Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Your Private Network
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is your own private, logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud. It acts like a gated community, where you control who enters, leaves, and communicates internally. Key VPC capabilities:| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Isolation | Logical separation from other AWS accounts |
| Customizable IP Range | Define your own CIDR block and segment with subnets |
| Hybrid Connectivity | Connect on-premises via VPN, Direct Connect, and VPC Peering |
| AWS Service Integration | Seamlessly integrates with EC2, RDS, ELB, Lambda, and more |

Remember: VPCs do not span Regions. Resources in one Region (and its AZs) cannot communicate with resources in another without a peer connection or VPN.
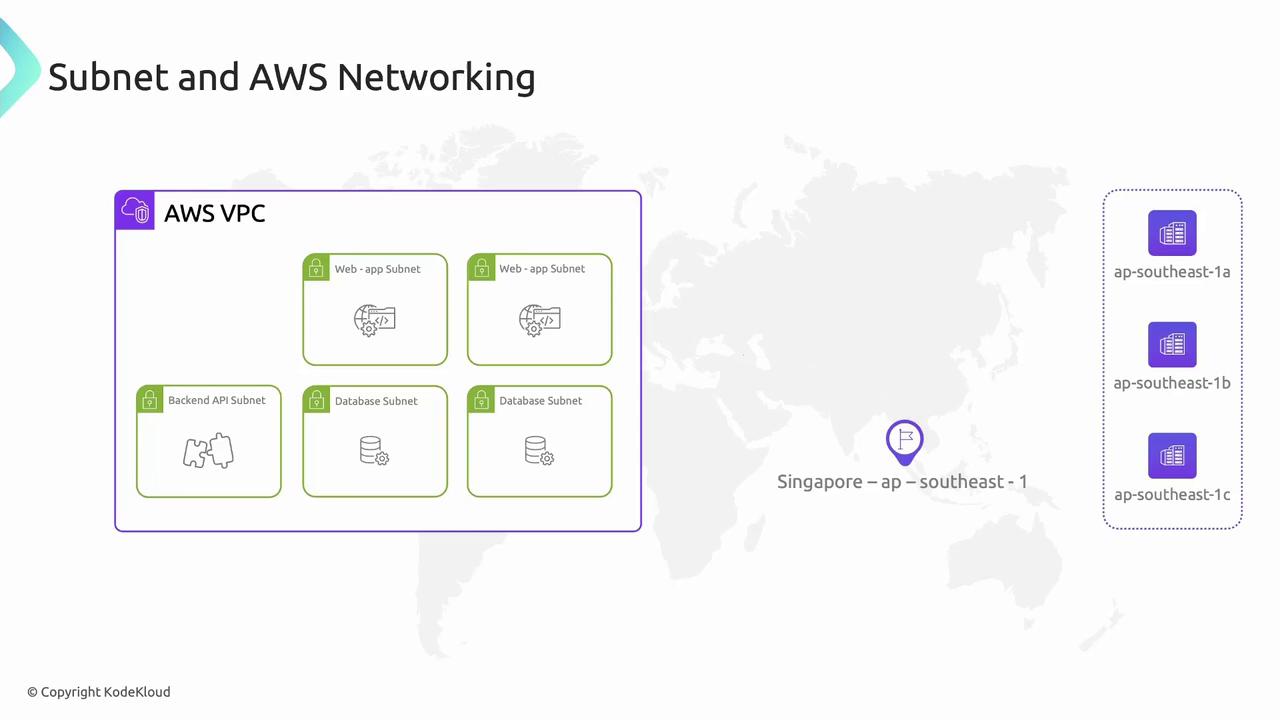
Subnets: Segmenting Your VPC
Subnets subdivide a VPC into smaller IP ranges within a single AZ—like dividing a housing lane into individual plots. Use subnets to isolate workloads (web servers, APIs, databases) based on security and routing needs.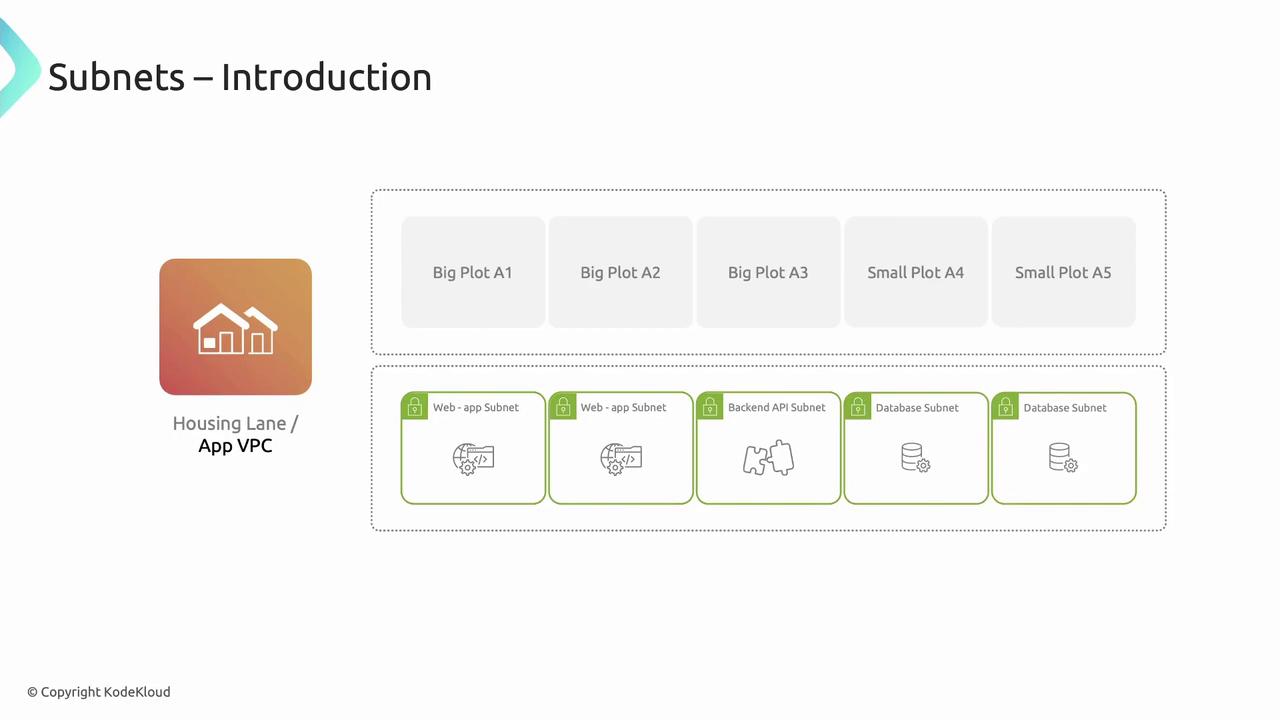
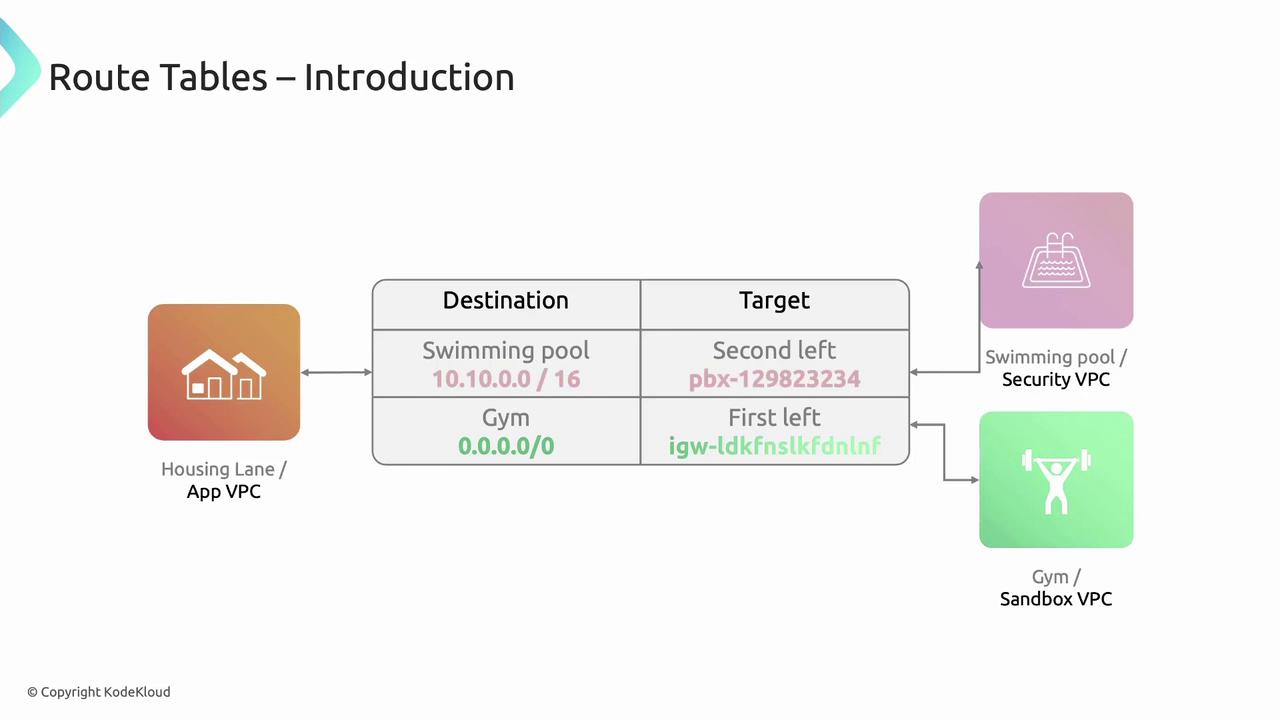
Route Tables: Traffic Signposts
Route tables control how packets flow between subnets, VPC peering connections, Internet Gateways, and NAT Gateways. Each entry maps a destination CIDR to a target. Example “App VPC” route table:| Destination | Target |
|---|---|
| 10.10.0.0/16 | VPC Peering Connection |
| 0.0.0.0/0 | Internet Gateway (igw-xxxx) |
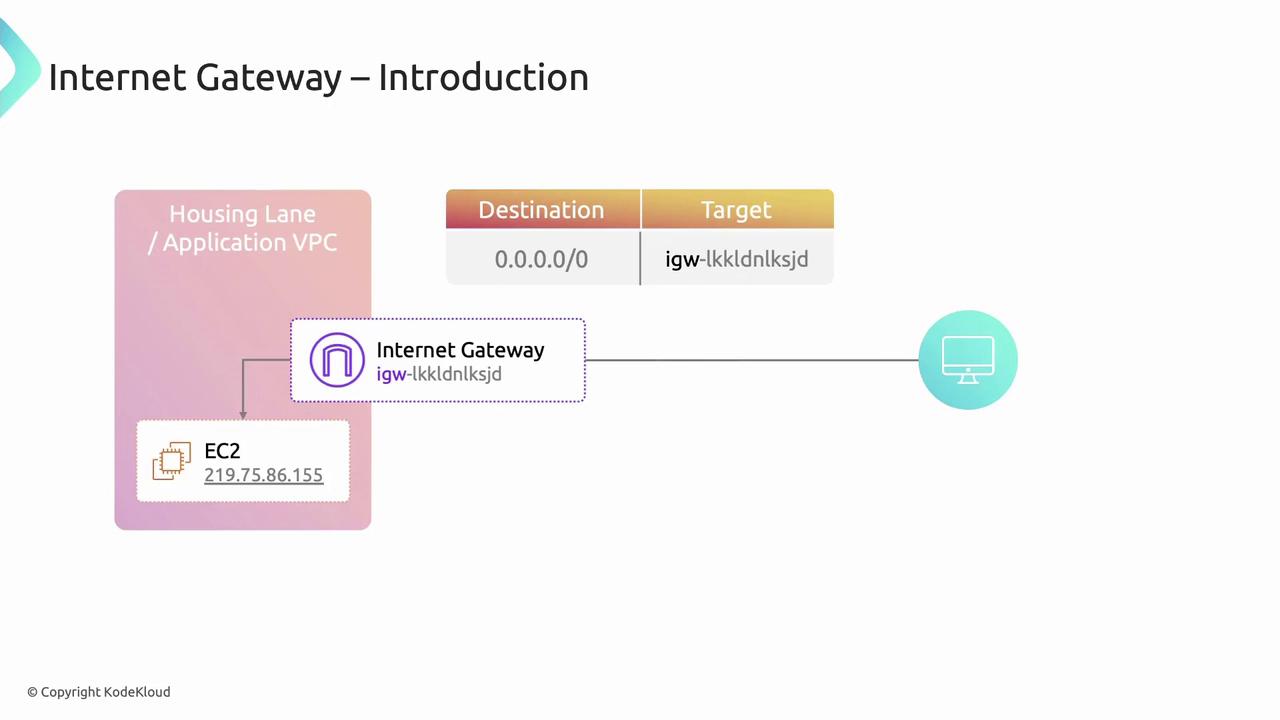
Internet Gateway: Public Access Point
An Internet Gateway (IGW) is a horizontally scaled, redundant VPC component that allows communication between your VPC and the Internet. To enable Internet access for a subnet:- Create and attach an IGW to your VPC.
- Add a route to your route table:
- Destination:
0.0.0.0/0 - Target:
igw-<gateway-id>
- Destination:
- Assign public or Elastic IPs to your EC2 instances.
NAT Gateway: Secure Outbound Connectivity
A NAT Gateway allows instances in private subnets to initiate outbound Internet traffic while preventing inbound connections. Setup steps:- Launch a NAT Gateway in a public subnet.
- Update the private subnet’s route table:
- Destination:
0.0.0.0/0 - Target:
nat-<gateway-id>
- Destination:
Each NAT Gateway incurs an hourly charge and data processing fees. Consider using a NAT instance for low-throughput scenarios.