Why Use a Load Balancer?
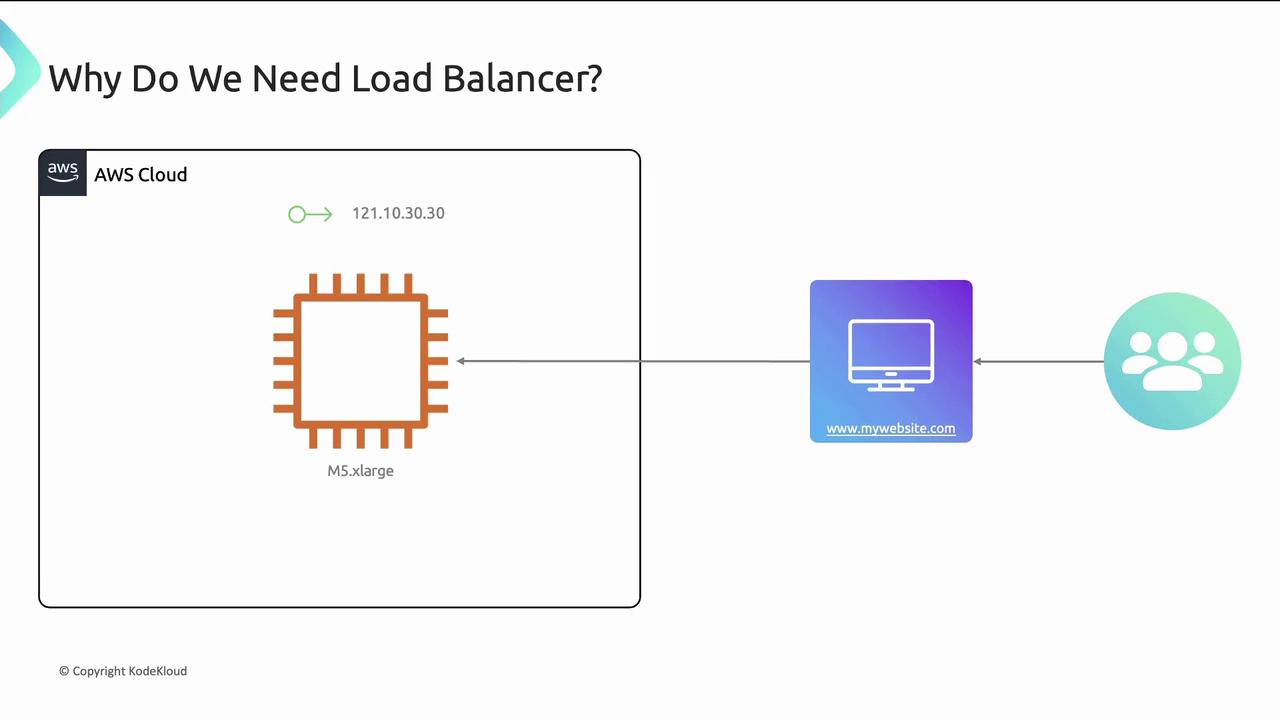
Running a single EC2 instance formywebsite.com can become a bottleneck as traffic grows. There are two primary scaling strategies:
Vertical ScalingScale up by increasing instance size.
Vertical scaling has limits and can be cost-inefficient when traffic is variable.
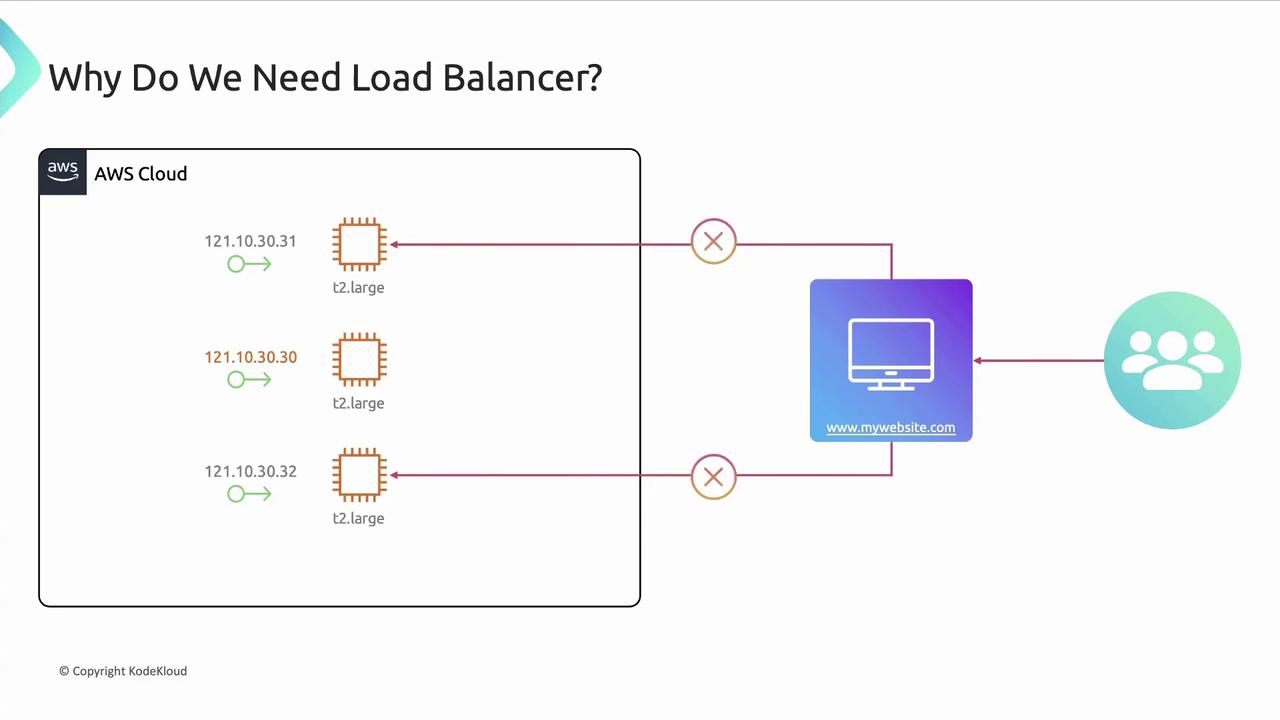
Run multiple identical instances behind a single endpoint. DNS still points to one IP, so without a load balancer new servers receive no traffic.
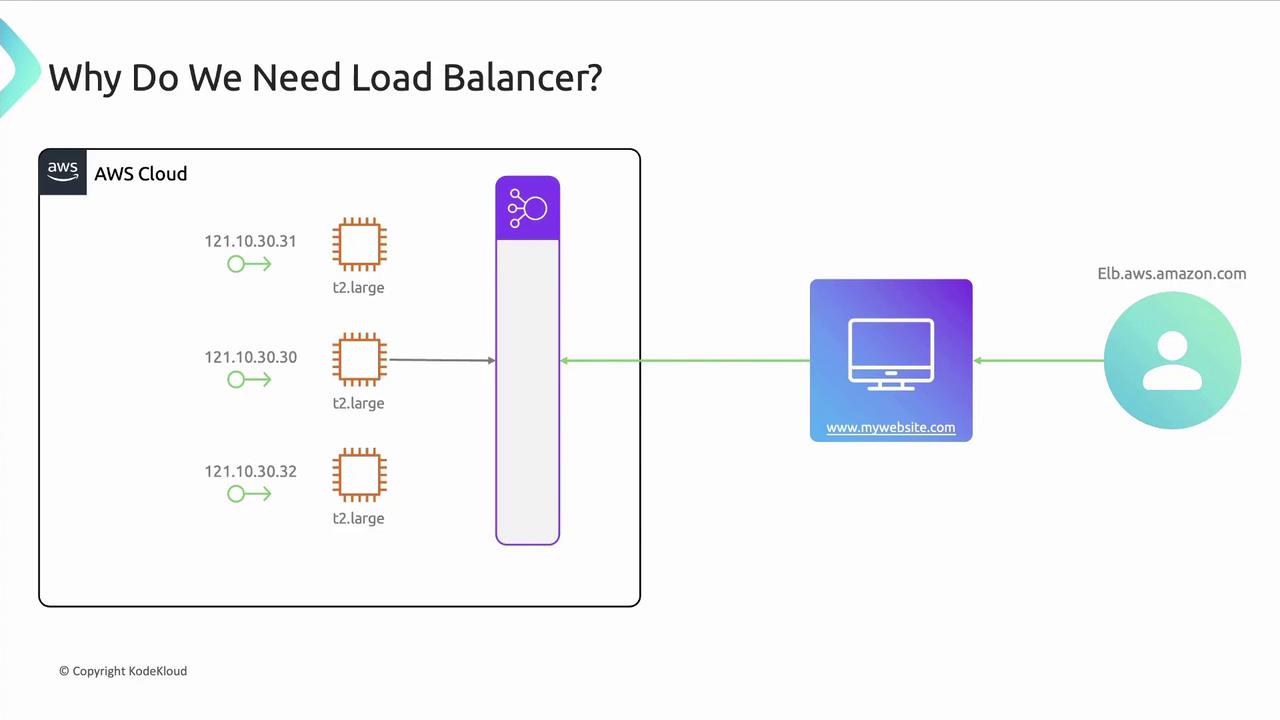
How Load Balancing Works in AWS
AWS ELB is highly available and fault tolerant across multiple Availability Zones (AZs). It distributes incoming traffic to target groups—collections of instances, IP addresses, or Lambda functions. Each load balancer uses one or more listeners to check for connections on a port (e.g., port 80 for HTTP). Listener rules determine how to forward requests: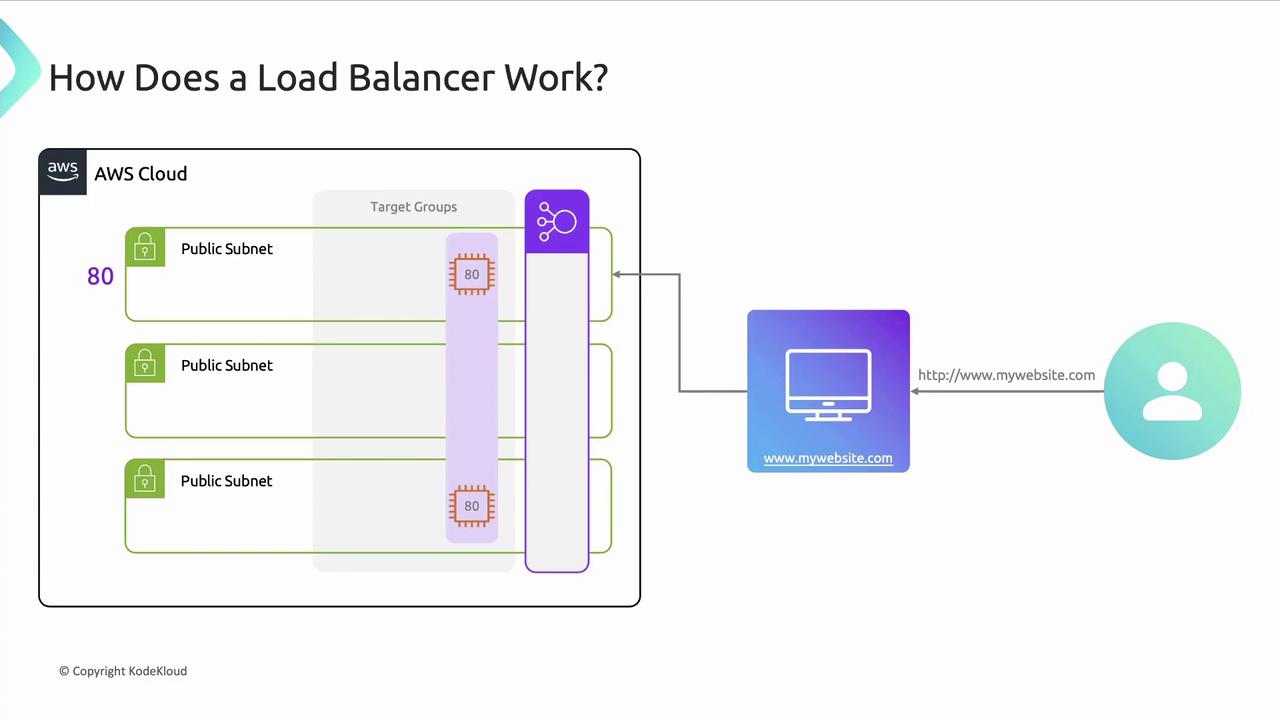
- Default HTTPS port: 443
- Custom listener ports are supported (e.g., 8080)
- Rules are evaluated by priority
- Load balancers can be public-facing or internal
Protocols and Ports
| Load Balancer Type | Default Port | Supported Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP/HTTPS | 80 / 443 | HTTP, HTTPS, HTTP/2, gRPC |
| TCP/UDP | Any | TCP, UDP, TLS |
Target Groups
A target group defines the routing and health-check configuration for one or more registered targets. You specify:- Protocol and port
- Health check path and thresholds
- Target type: instance, IP, or Lambda
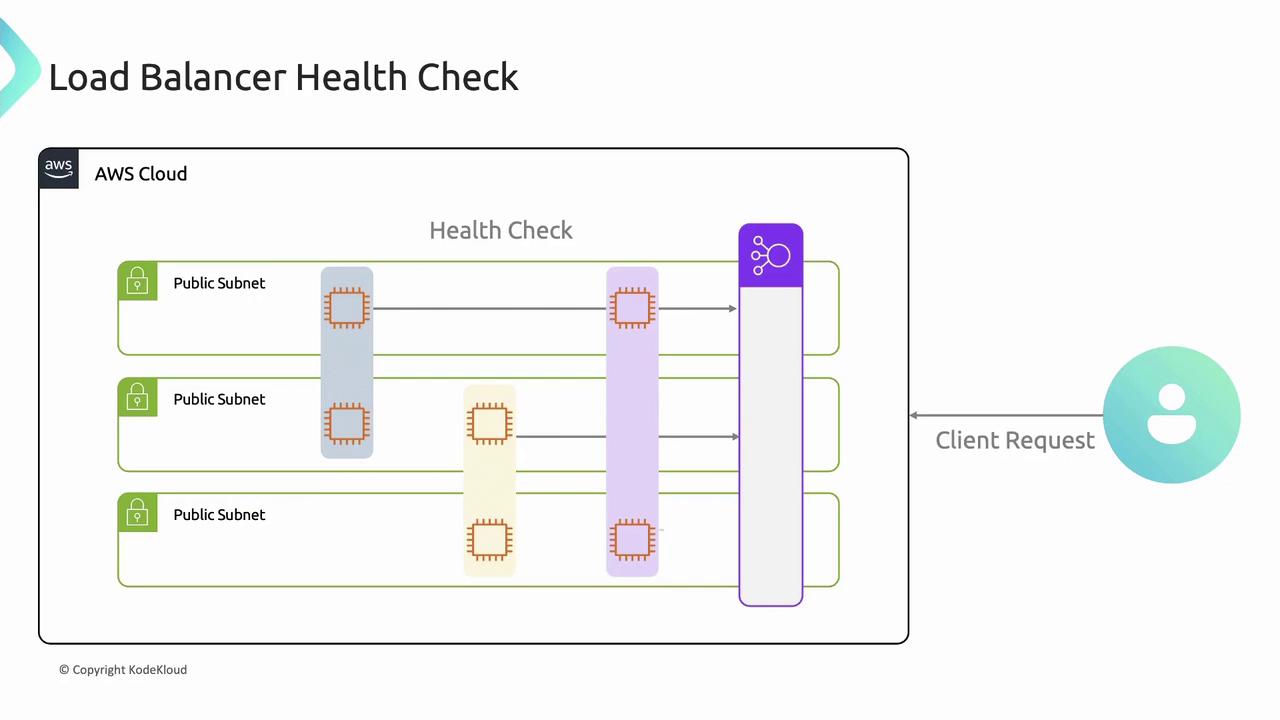
Health Checks
Load balancer nodes perform periodic health checks on each target. Unhealthy targets are removed from rotation until they recover.Configure health check intervals and thresholds to balance rapid failover with avoiding false positives.
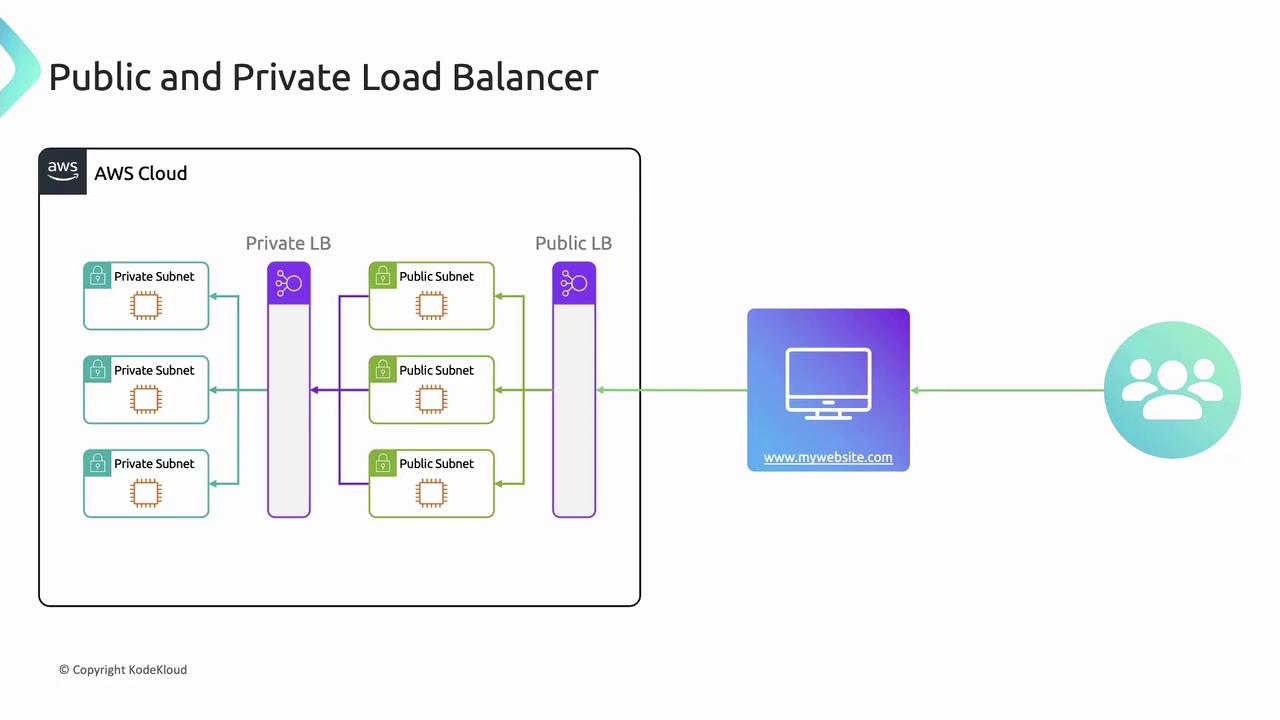
Public vs. Private Load Balancers
| Type | Internet-Facing | Within VPC |
|---|---|---|
| Public Load Balancer | Yes | No |
| Private Load Balancer | No | Yes |
Cross-Zone Load Balancing
With cross-zone load balancing enabled, each ELB node evenly distributes traffic across all registered targets in every AZ. This prevents hotspots and idle instances.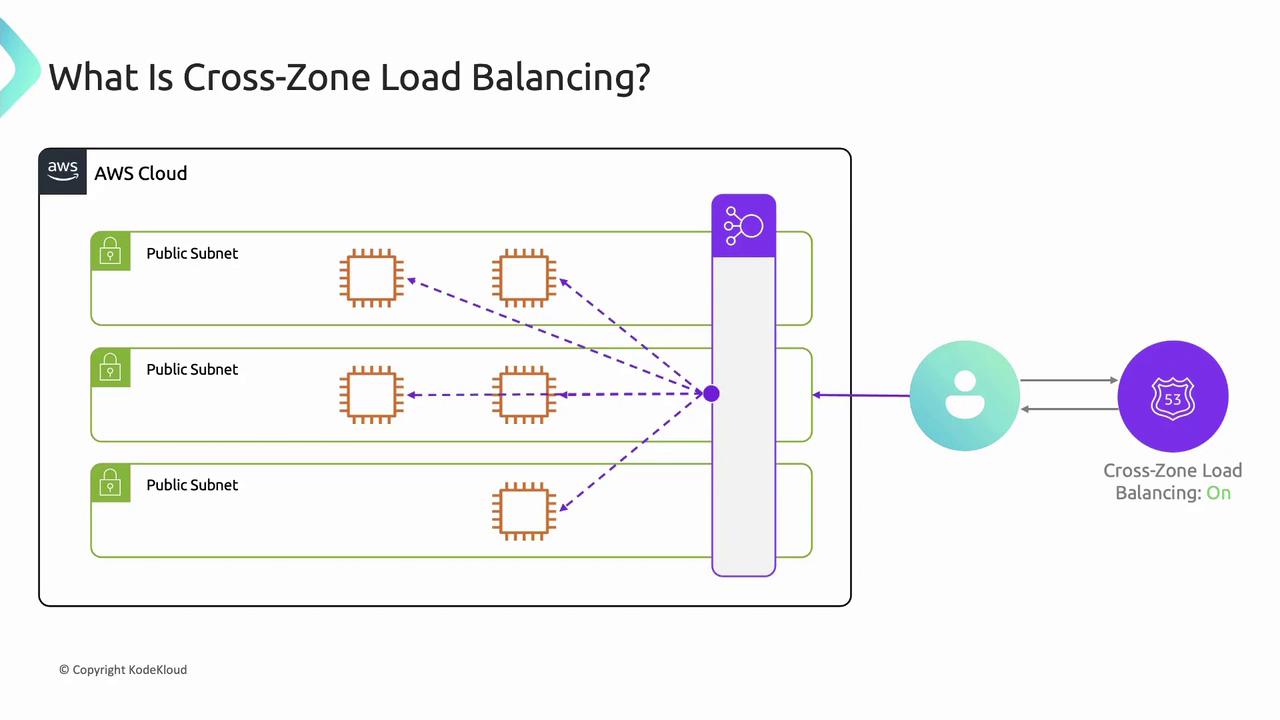
Disable cross-zone load balancing only for very specific network requirements. Most deployments should keep it enabled.
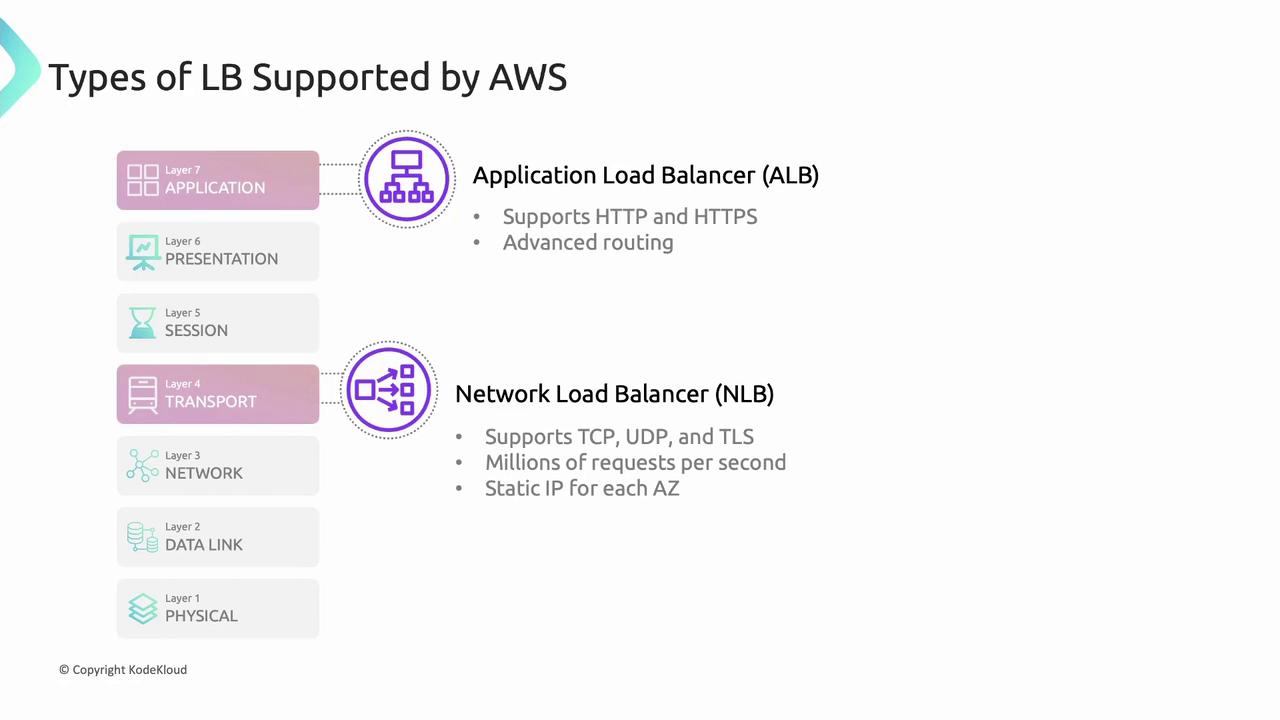
Types of AWS Load Balancers
| Load Balancer Type | OSI Layer | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Application Load Balancer (ALB) | Layer 7 | Advanced HTTP/HTTPS routing and features |
| Network Load Balancer (NLB) | Layer 4 | High performance TCP/UDP load balancing |
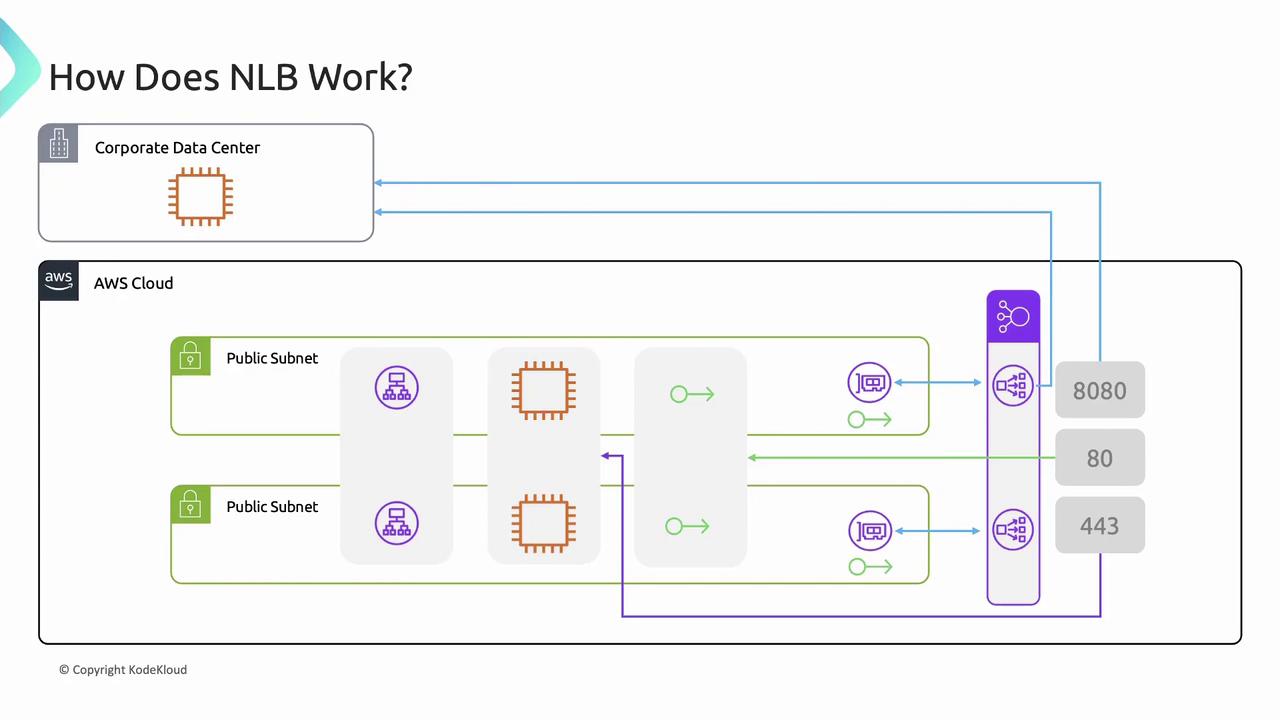
Network Load Balancer (NLB)
- Targets: instance IDs, IP addresses, or ALBs
- One network interface per AZ for a static IP
- Optionally assign Elastic IPs to each subnet
- Routes TCP/UDP/TLS to target groups by port
- Can route to resources outside the VPC (VPN or Direct Connect)
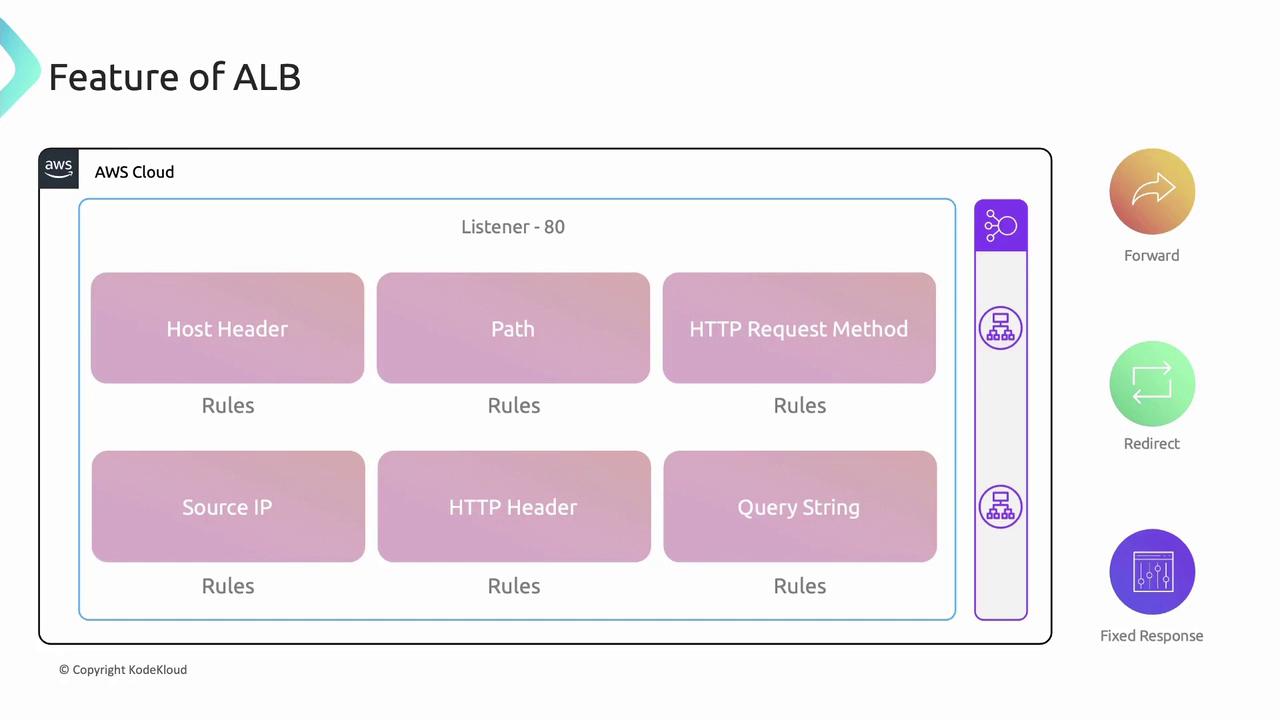
Application Load Balancer (ALB)
ALB rules consist of conditions and a single action (forward, redirect, or fixed-response). Supported conditions:
- Host header
- Path
- HTTP method
- Source IP
- HTTP header
- Query string
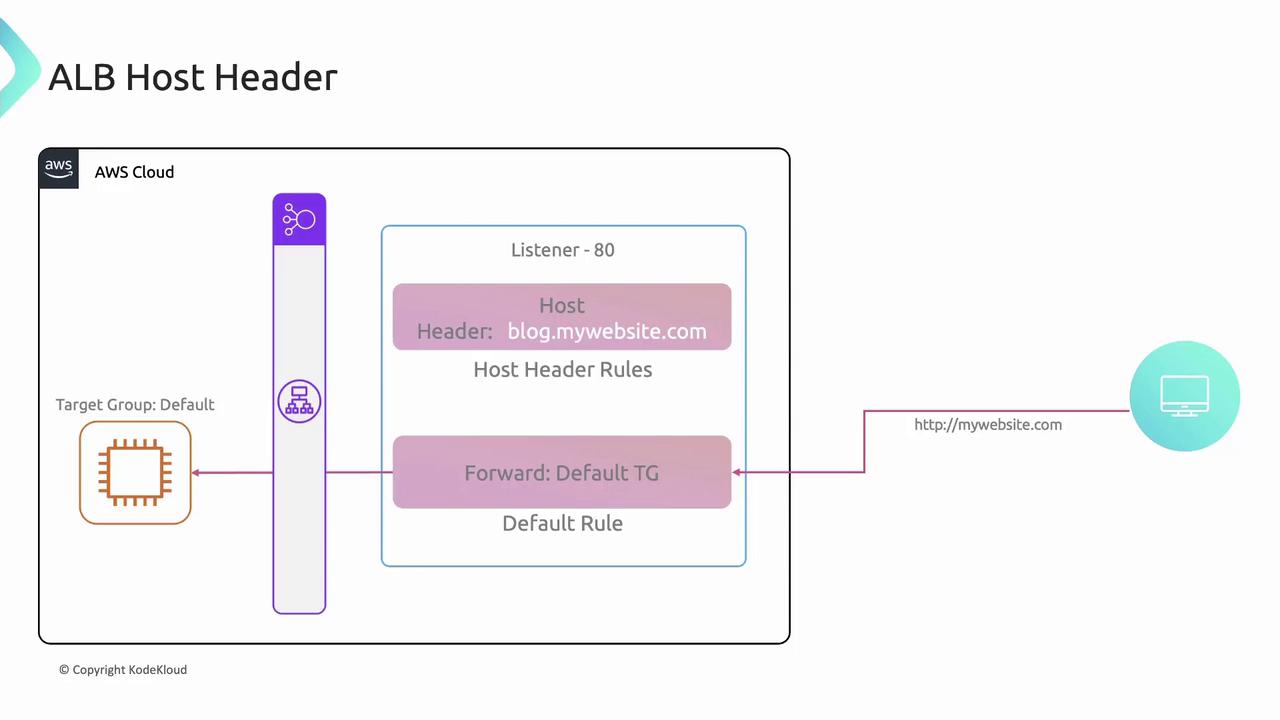
Host Header Routing
Forward requests based on theHost header.Example:
- If
Host: blog.mywebsite.com, route toblogtarget group. - Default: route all other traffic to
default.
Path-Based Routing
Match URL paths (e.g.,/blog) and forward to the corresponding target group.
HTTP Method Routing
Match HTTP methods (e.g.,POST) and forward to an API target group.
Source IP Routing
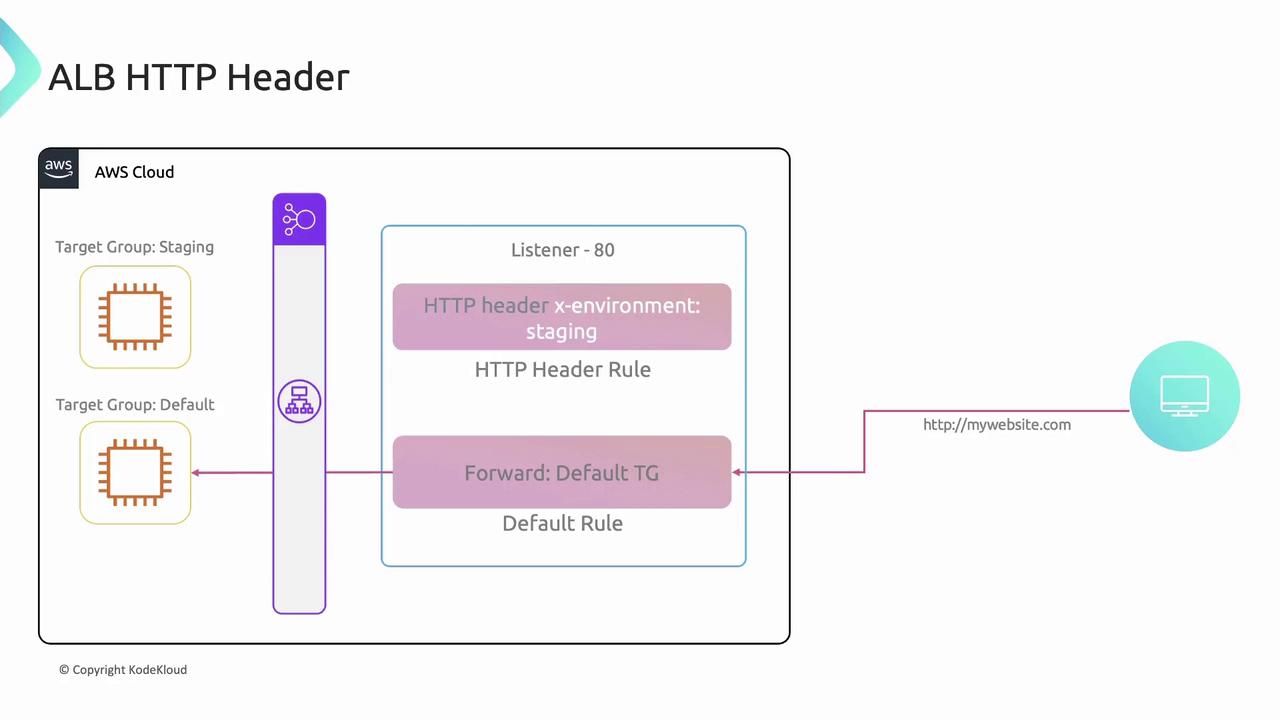
Allow requests from specific IP addresses to a designated group.HTTP Header Routing
Match custom headers (e.g.,x-environment: staging) to route to a staging environment:
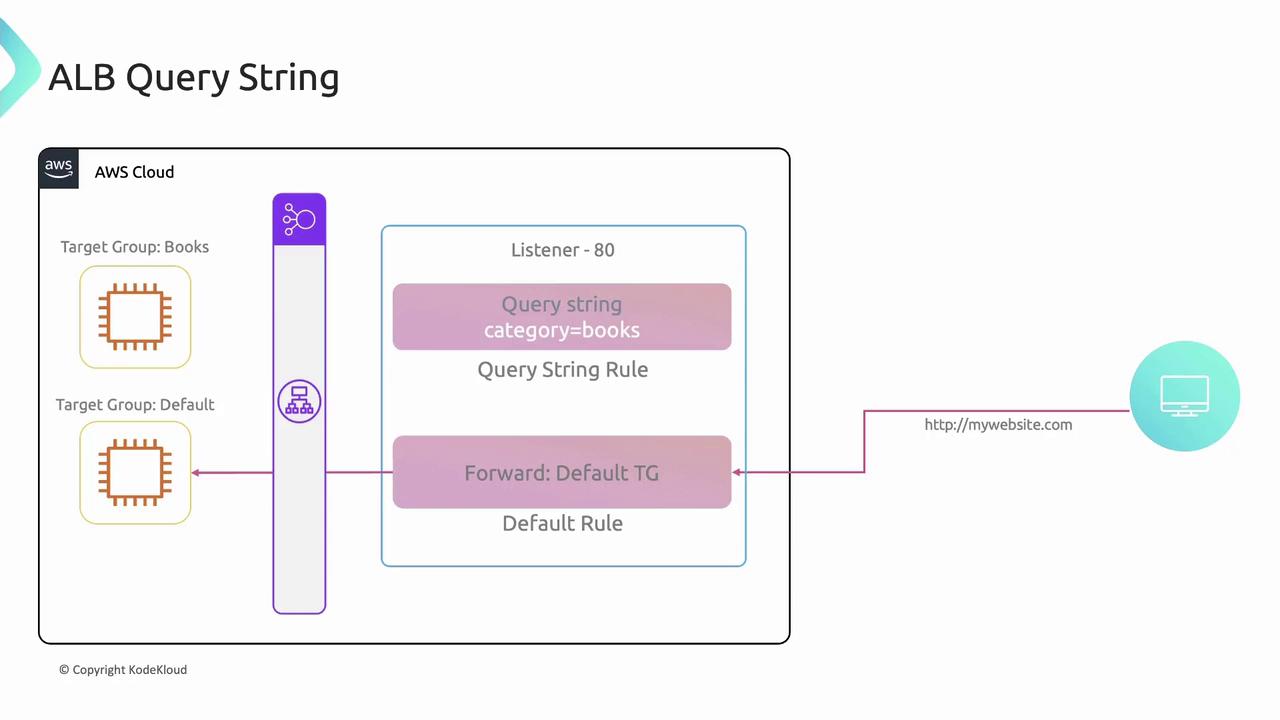
Query String Routing
Inspect query parameters (e.g.,?category=books) and forward accordingly:
Rule Priority Example
- Priority 1: Path
/api+ headerx-client: premium→large - Priority 2: Path
/api+ headerx-client: medium→medium - Default: All other
/api→default-api
Elastic Load Balancer Integrations
ELBs integrate with many AWS services to deliver end-to-end, scalable architectures: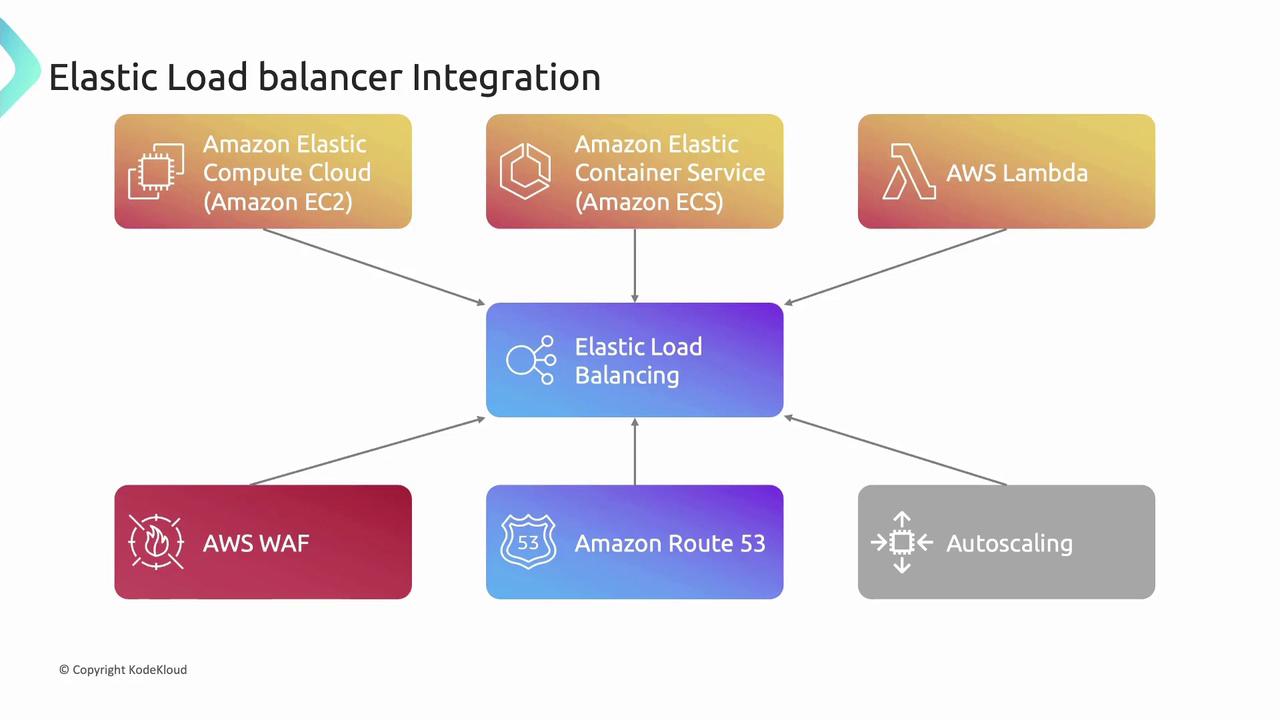
- EC2: Distribute incoming traffic across instances
- ECS: Balance containerized workloads
- Lambda: Route requests to serverless functions
- WAF: Apply security rules to incoming traffic
- Route 53: Use DNS to map domains to load balancers
- Auto Scaling: Automatically adjust capacity and register/deregister targets