What Is an AWS Placement Group?
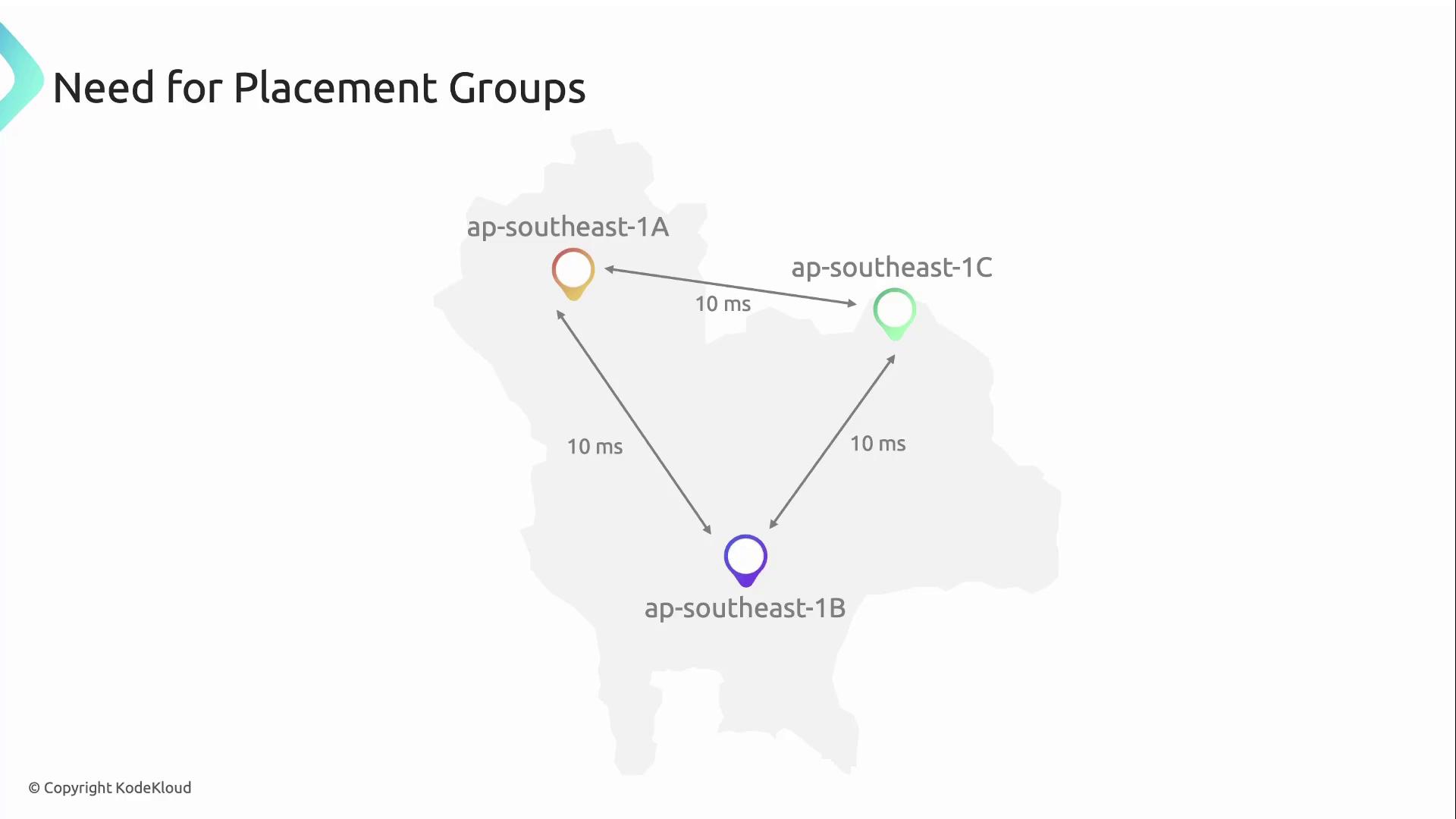
An AWS Placement Group is a logical construct that influences the physical placement of EC2 instances to optimize for:- Low network latency and high throughput
- Hardware-failure isolation
- Minimized blast radius for critical services
| Strategy | Description | Best for |
|---|---|---|
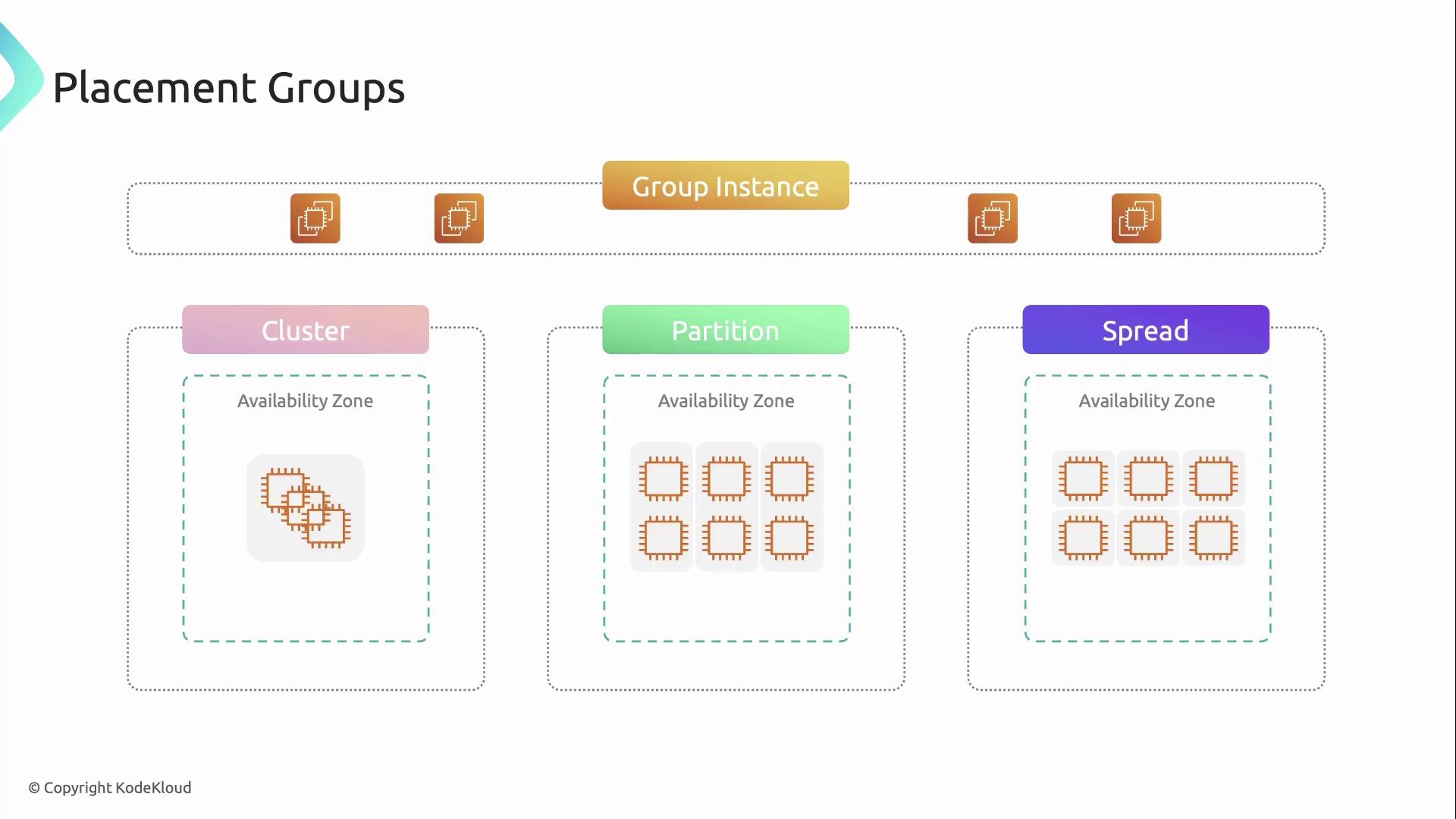
| Cluster | Packs instances closely in one AZ for low latency & high throughput | HPC, tightly coupled compute |
| Partition | Divides instances into partitions with separate racks | Large distributed systems requiring fault isolation |
| Spread | Distributes a small number of instances across racks or AZs | Critical components that need failure containment |
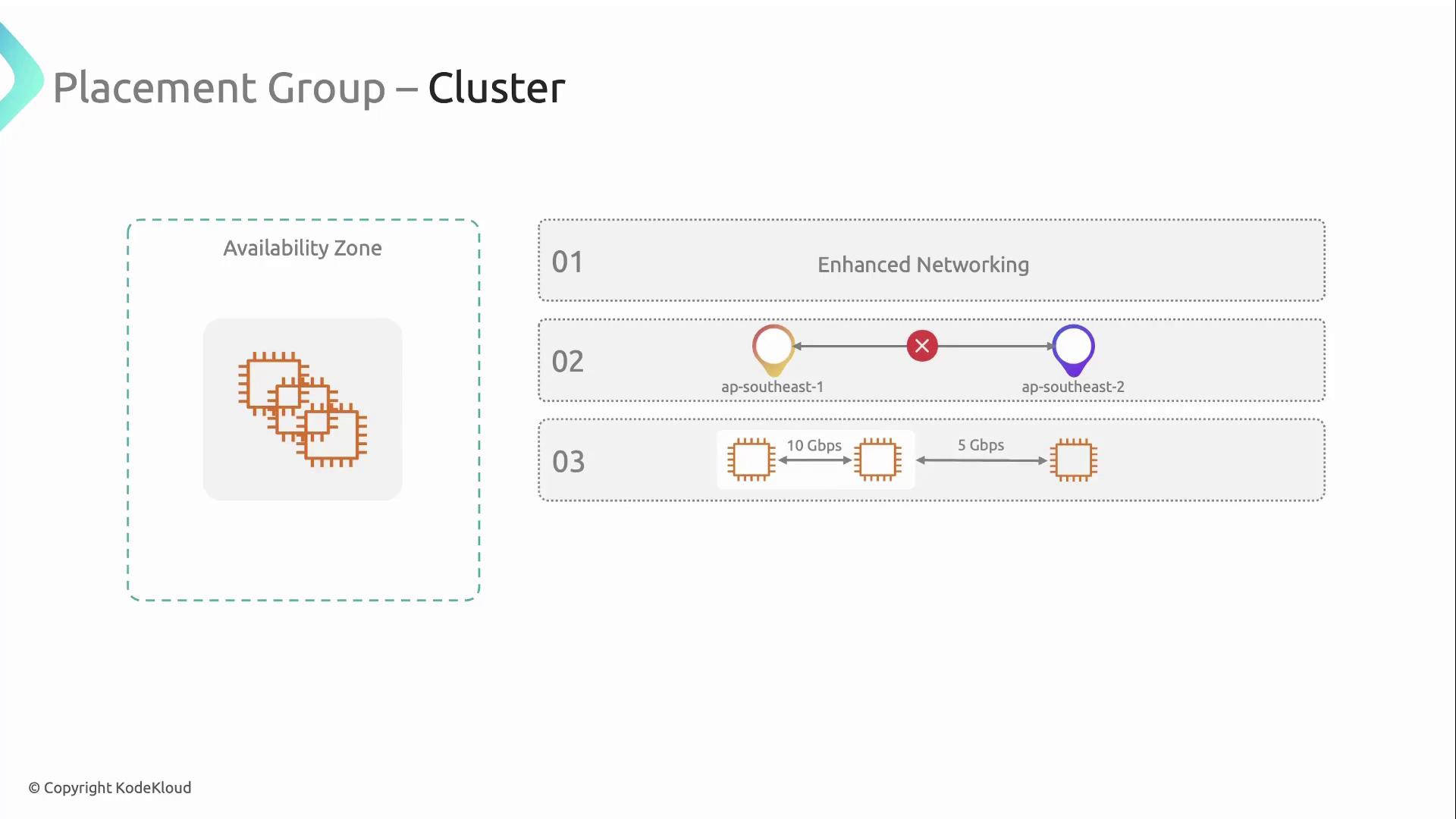
Cluster Placement Groups
A cluster placement group co-locates instances within a single Availability Zone. This yields ultra-low latency and high network throughput, ideal for HPC clusters or big-data workloads. Key requirements and benefits:- Instances must support enhanced networking (
ENAorElastic Fabric Adapter) - All instances reside in the same AZ (no cross-AZ placement)
- Network throughput can exceed 10 Gbps on supported instance types
- Use the same instance type within the group for maximum performance
To leverage the highest network performance, ensure your AMI and instance types support the Elastic Network Adapter (ENA) or Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA).
Partition Placement Groups
A partition placement group segments your fleet into logical partitions. Each partition is mapped to its own set of racks with isolated power and network infrastructure, reducing the risk of simultaneous hardware failures. Highlights:- Can span multiple Availability Zones in a single region
- Up to 7 partitions per AZ, each on separate racks
- Racks in different partitions do not share power or network gear
Do not exceed 7 partitions per Availability Zone. If you need more partitions, consider multiple placement groups.
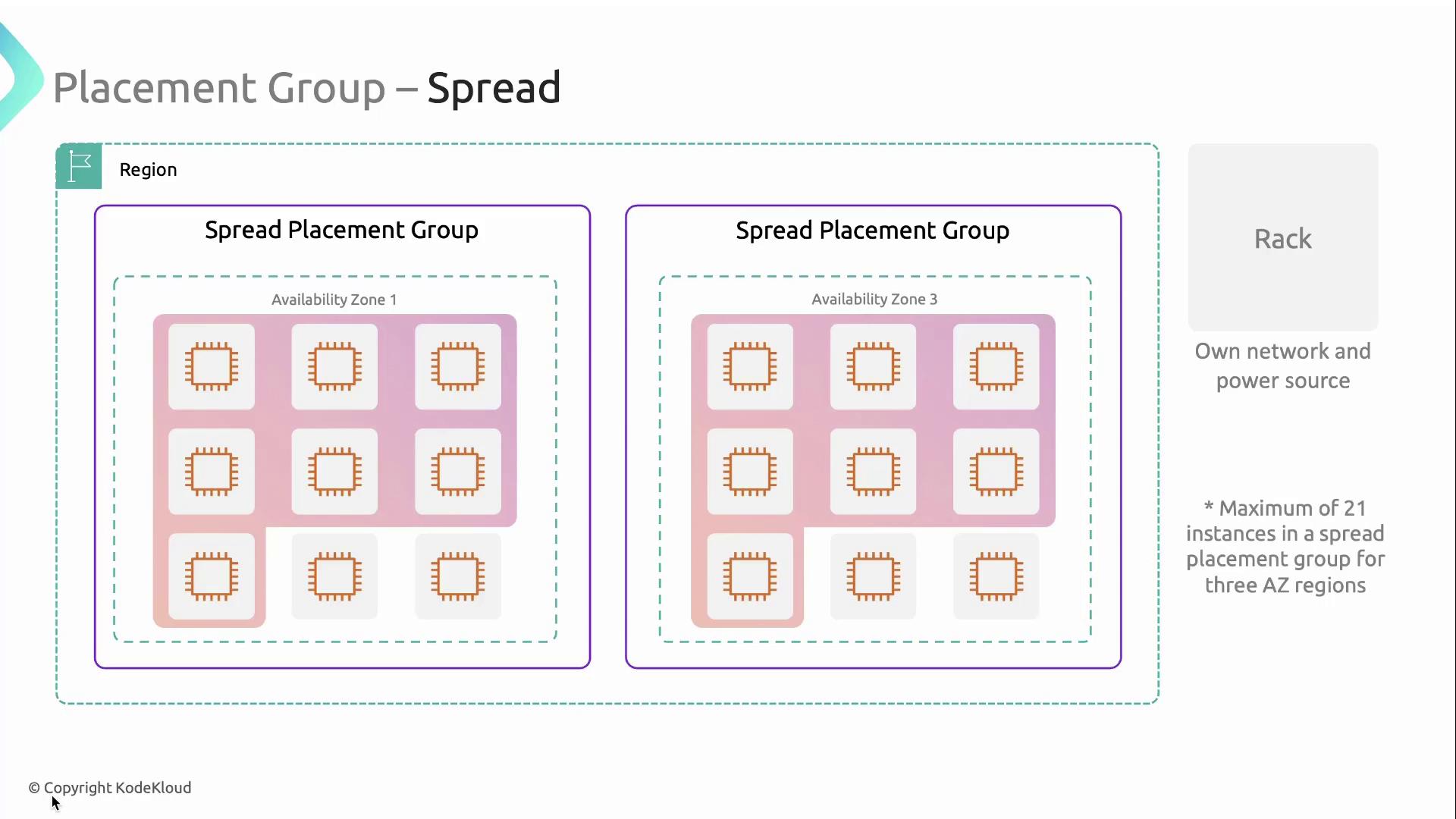
Spread Placement Groups
A spread placement group distributes a small number of instances across distinct racks, AZs, or both. This strategy minimizes the blast radius of hardware failures for critical application components. Key limits:- Can span multiple AZs within a region
- Maximum 7 running instances per AZ per spread group
- In a region with 3 AZs, you can have up to 21 instances in one spread group