- What cert-manager is and how to install it.
- An introduction to Let’s Encrypt and its ACME workflow.
- How to integrate cert-manager with Let’s Encrypt for automatic certificate issuance and renewal.

What Is cert-manager?
cert-manager is an open-source Kubernetes add-on that automates the issuance, renewal, and management of TLS certificates. It supports multiple issuers—such as Let’s Encrypt, HashiCorp Vault, and self-signed certificates—and integrates seamlessly with Kubernetes resources like Ingress. Key features include:- Automated certificate requests & renewals
- Support for standard, wildcard, and self-signed certificates
- Kubernetes-native CRDs: Issuer, ClusterIssuer, and Certificate
- Secrets storage for TLS key/cert pairs
cert-manager Architecture
cert-manager runs as a set of controllers that watch CRDs and reconcile the desired certificate state. Each controller interacts with the Kubernetes API to request, store, and renew certificates.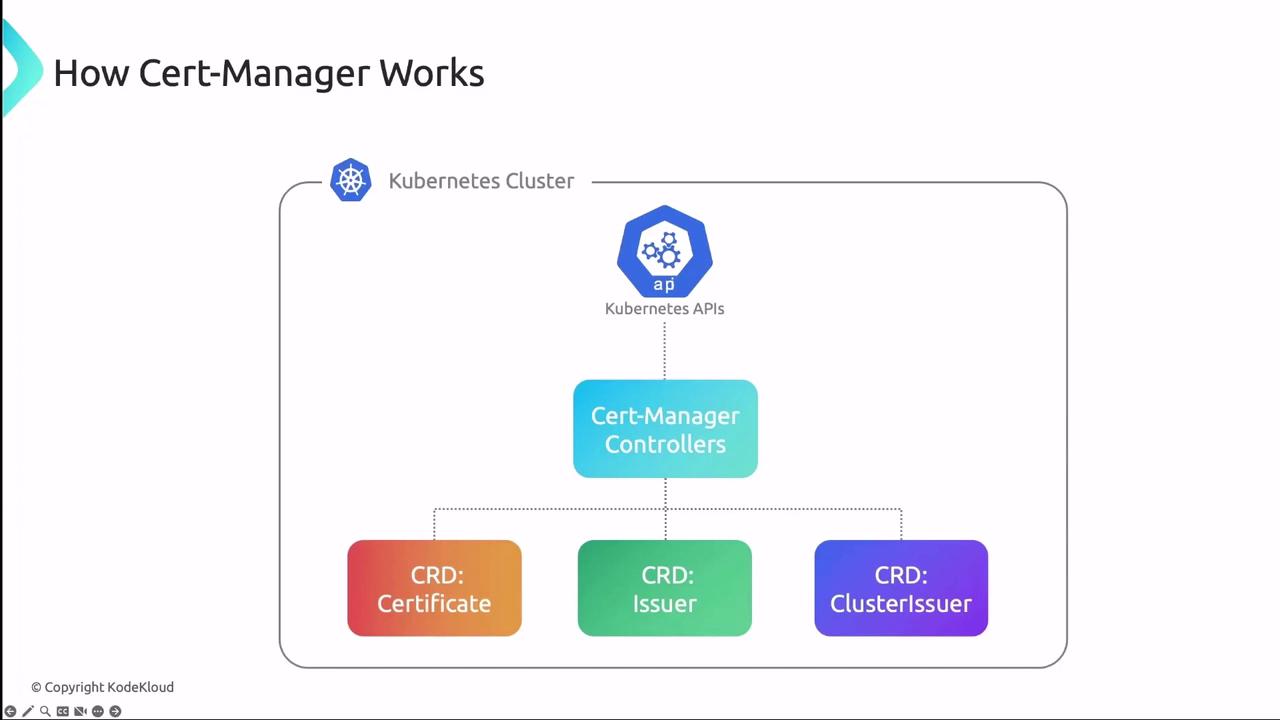
| CRD | Scope | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Namespaced | Defines how to request certificates within a namespace |
| ClusterIssuer | Cluster | Defines certificate requests at the cluster level |
| Certificate | Namespaced | Specifies desired certificate, secret name, and DNS |
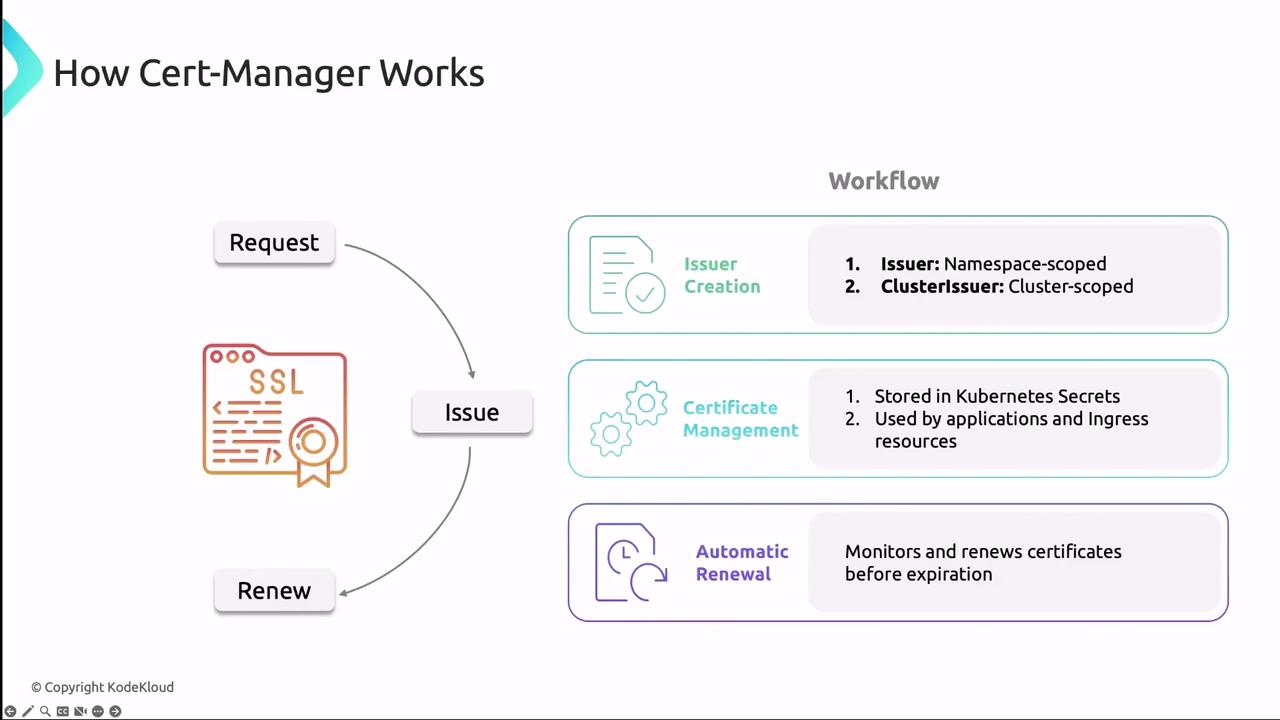
cert-manager can issue both standard and wildcard certificates. Use wildcard certificates to secure multiple subdomains with a single certificate.
Installing cert-manager
The easiest way to install cert-manager and its CRDs is with Helm:kubectl:
Always match the
<VERSION> placeholder with the latest stable release from the cert-manager GitHub releases.cmctl:
Let’s Encrypt Overview
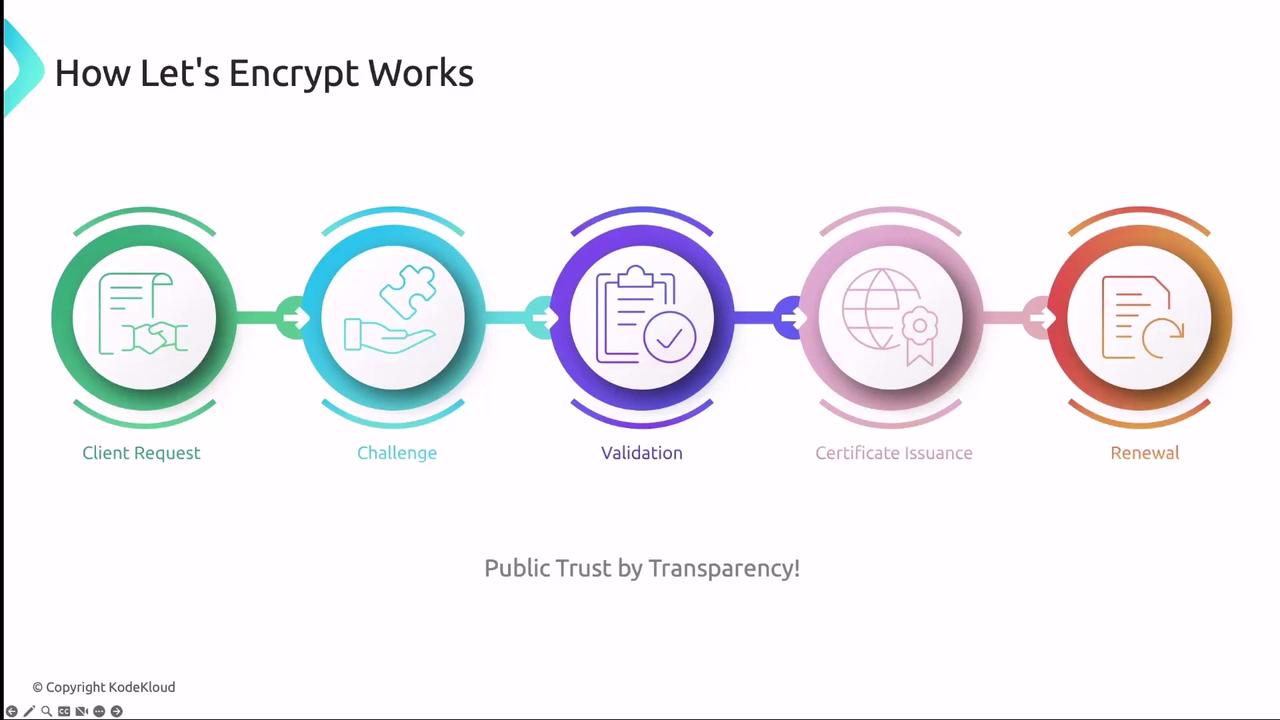
Let’s Encrypt is a free, automated, and open certificate authority (CA) that uses the ACME protocol to issue SSL/TLS certificates. It empowers Kubernetes users to secure applications without manual certificate provisioning.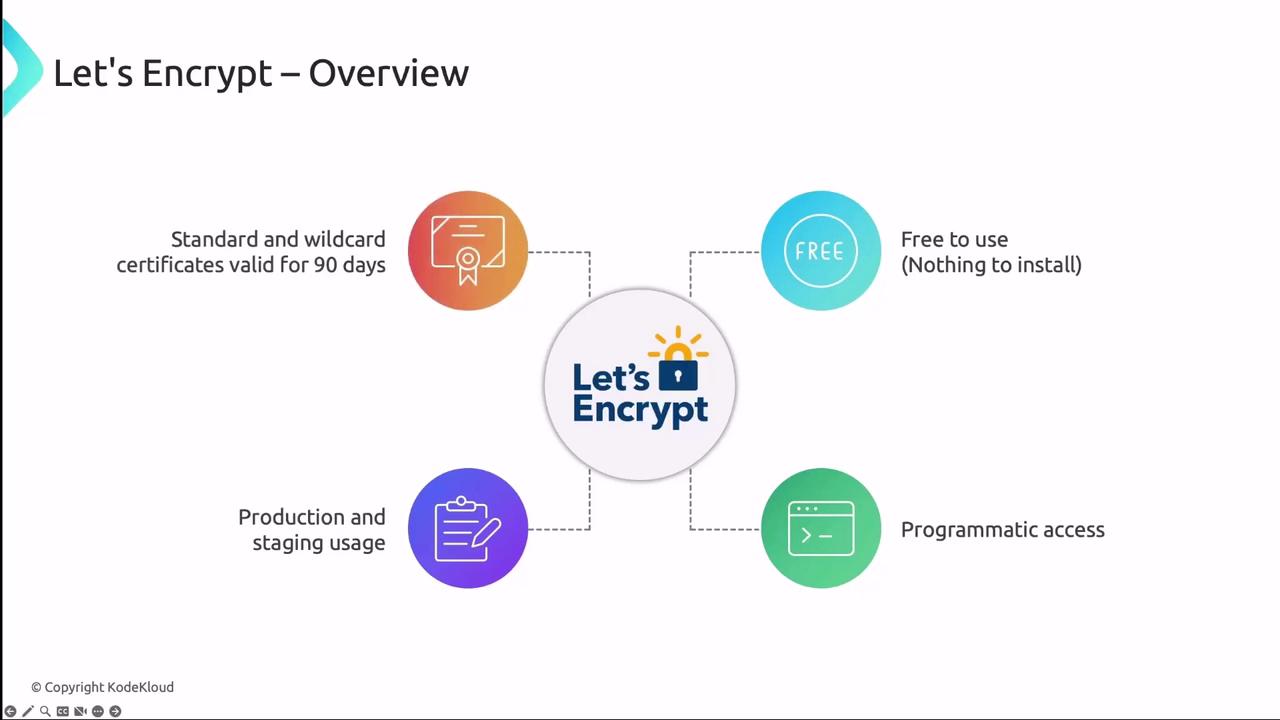
- Certificates are valid for 90 days.
- Offers Production and Staging endpoints.
- ACME challenges: HTTP-01 or DNS-01.
- Publicly logged for transparency.
| Environment | ACME Endpoint | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Staging | https://acme-staging-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory | Testing automation workflows |
| Production | https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory | Live environments |
- Client generates a key pair and creates a
CertificateRequest. - Let’s Encrypt returns an HTTP-01 or DNS-01 challenge.
- Client fulfills the challenge by serving a token or adding a DNS record.
- After validation, Let’s Encrypt issues the certificate.
- Client fetches and stores the certificate in Kubernetes.
Integrating cert-manager with Let’s Encrypt
To use Let’s Encrypt as your certificate authority, define an Issuer or ClusterIssuer in cert-manager: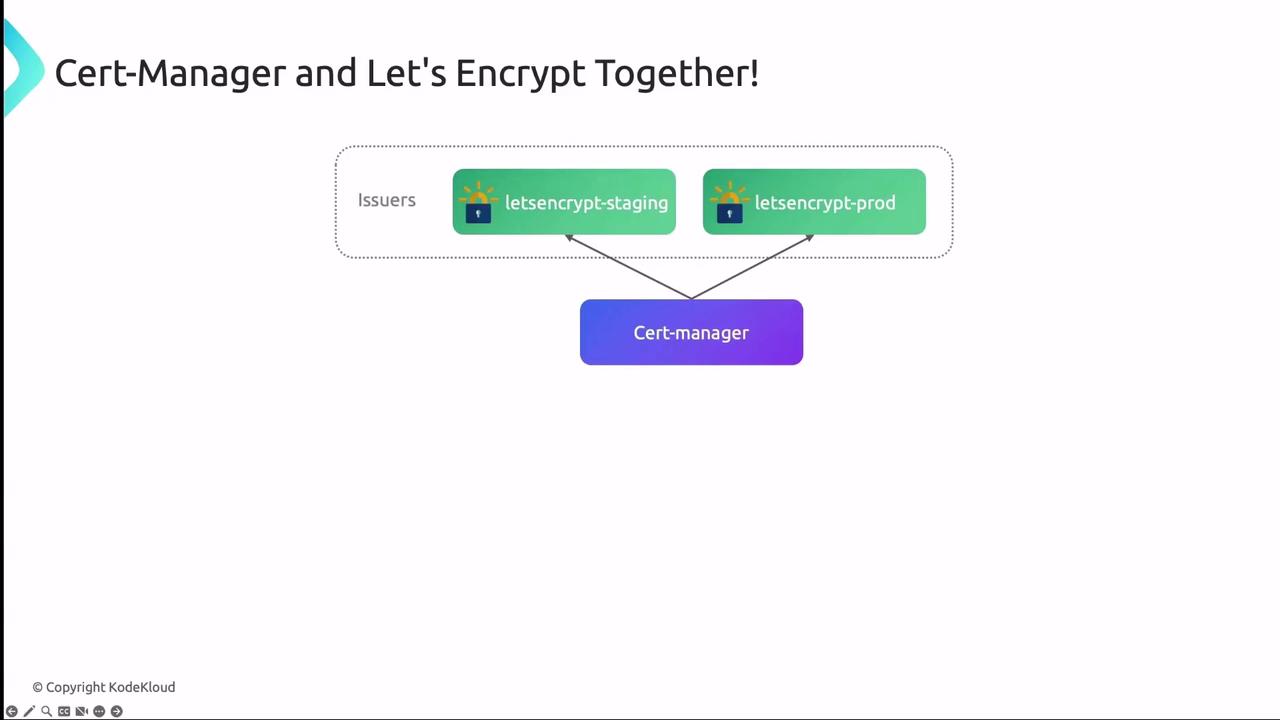
Example: Staging Issuer
When moving to production, update the
server URL to the production ACME endpoint and rename secrets accordingly.Configuring Kubernetes Ingress
Annotate your Ingress resource to reference the Issuer and specify TLS settings:web-tls Secret. Certificates are renewed automatically before expiration.