Architectural Overview
The architecture employs multiple GCP services to ensure efficient log processing:-
Microservice Deployment:
The microservice is deployed using container-based platforms such as Kubernetes or Cloud Run. -
Log Collection and Storage:
Logs generated by the microservice are captured and stored using one of two methods:- Batch Mode: Logs are periodically saved to a Cloud Storage bucket.
- Real-Time Streaming: Logs are streamed directly to Pub/Sub for immediate processing.
-
Log Processing and Aggregation:
Dataflow processes the log data by aggregating events and extracting valuable insights. For example, it can:- Count the number of errors.
- Filter logs by specific IP addresses.
-
Data Analysis and Reporting:
The processed and enriched log data is then stored in BigQuery, which serves as a powerful platform for detailed analysis and reporting.
Leveraging GCP’s integrated services not only optimizes resource usage but also improves the scalability and reliability of log processing environments.
Log Processing Workflow Diagram
Below is the diagram that illustrates the complete flow of log processing—from the microservice generating logs to the final analytics in BigQuery: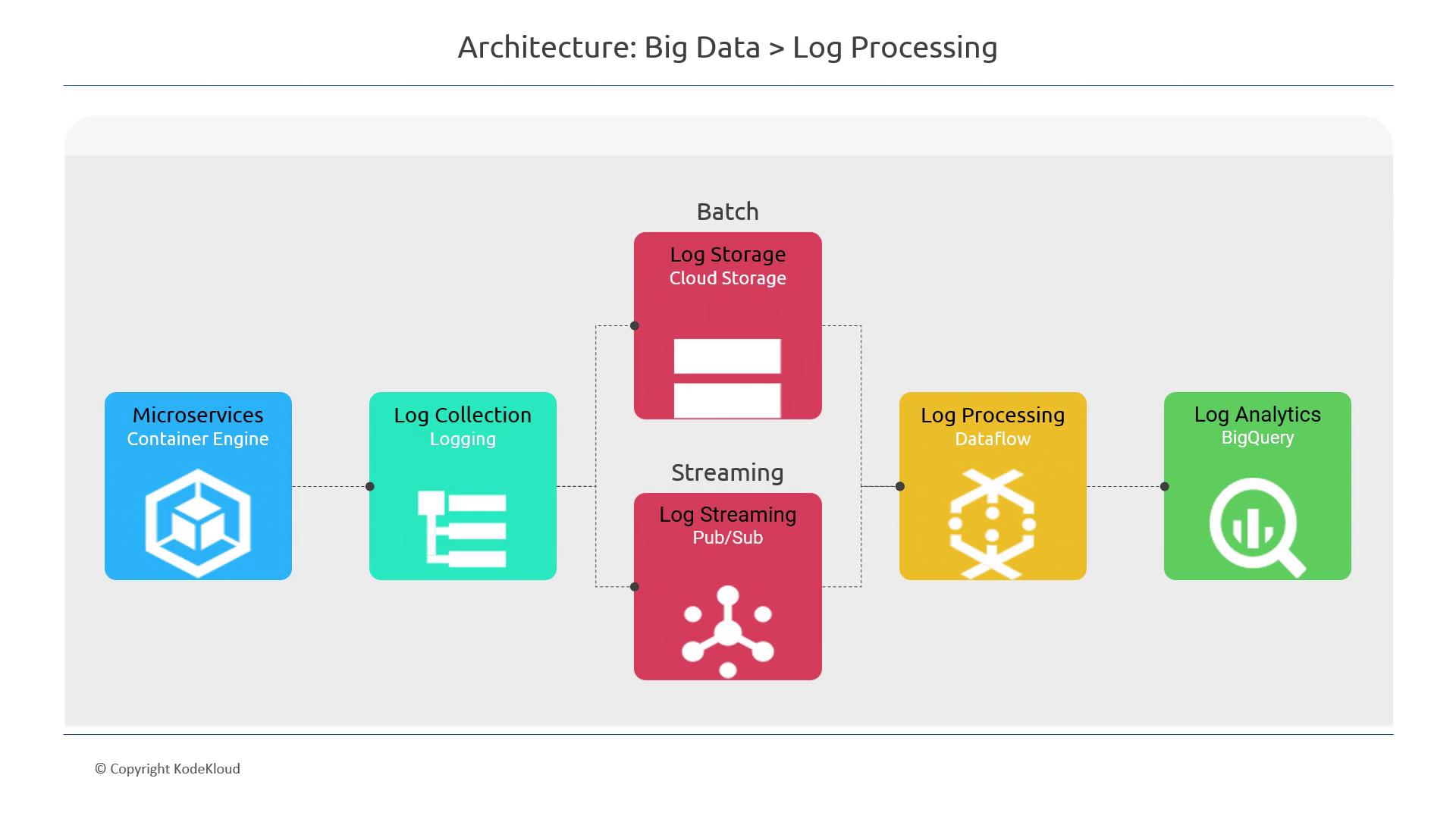
Scaling and Enterprise Considerations
In complex organizations, such as those in the pharmaceutical industry, hundreds of microservices may be deployed concurrently. Consolidating logs into a centralized repository is crucial for:- Performing comprehensive analytics.
- Detecting and mitigating security threats.
- Deriving meaningful metrics for a holistic view of the operational ecosystem.
When designing a multi-microservice architecture, ensure that the centralized log management system is scalable and secure, as failures or breaches can impact downstream analytics and reporting.