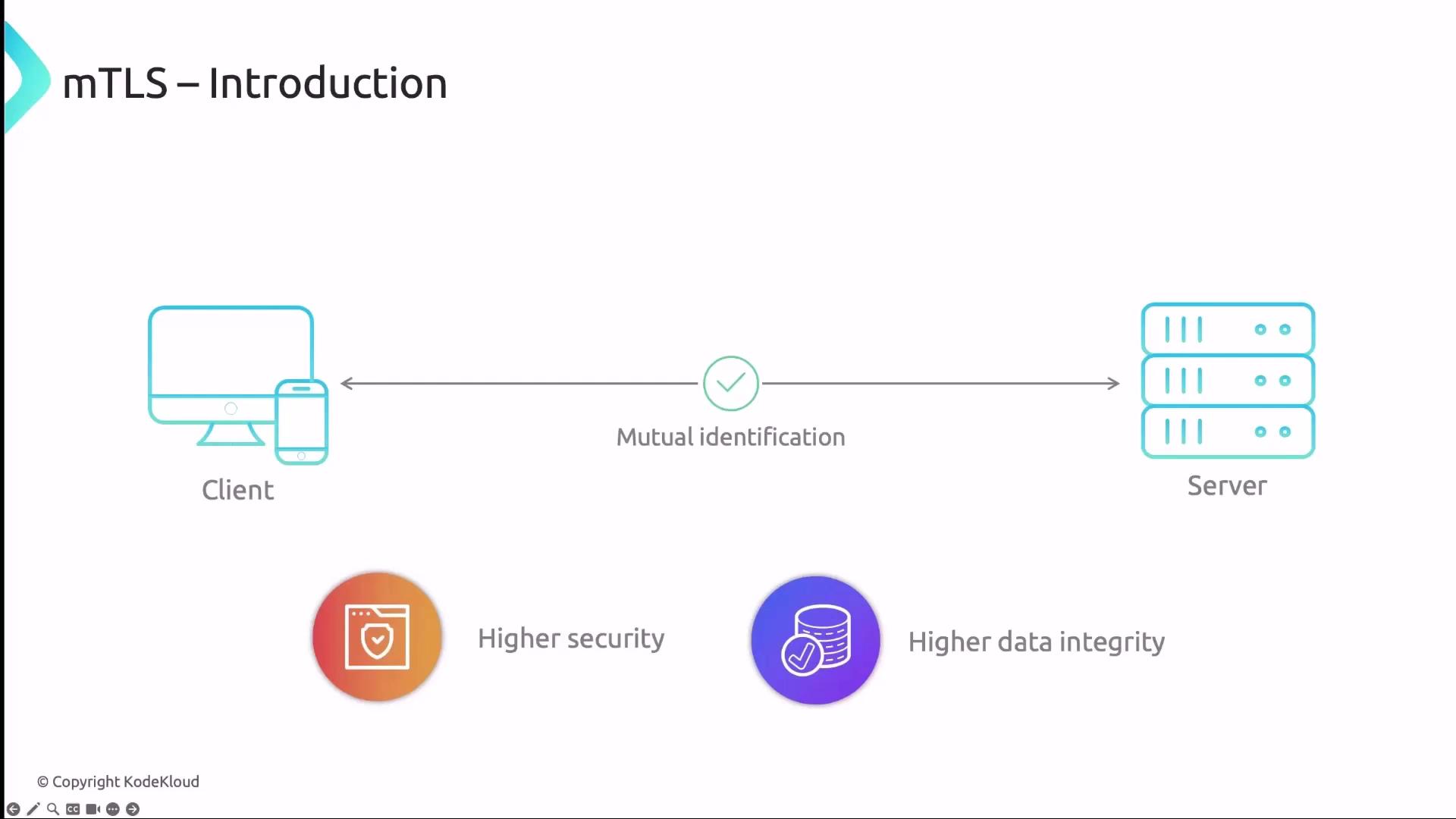
What Is mTLS?
Mutual TLS (mTLS) is an extension of standard TLS that enforces authentication for both client and server using X.509 certificates. In a traditional TLS handshake:- Client sends a Client Hello.
- Server responds with a Server Hello and presents its certificate.
- Client verifies the server’s certificate.
- Client sends its own certificate to the server.
- Server verifies the client’s certificate.
Before deploying mTLS, ensure you have a Certificate Authority (CA) in place. Tools like Cert-Manager can automate certificate issuance, rotation, and revocation.
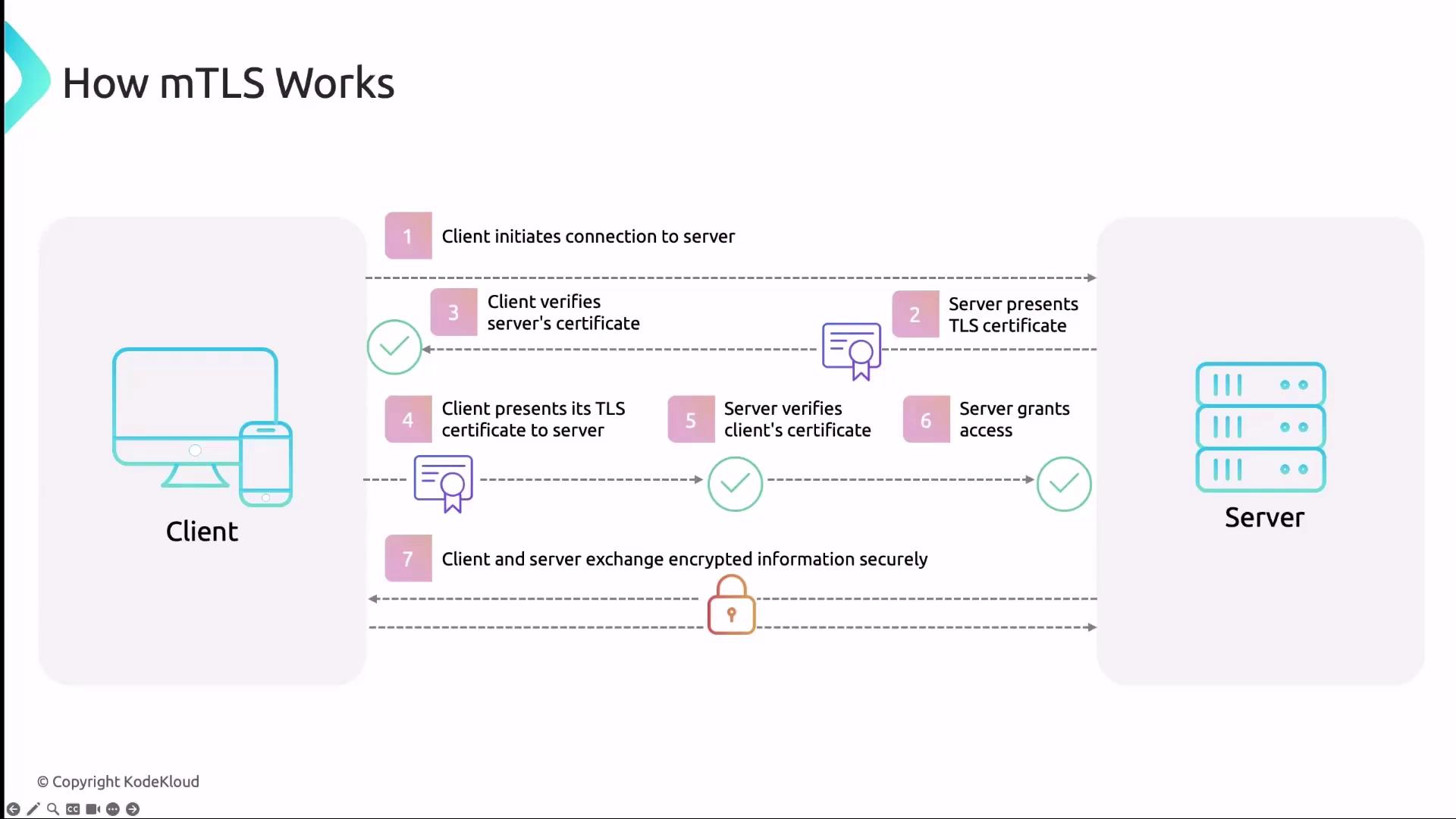
How mTLS Works
The mTLS handshake extends the standard TLS flow with certificate exchange on both sides:- Client Hello: Client initiates the handshake.
- Server Hello + Certificate: Server replies with its certificate.
- Server Verification: Client validates the server’s certificate against a trusted CA.
- Client Certificate: Client presents its certificate to the server.
- Client Verification: Server validates the client’s certificate.
- Secure Channel Established: Both parties exchange encrypted data over the secure channel.
Key Benefits of mTLS in Kubernetes
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Security | Enforces mutual authentication to confirm both endpoints’ identities. |
| Man-in-the-Middle Protection | Prevents interceptors from decrypting or spoofing messages without valid certificates. |
| Data Integrity | Guarantees end-to-end encryption to protect confidentiality and message integrity. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Helps meet GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and other security standards. |
| Automated Certificate Management | Offloads cert lifecycle tasks (issuance, renewal, revocation) to tools like Cert-Manager. |
| Zero-Trust Alignment | Requires authentication for every connection, reinforcing a zero-trust security posture. |
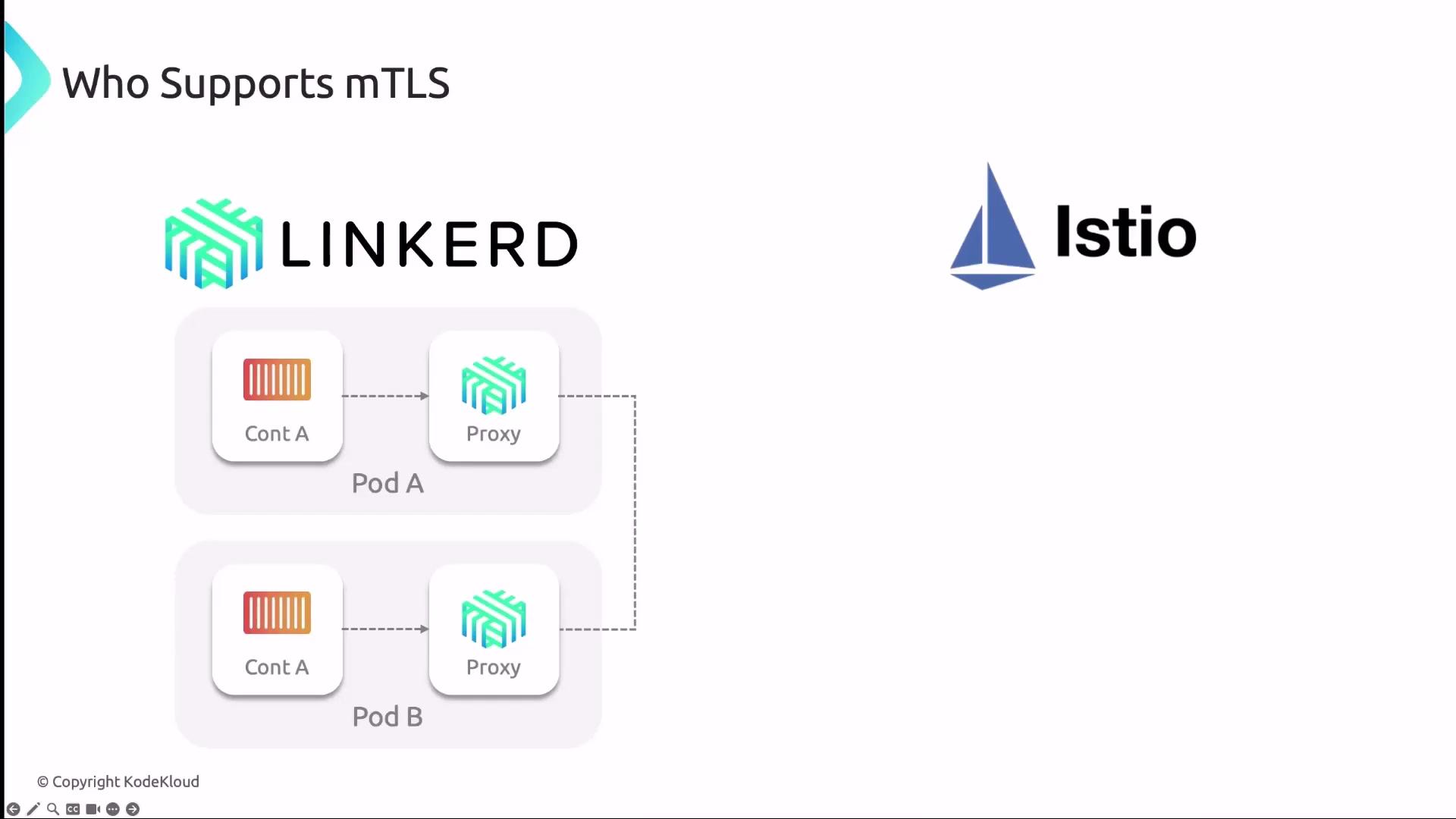
mTLS in Service Meshes
Several service meshes and CNI plugins offer built-in mTLS capabilities:Linkerd
Linkerd injects a lightweight sidecar proxy into each pod to:- Manage all inbound/outbound traffic.
- Perform mTLS handshakes automatically.
- Rotate short-lived certificates via its control plane.
Istio
Istio leverages Envoy sidecars:- Istio’s built-in CA issues and auto-rotates certificates.
- Sidecars exchange and verify credentials against the Istio root CA.
- Establish encrypted tunnels between services.
Cilium (Beta)
Cilium’s mTLS support is currently in beta. Refer to the official Cilium documentation for setup instructions and caveats.Best Practices for mTLS in Kubernetes
- Automate certificate lifecycle with Cert-Manager or a similar tool.
- Deploy a service mesh (Istio, Linkerd) to simplify policy enforcement and certificate rotation.
- Integrate mTLS validation into CI/CD pipelines to catch misconfigurations early.
- Provide training and run regular workshops on certificate troubleshooting.
- Keep operational runbooks and troubleshooting guides up to date.
mTLS adds CPU/memory overhead for encryption and certificate checks. Plan resource allocation accordingly.
Challenges and Considerations
- Performance overhead from encryption/decryption and additional handshakes.
- Increased infrastructure and tooling costs.
- Complexity in configuring and managing certificates—even with automation.
- Compatibility gaps in legacy or third-party services.
- Operational complexity requiring deeper security expertise.