Storing configurations in Git allows teams to effortlessly rollback to a previous state and maintain a complete audit trail for all changes.
Automated CI/CD and Continuous Deployment
CI/CD automation is a cornerstone of GitOps. By leveraging automation:- Building, testing, and deployment tasks are triggered automatically based on the desired state stored in Git.
- Continuous deployment becomes seamless and consistent, as applications are deployed automatically to clusters without manual intervention.
Extending GitOps to Infrastructure and Cluster Resources
Once GitOps is established for application deployment, extend these practices to manage both cluster resources and Infrastructure as Code. For instance, in Kubernetes environments, you can manage various resources including:- Secrets management
- Networking agents and service mesh configurations
- Database provisioning
- Prometheus monitoring
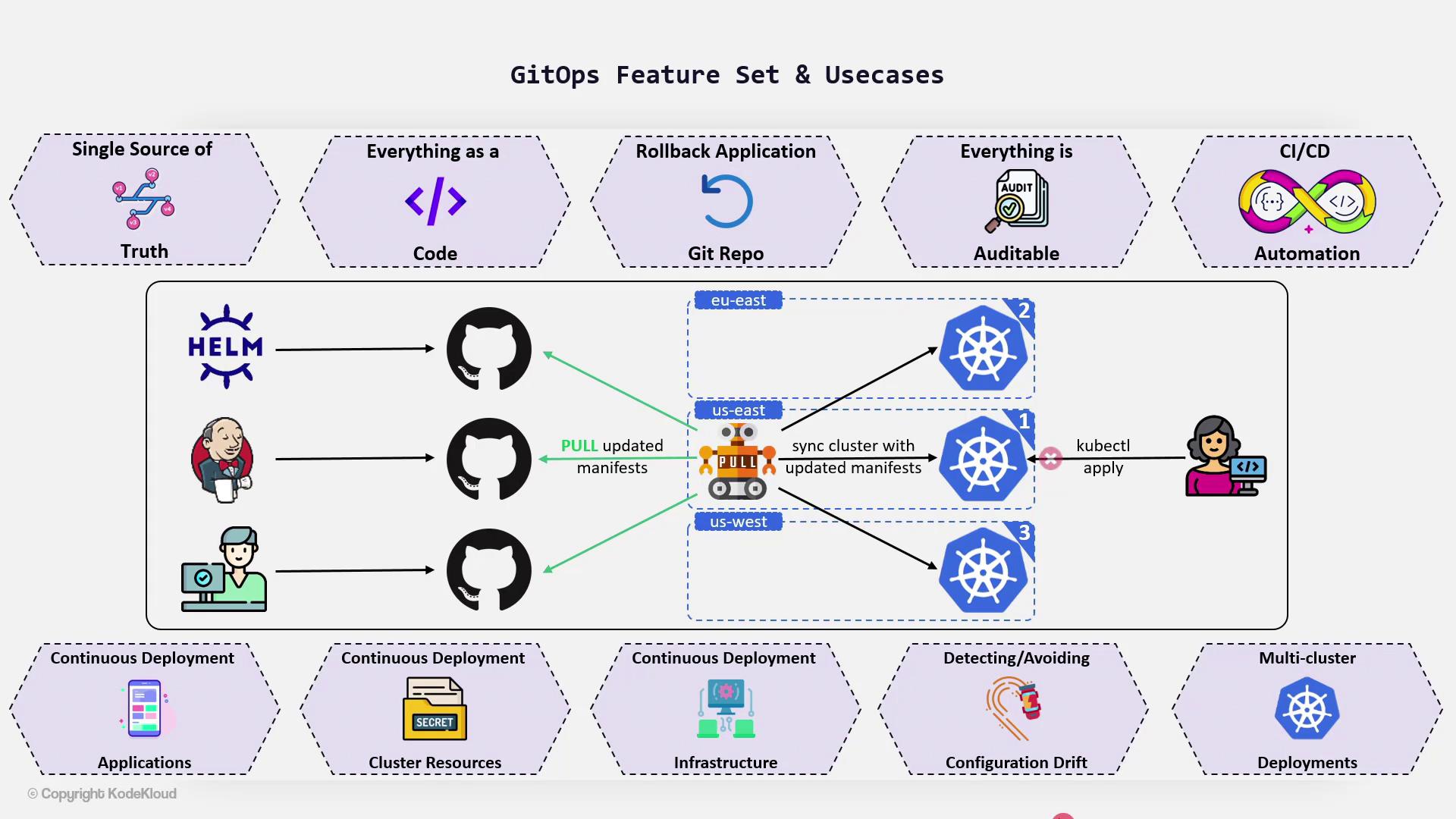
GitOps continuously compares Git’s desired state against the actual runtime state and reverts any drift, maintaining alignment across your infrastructure.
Detecting and Preventing Configuration Drift
Early detection of configuration drift is a fundamental aspect of GitOps. Identifying drift as soon as it happens allows teams to resolve inconsistencies before they evolve into significant issues. This proactive stance distinguishes GitOps from other deployment methodologies.Multi-Cluster Deployment Made Easy
Managing multiple clusters, especially across different geographical locations, can be challenging. GitOps simplifies this process by centralizing cluster state within Git. This means:- A single operator can deploy applications across multiple clusters.
- There is no need to install or set up the operator individually on each cluster.
- The deployment process is streamlined and significantly more efficient.