What Is an Instance Group?
Instead of launching multiple virtual machines (VMs) independently, you can deploy them under a single instance group. This approach allows you to manage multiple VMs as one entity. When creating an instance group, you can configure essential parameters such as the desired number of VMs and set minimum and maximum limits for the group. Additionally, autoscaling rules can be defined to automatically add or remove VMs based on resource usage. For example, consider the following architecture: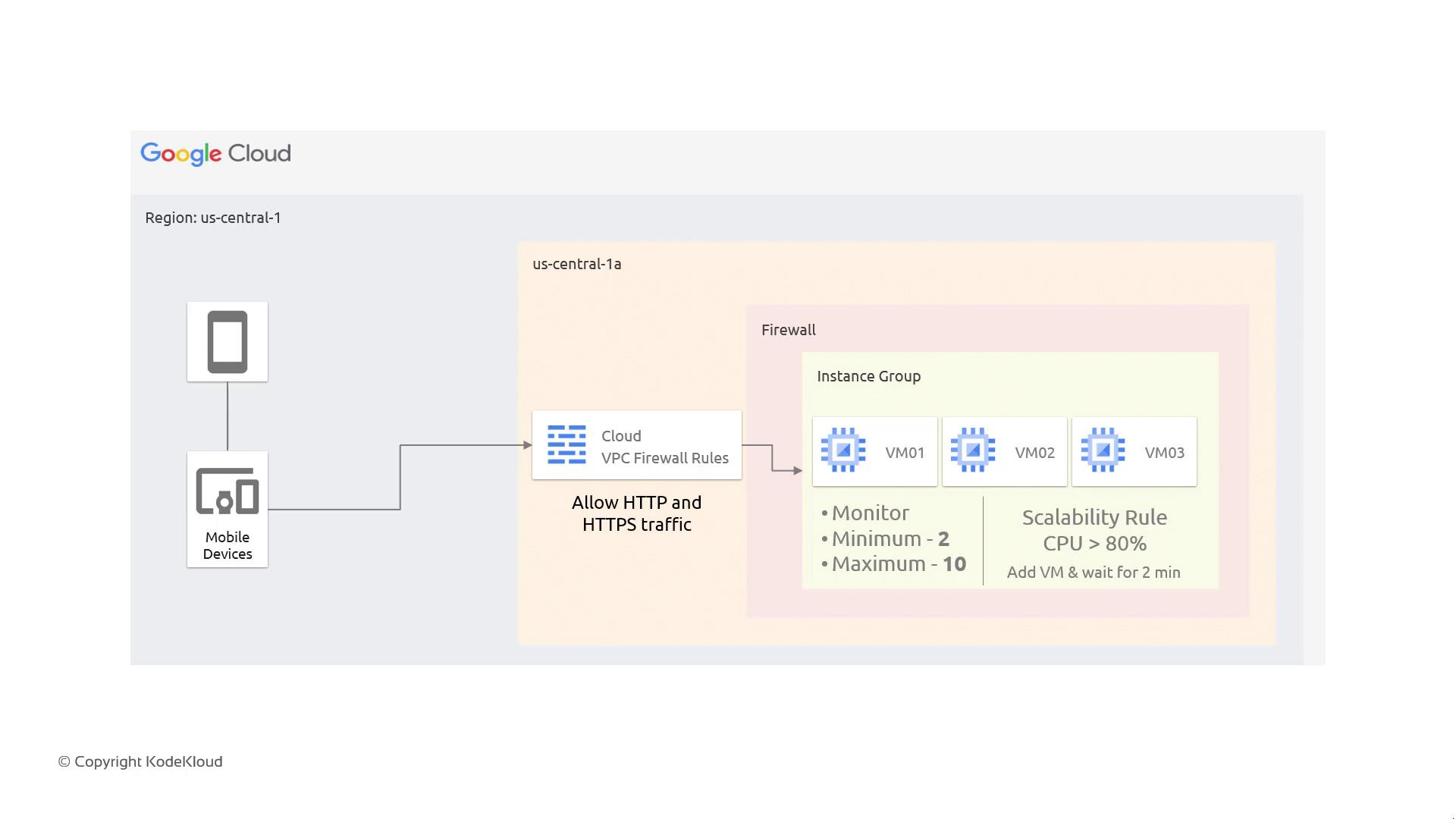
In application deployment, instance groups are invaluable. Deploy a new instance group, thoroughly test your software, and then seamlessly route traffic to the updated instances.
High Availability and Self-Healing
Relying on a single VM for high availability can be risky—if the VM fails, there’s no backup. Instance groups address this risk by automatically spinning up a replacement if a VM becomes unresponsive. Consider a scenario where an instance group comprises three VMs—VM01, VM02, and VM03. If VM01 fails, dropping the active count to two, the autoscaling mechanism detects this deficit and launches a replacement (e.g., VM04). The problematic VM is then marked as out of service, and the instance group self-heals to maintain the desired capacity.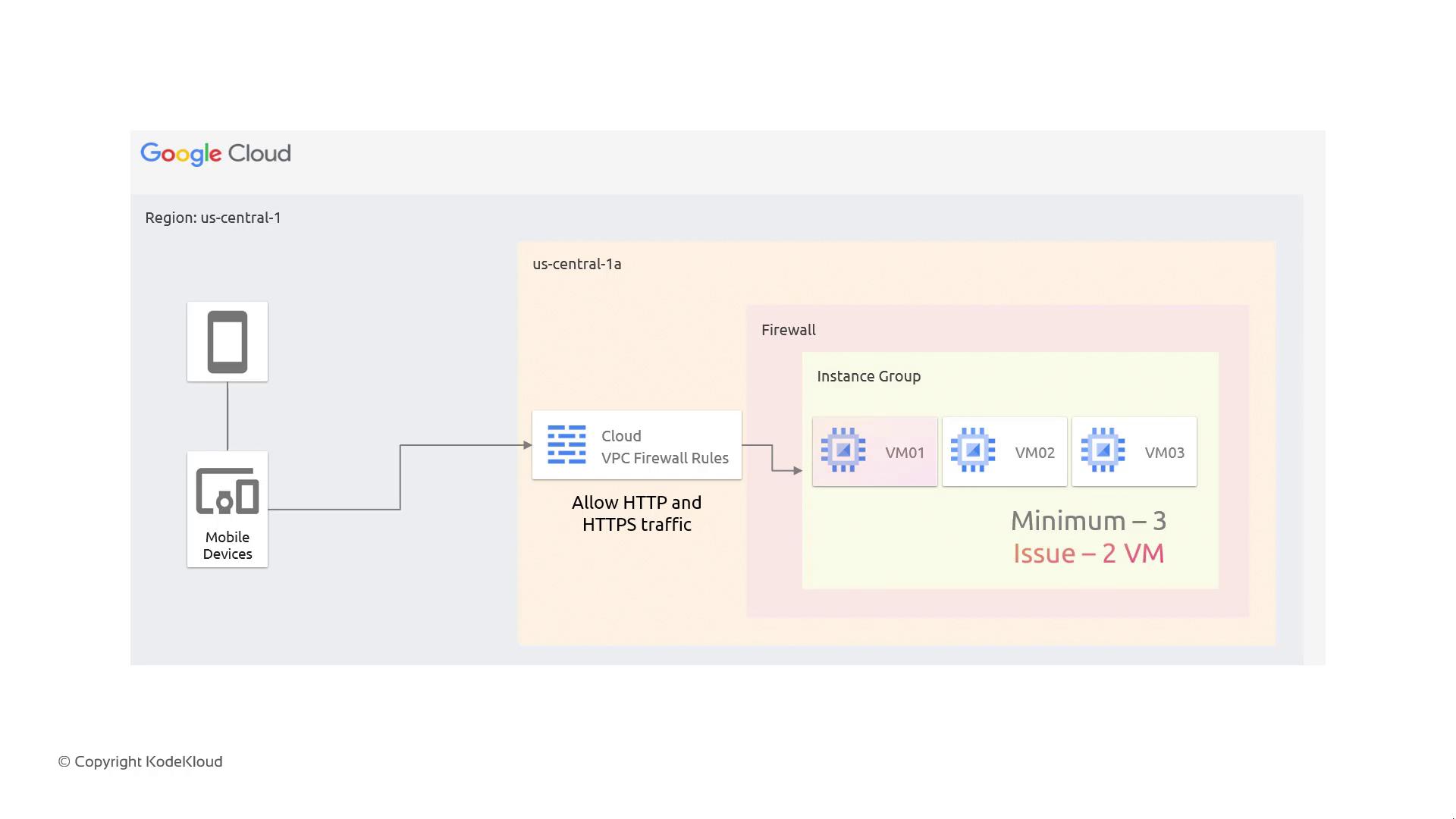
The ability of instance groups to self-heal minimizes downtime and reduces the need for manual intervention, ensuring continuous service availability.
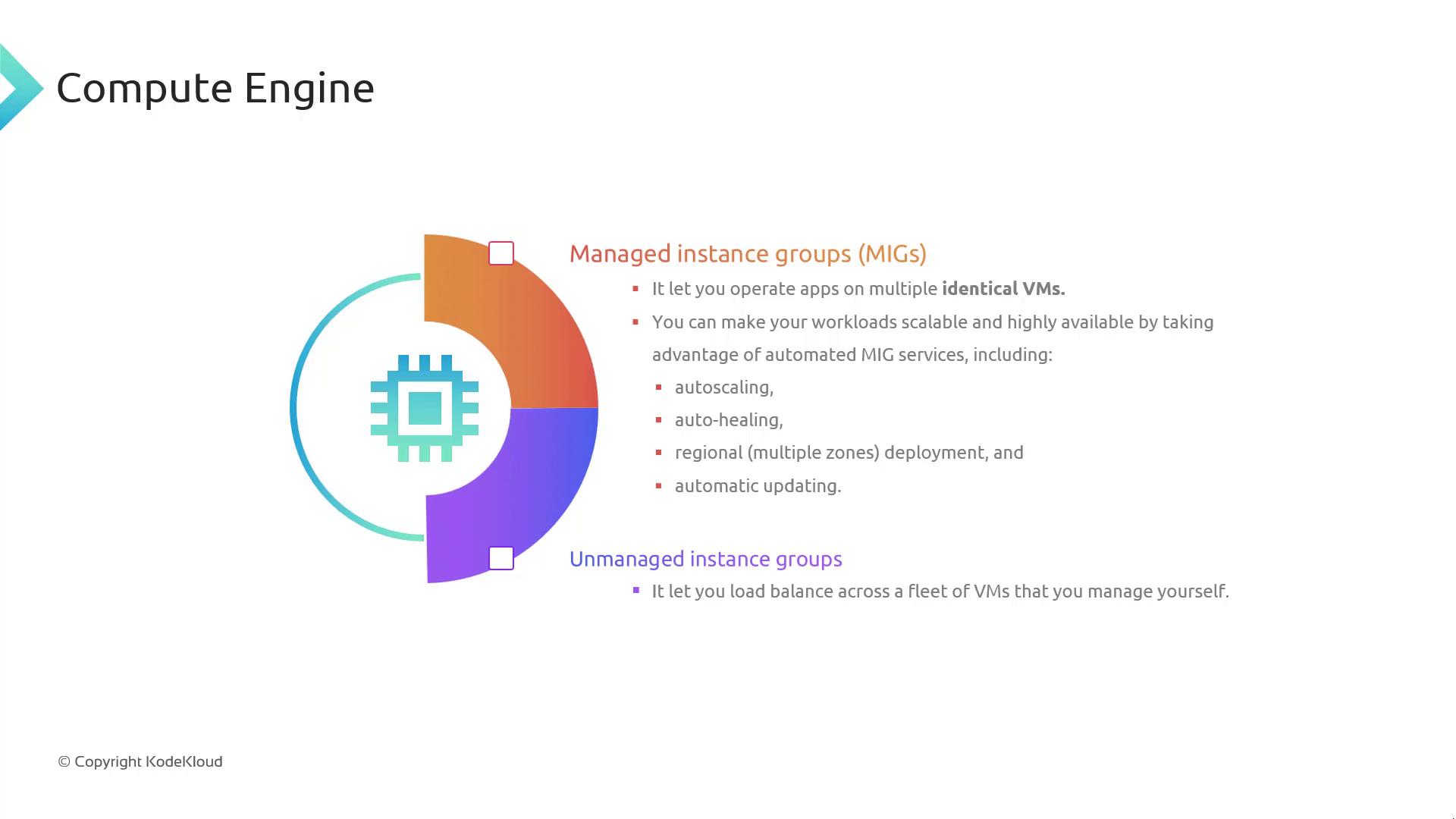
Types of Instance Groups
An instance group is a collective of VMs managed as a single entity. There are two primary types:
-
Managed Instance Groups:
These groups consist of identical VMs that are automatically created and maintained. Features such as autoscaling, automated updates, self-healing, and high availability make Managed Instance Groups ideal for production environments. -
Unmanaged Instance Groups:
In unmanaged instance groups, VMs are created independently and require separate management. Lacking built-in autoscaling and self-healing capabilities, they are less suited for scenarios where high availability and scalability are critical.