- Generate New Code Snippets (Command K / Ctrl + K)
- Inline Chat for Refactors (Command L / Ctrl + L)
- Quick Inline Completions (Comments + Tab)
Project Setup
- Create a folder named
Quick Demo. - Inside it, add:
test.pymockdata.csvcontaining headers and rows of user data.
Ensure
mockdata.csv is in the same directory as test.py so the script can locate it.1. Generate Code with Command K
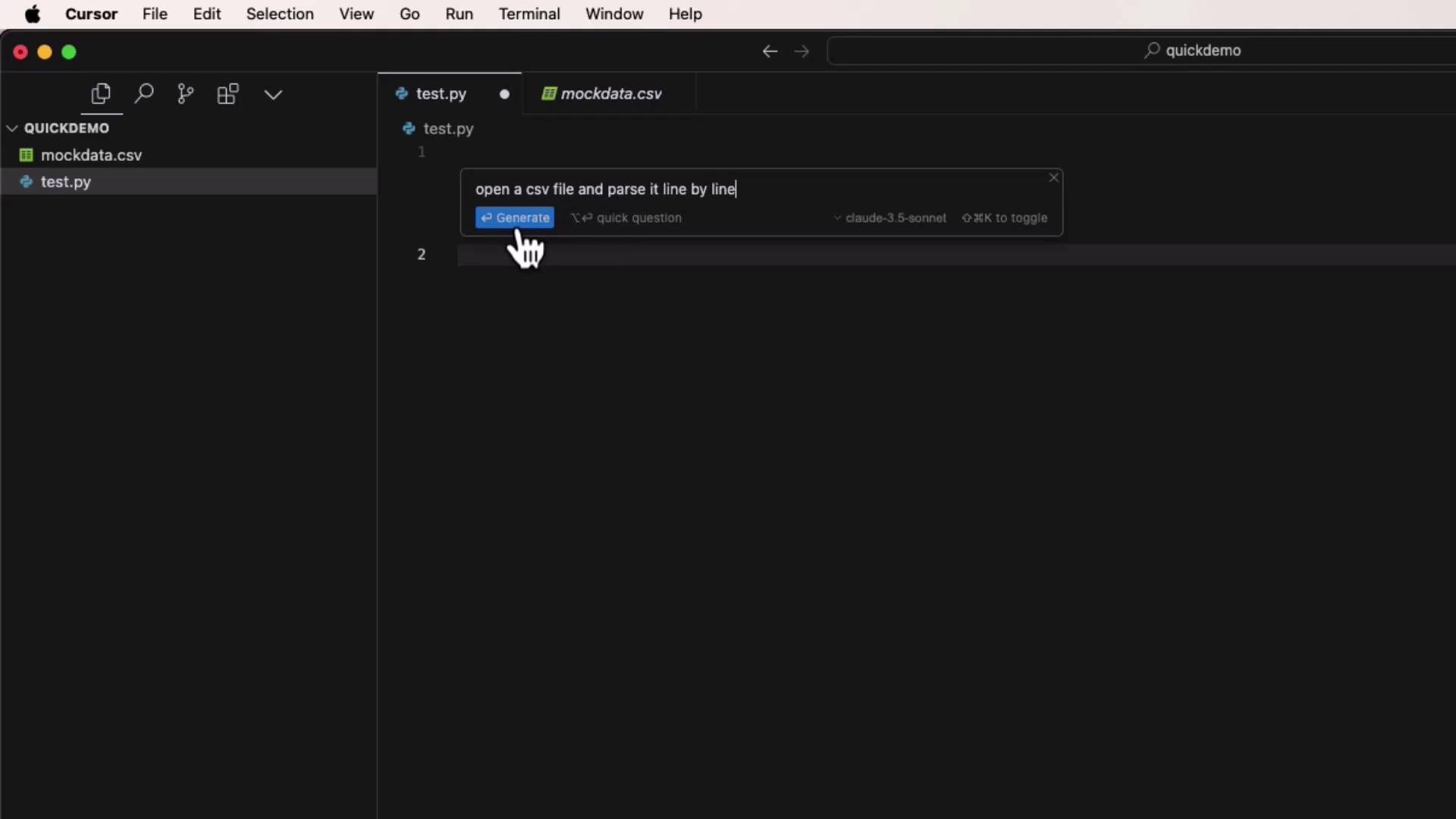
Withtest.py open, press Command K (macOS) or Ctrl + K (Windows/Linux).Prompt:
Open mockdata.csv and parse it line by line.
Select a model (e.g., Claude 3.5 Sonnet) and accept the generated snippet:
2. Wrap in main() with Inline Chat (Command L)
To structure your script entry point:
- Press Command L (macOS) or Ctrl + L (Windows/Linux).
- Enter:
“Please wrap this code in a
main()function and add theif __name__ == '__main__'guard.”
Using Command L lets Cursor AI review your entire file (or project) for context-aware refactors.
3. Quick Inline Edits with Comments + Tab
For one-line tweaks, simply write a comment and hit Tab.For example, to print only IP addresses that aren’t
192.168.1.1:
4. When to Use Each Mode
| Mode | Shortcut | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Generate New Code | Command K / Ctrl + K | Creating new functions or large code blocks |
| Inline Chat | Command L / Ctrl + L | Wrapping, refactoring, or multi-line edits |
| Quick Inline Edits | Comments + Tab | Small, one-line improvements |
Avoid overusing auto-generated code without review—always test and validate generated snippets.
5. Controlling Context Scope
- Inline Comments & Command K
Scope is limited to the open file and surrounding lines. - Command L (Chat)
Can reference the full project, additional files, or external sources (when enabled).
Intelligent code suggestions from Cursor AI can dramatically accelerate Python development by handling boilerplate and routine edits. Next, we’ll build a full project from scratch using these tools!