- What is Encryption in S3?
- Client-Side vs. Server-Side Encryption
- Server-Side Encryption Methods (SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C)
- Per-Object Encryption and Bucket Defaults
- Practical Code Examples for Each SSE Method
What Is Encryption?
Encryption transforms readable data (plaintext) into unreadable ciphertext using cryptographic keys. Only holders of the correct key can decrypt the data. In Amazon S3, encryption happens at two layers:- In transit: Secured by SSL/TLS between your client and S3.
- At rest: Data stored on AWS servers is encrypted on disk.
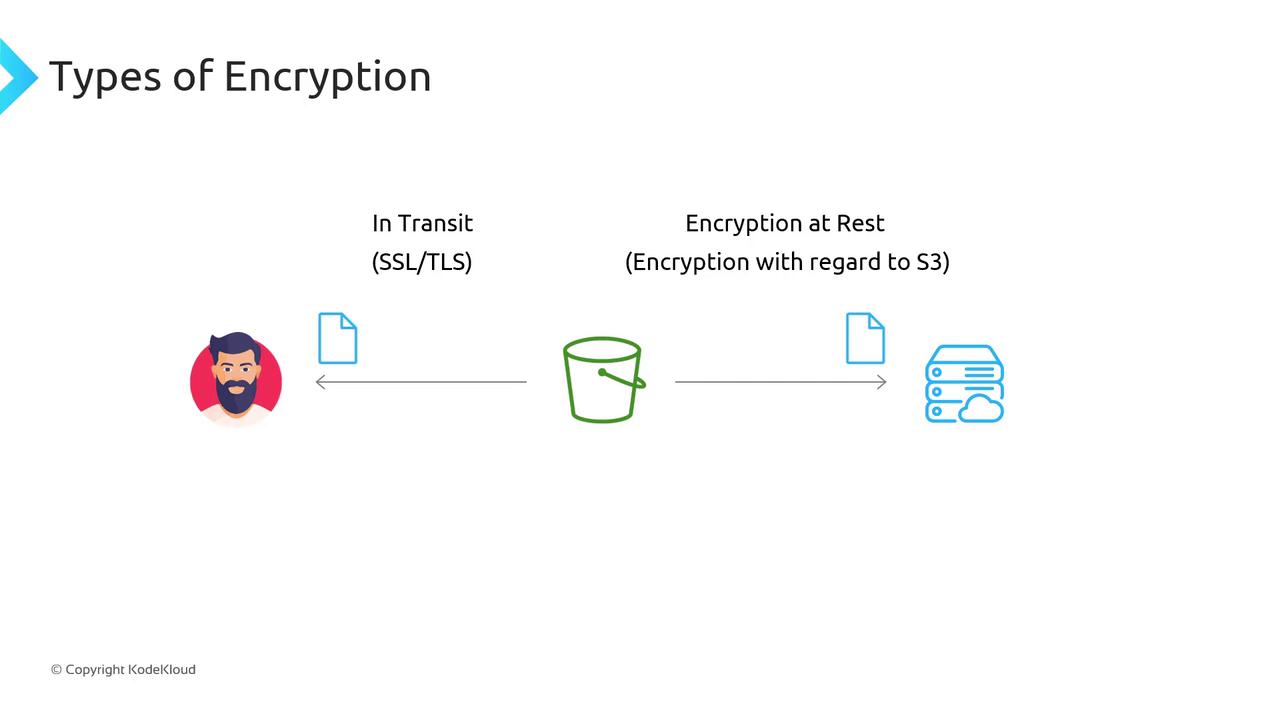
- In transit: Automatic over HTTPS (SSL/TLS).
- At rest: Must be enabled so S3 stores your objects encrypted on disk.
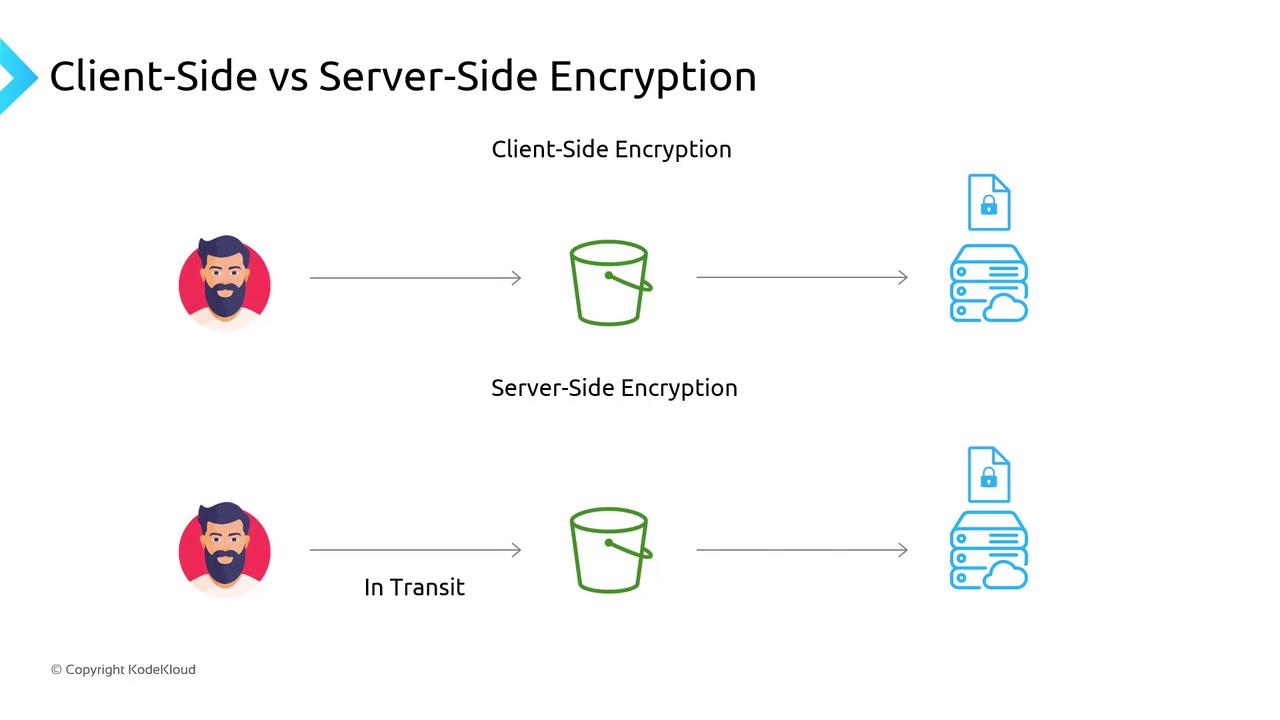
Client-Side vs. Server-Side Encryption
- Client-Side Encryption: You generate, manage, and store keys. You encrypt data locally, then upload only ciphertext to S3.
- Server-Side Encryption: You send plaintext over HTTPS; AWS encrypts it at rest using the method you choose.

Per-Object Encryption and Bucket Defaults
- Encryption is configured per object.
- You can set a default encryption on the bucket so that any upload without explicit encryption uses the bucket’s setting.
- You can still override the default on a per-object basis.

When you enable default encryption on a bucket, uploads without specified encryption inherit the bucket’s default settings.
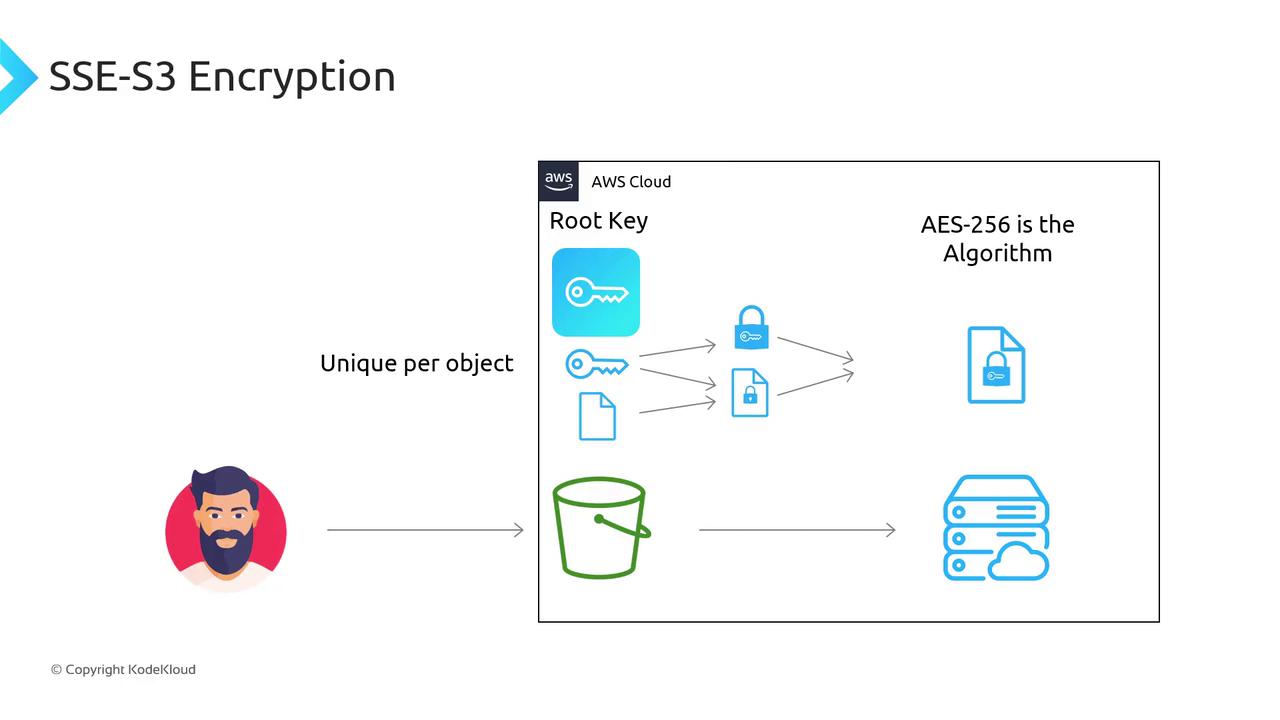
SSE-S3 (Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys)
With SSE-S3, AWS handles all key management using AES-256:- Key generation & management: AWS
- Encryption algorithm: AES-256
- Responsibilities: AWS S3
- AWS maintains a master root key (opaque to you).
- For each object, S3 generates a unique data key.
- The object is encrypted with the data key (AES-256).
- The data key is encrypted with the root key.
- Both encrypted object and encrypted data key are stored.
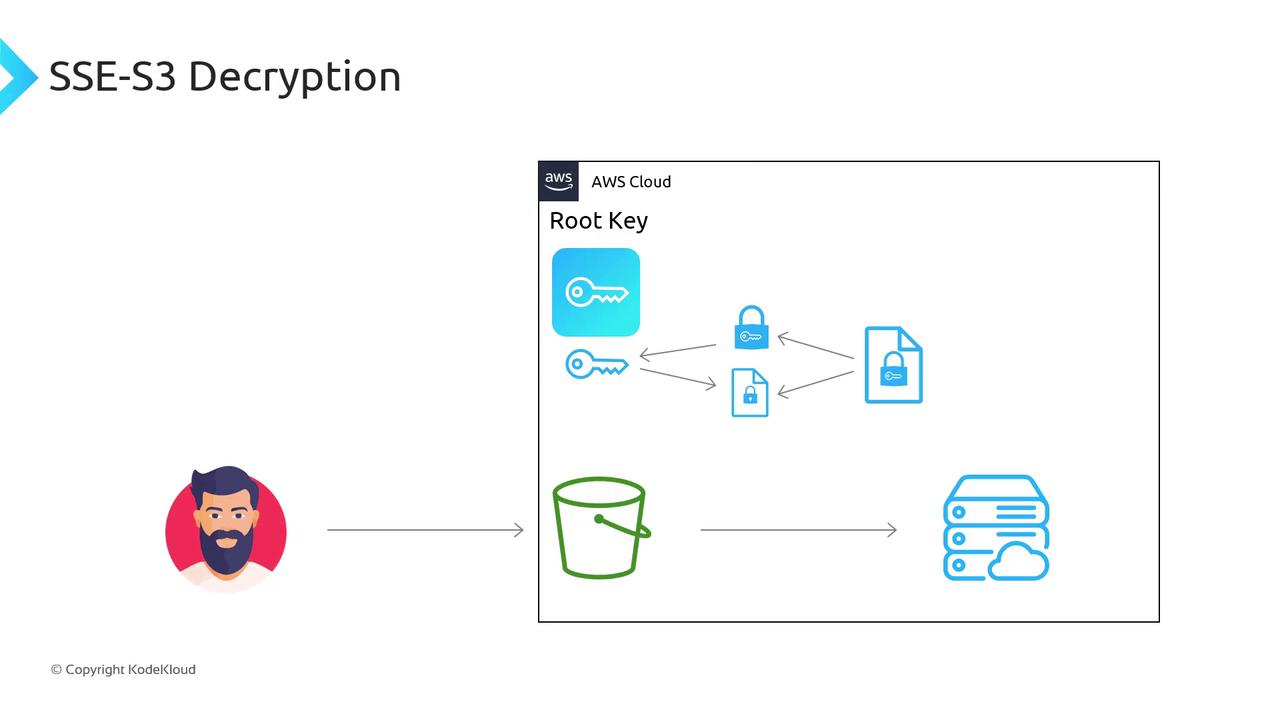
- S3 decrypts the data key using the root key.
- S3 decrypts your object with the data key.
- Plaintext is returned to you.
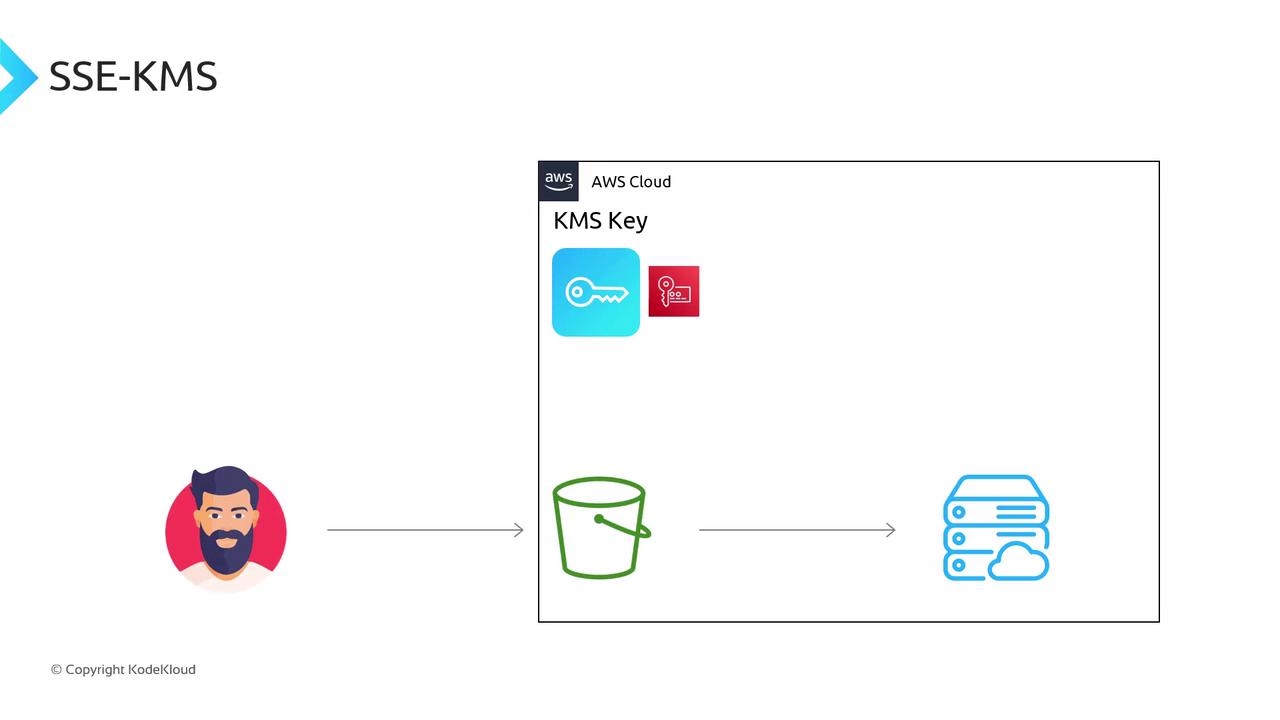
SSE-KMS (Server-Side Encryption with AWS KMS Keys)
SSE-KMS integrates AWS Key Management Service for advanced control:- Key management: AWS KMS
- Encryption/decryption: AWS KMS invoked by S3
- Features: Key policies, automatic rotation, CMK metadata
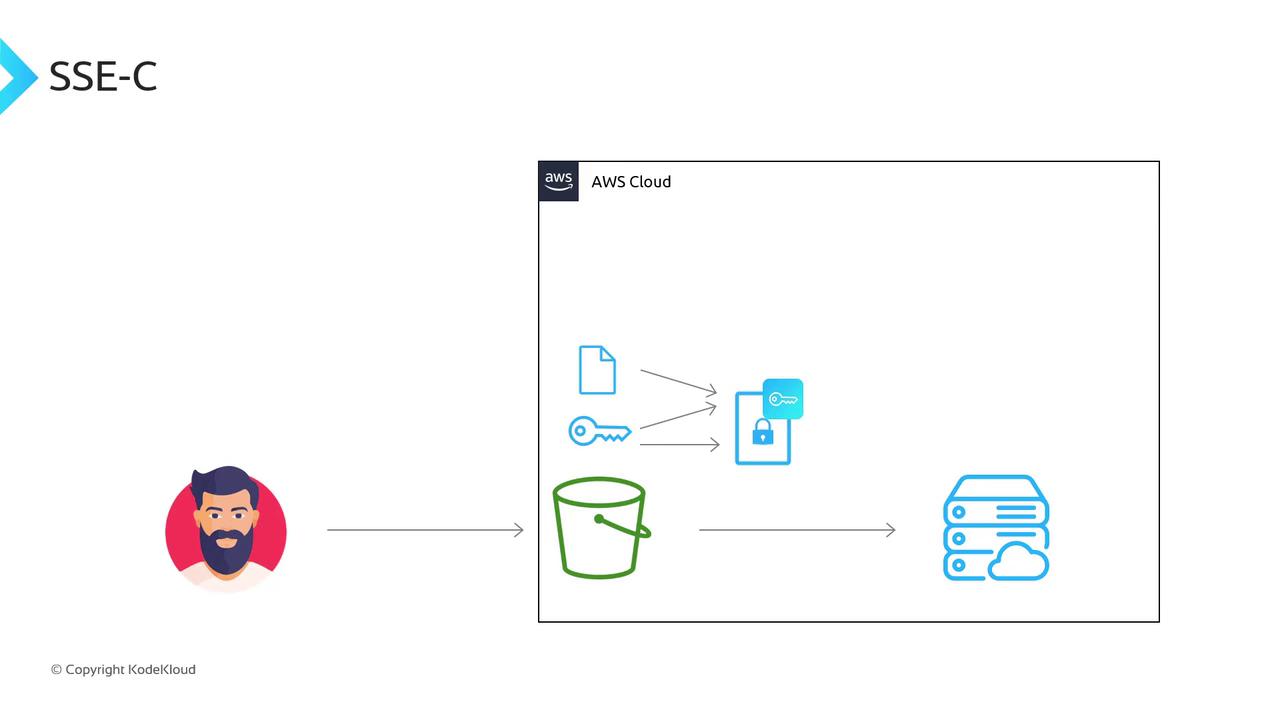
SSE-C (Server-Side Encryption with Customer-Provided Keys)
With SSE-C, you provide the encryption key on each request:- Key management: Client
- Encryption/decryption: S3
- S3 stores only the MD5 hash of your key for verification
x-amz-server-side-encryption-customer-algorithm: AES256x-amz-server-side-encryption-customer-key: <Base64-encoded key>x-amz-server-side-encryption-customer-key-MD5: <Base64-encoded MD5 of key>
AWS does not store your customer-provided key. If you lose the key, your data cannot be decrypted.
Encryption Headers and Comparison Summary
Below is a quick reference of S3 server-side encryption headers:
| Encryption Method | Key Management | Encryption/Decryption |
|---|---|---|
| Client-Side | Client | Client |
| SSE-C | Client | S3 |
| SSE-S3 | AWS S3 | AWS S3 |
| SSE-KMS | AWS KMS | AWS S3 / AWS KMS |
