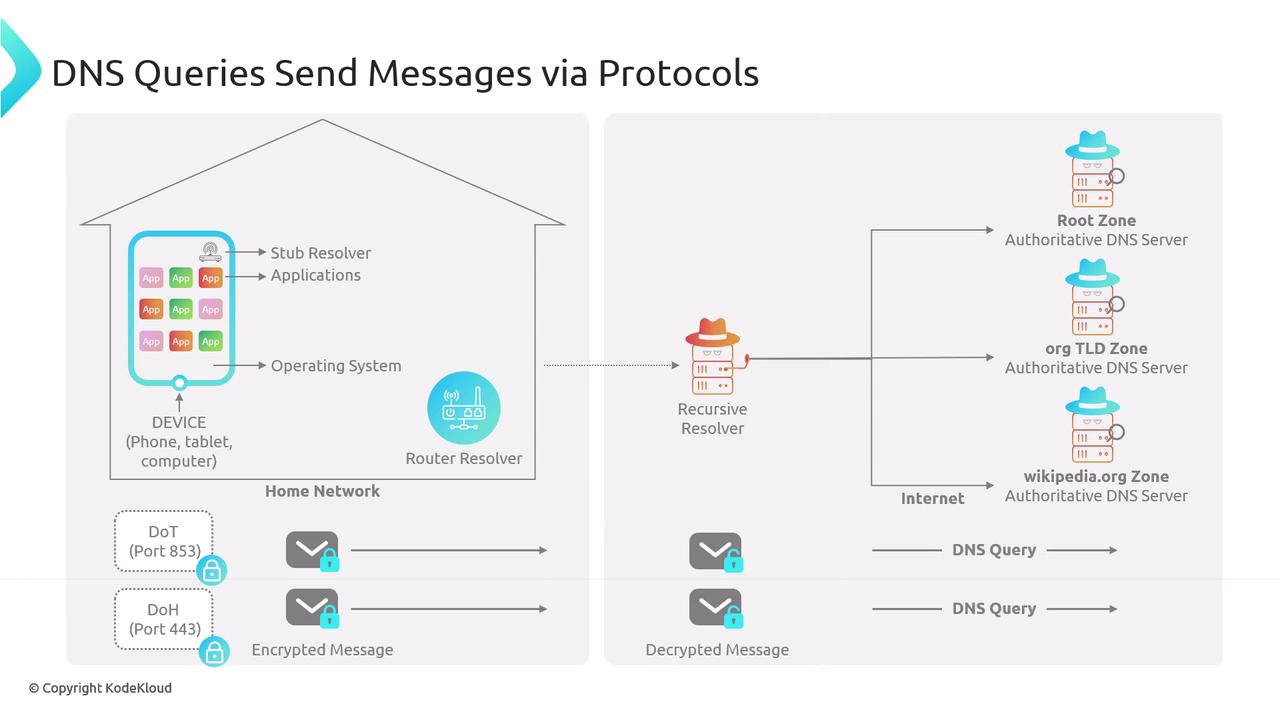
Secure DNS: DoH and DoT
- DoH (DNS over HTTPS): Encapsulates DNS queries within HTTPS, encrypting the data in transit.
- DoT (DNS over TLS): Utilizes TLS encryption to secure DNS queries.
Understanding DNSSEC
In addition to these secure transport protocols, DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) enhances DNS security by digitally signing DNS records. Unlike DoH and DoT, which focus solely on encrypting data during transit, DNSSEC ensures the authenticity and integrity of the DNS data itself.
Key Differences: DNS Encryption vs. DNS Data Validation
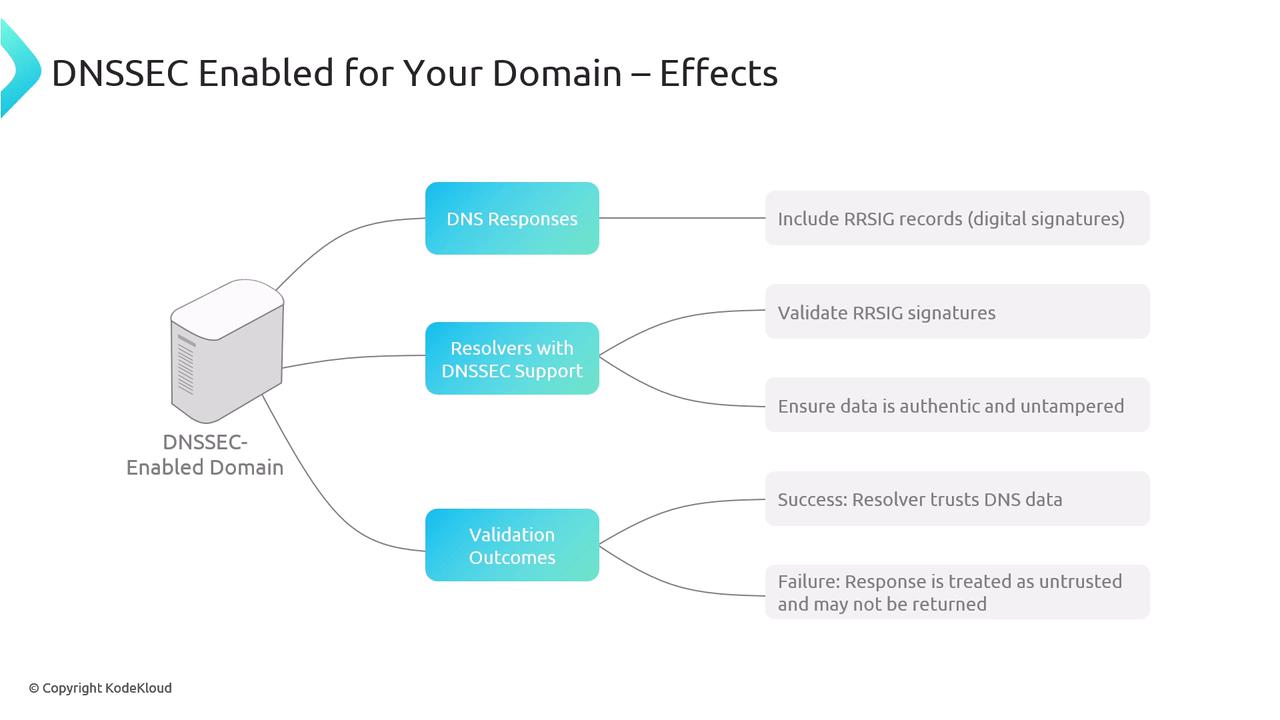
When using DoH, HTTPS encryption (SSL/TLS) secures the data in transit, including the required HTTP headers. In contrast, DNSSEC embeds cryptographic signatures (e.g., RRSIG records) within DNS responses, enabling client resolvers to validate that the data originates from a trusted authoritative server.
How DNSSEC Works
The validation process with DNSSEC begins when a client sends a DNS query. Often, the query includes an OPT record with the DNSSEC OK (DO) flag set, indicating the client’s request for DNSSEC data. When a domain is DNSSEC-enabled, the resolver uses the appropriate public keys to verify digital signatures included in the response.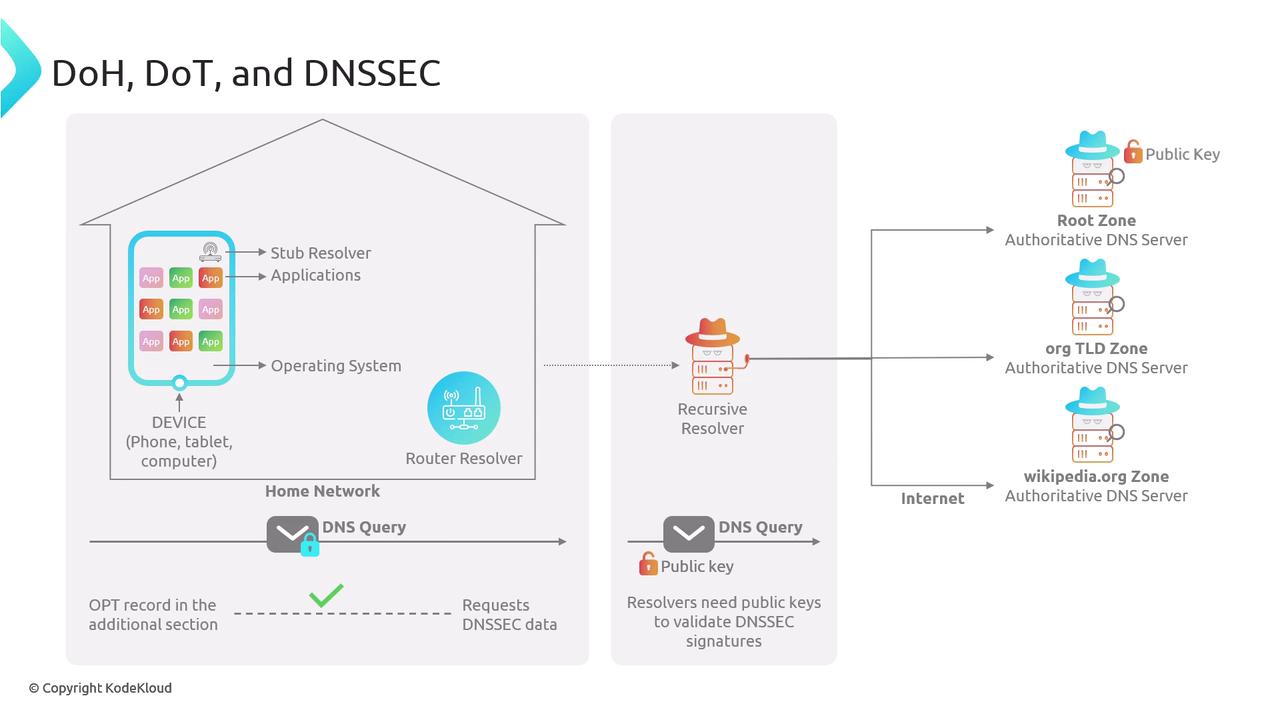
Using DIG with DNSSEC
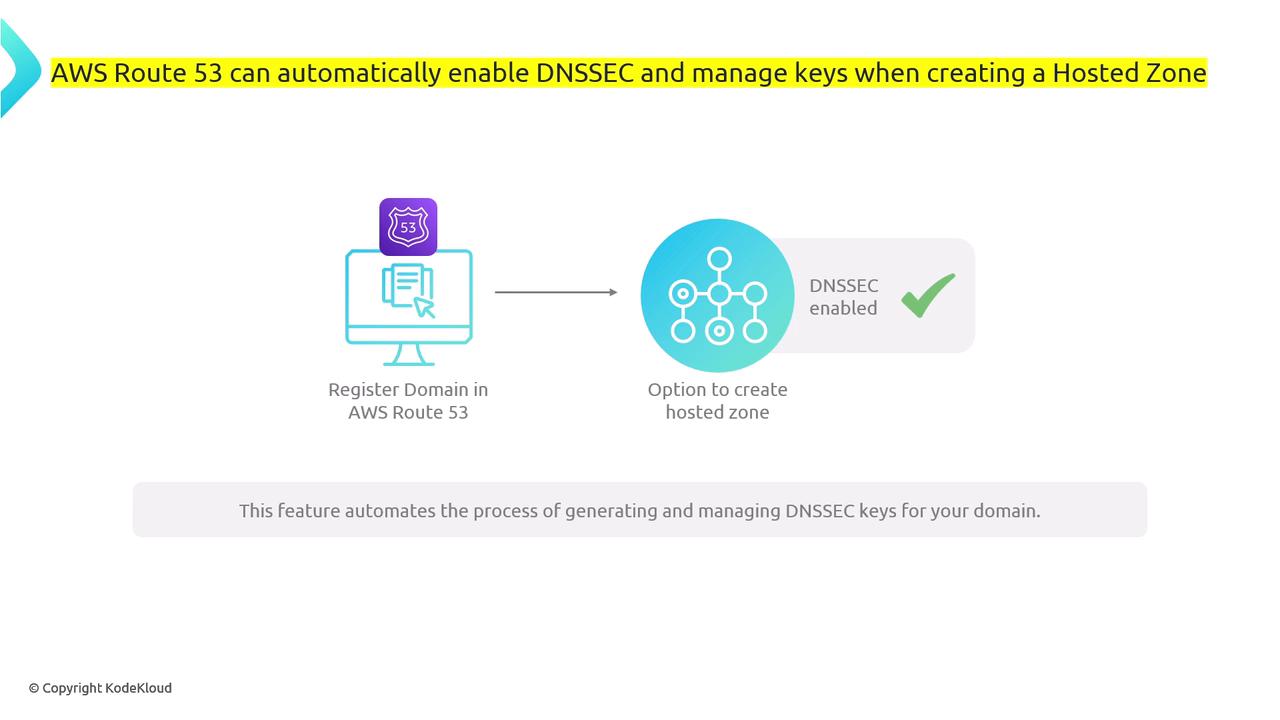
You can verify DNSSEC-enabled domains using the DIG command by adding the “+dnssec” flag. For example:AWS Route 53 offers integration with DNSSEC, allowing you to create hosted zones with automated DNSSEC key management. This automation simplifies processes like key generation, publication (via DNSKEY records), and resource record signing (with RRSIG records).
AWS Route 53 and DNSSEC Automation
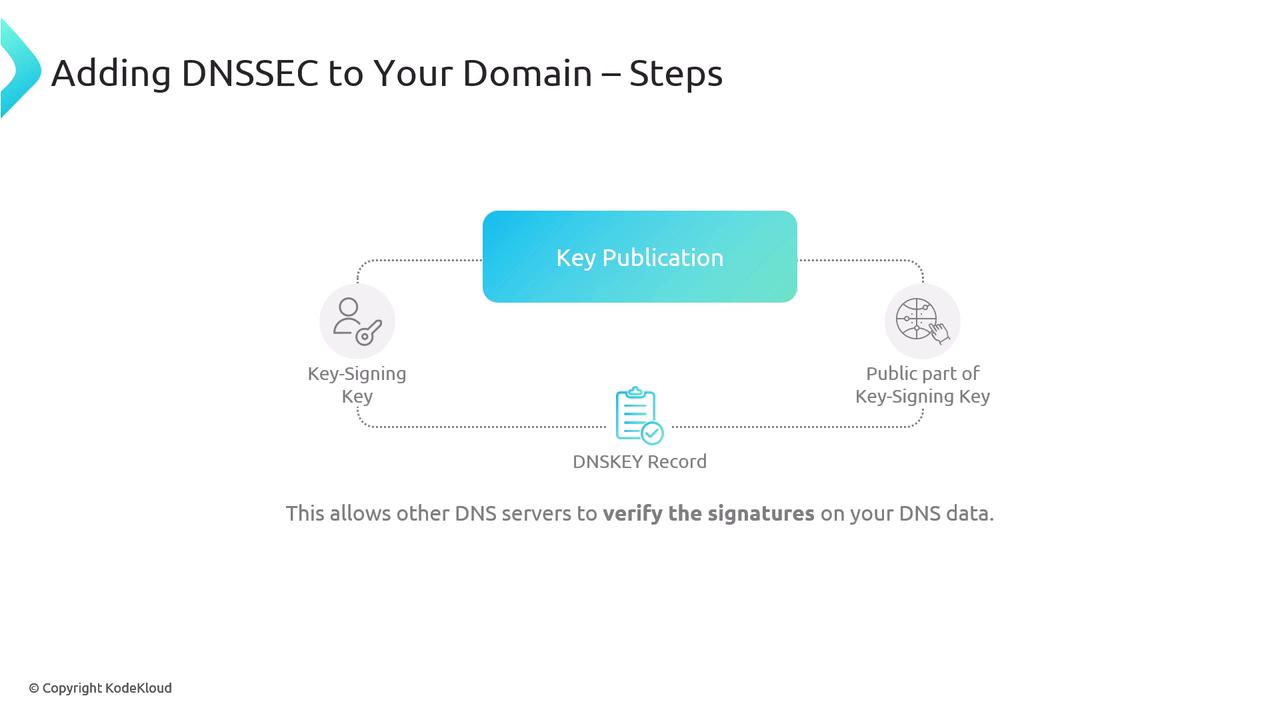
When DNSSEC is enabled with AWS Route 53, the process is largely automated:- Key Generation: New DNSSEC keys are generated for your domain.
- Key Publication: The public key is published as a DNSKEY record, enabling other servers to verify signatures.
- Data Signing: DNS resource records are signed digitally using a zone signing key; the digital signatures are stored in RRSIG records.
- Parent Zone Interaction: The parent zone or TLD is informed about the DNSSEC keys, establishing a trust chain from the root domain.
Summary
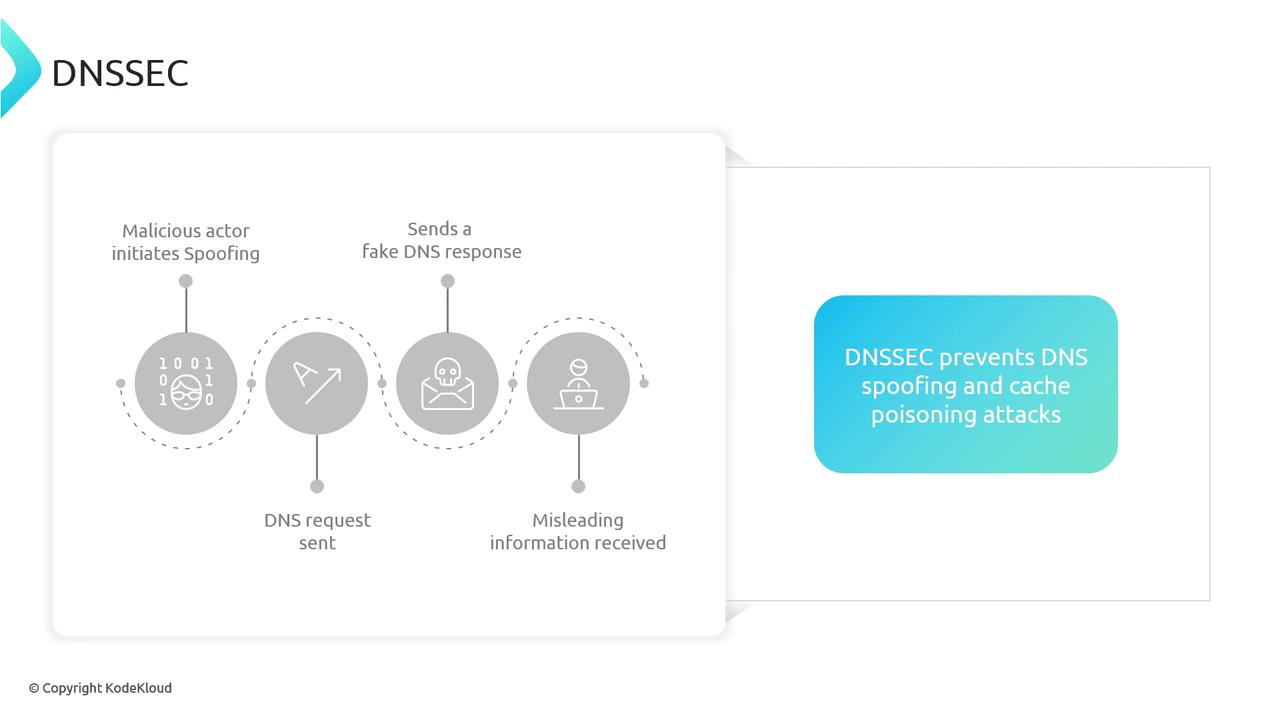
In summary, this article explains that:- DoT and DoH secure DNS communication by encrypting the data using TLS/HTTPS protocols.
- DNSSEC enhances DNS security by digitally signing DNS records, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of data, thereby defending against spoofing and cache poisoning attacks.
