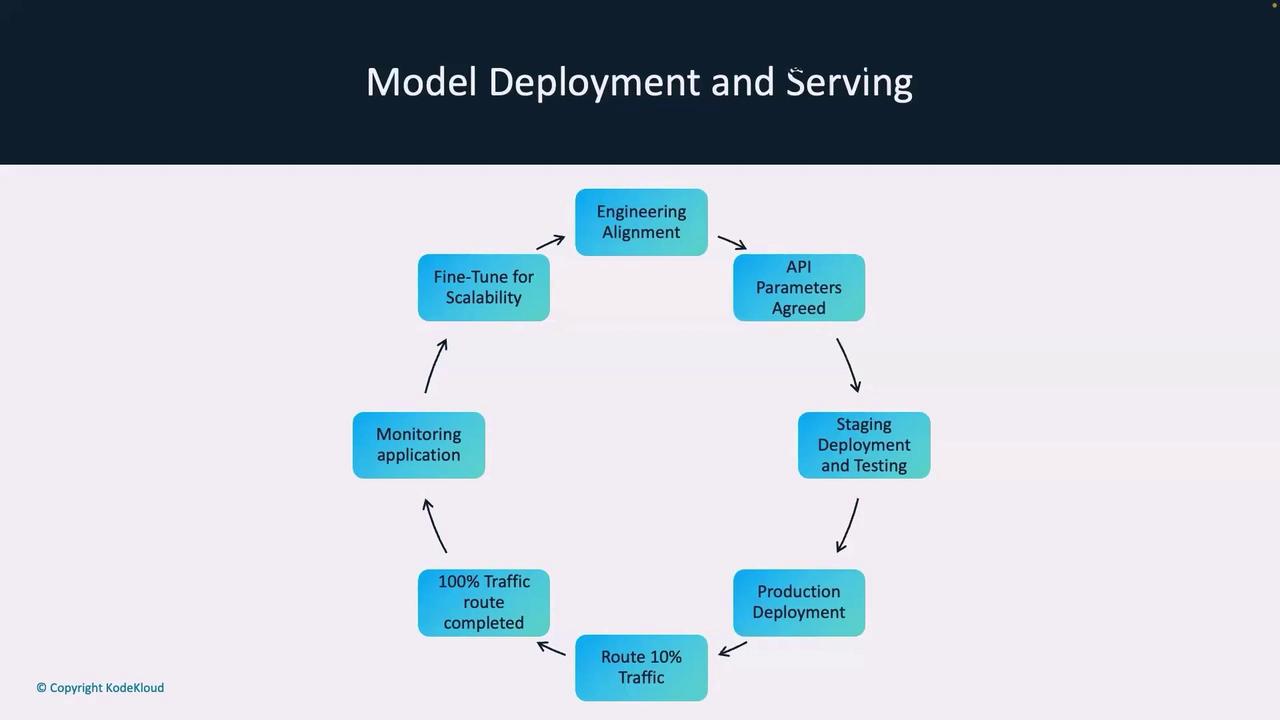
Visualizing the Deployment Lifecycle
The entire process can be visualized as a lifecycle encompassing:- Engineering alignment
- API parameter agreements
- Staging deployments with thorough testing
- Production deployments with incremental traffic routing
- Continuous monitoring and fine-tuning for scalability
Summary
This guide has outlined how a simple ML model (e.g., stored in a pickle file) is transformed into a production-ready deployment within a microservices architecture. We demonstrated the roles of DevOps and MLOps engineers and underscored the importance of collaboration and adherence to microservices principles.In the next lesson, we will delve into the differences between online serving and offline serving and discuss the concept of model drift.