AKS Autoscaling Components
AKS provides two core autoscaler types to ensure your workloads have the right resources:| Autoscaler | Purpose | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Cluster Autoscaler | Adds or removes nodes based on unschedulable pods and node utilization | Node pool level |
| Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) | Adjusts pod replica count based on real-time CPU/memory metrics | Deployment/ReplicaSet level |
Cluster Autoscaler
The Cluster Autoscaler watches for pending pods that cannot be scheduled due to insufficient node capacity. When required, it scales out the node pool by adding new VMs. Conversely, when nodes are underutilized, it can remove nodes after cordoning and draining them.If you set both the minimum and maximum node count to the same value, the Cluster Autoscaler cannot expand or shrink your node pool.
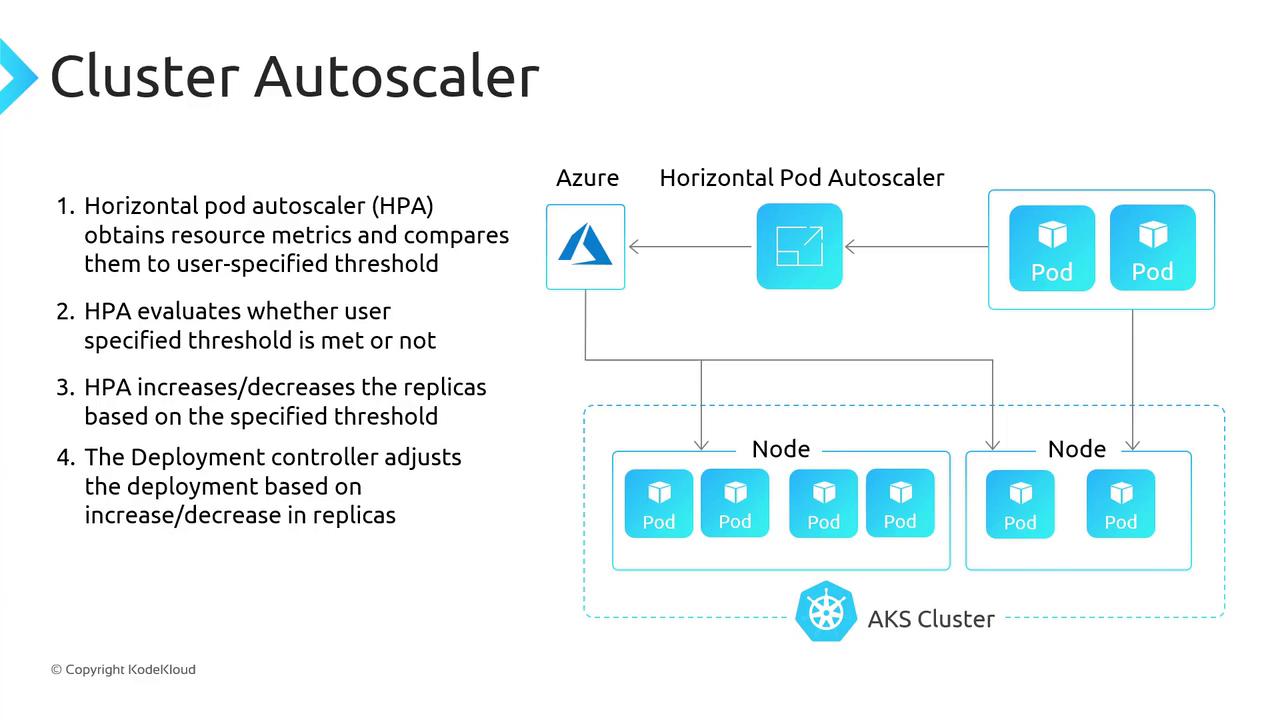
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA)
The HPA relies on the Kubernetes Metrics Server to monitor pod resource usage (CPU, memory, custom metrics, etc.). When usage crosses user-defined thresholds, HPA automatically increases or decreases the number of pod replicas.How HPA Works
- Polls metrics every 60 seconds by default.
- Retrieves current resource usage from the Metrics Server.
- Compares usage against your target thresholds.
- Adjusts the replica count via the deployment controller.
You can customize the HPA polling interval and thresholds in your
HorizontalPodAutoscaler manifest.Manually Scaling the AKS Node Pool
Since our Cluster Autoscaler is locked to a fixed node count (1–1), we’ll use Azure CLI to increase the pool to two nodes.1. Verify System Pods
Run the following commands to confirm that system components are healthy:2. Scale the Node Pool
Useaz aks scale to adjust the node count:
3. Confirm Two Ready Nodes
After scaling, verify the node count:Ready state.