- How to export logs to a specific path using environment variables
- Generating and configuring debug log levels
- Enabling logging for an OpenTofu project
- Tainting and replacing Terraform resources (AWS EC2 example)
1. Environment Variables for Debugging
OpenTofu uses two key environment variables to control logging:| Variable | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| TF_LOG | Sets the log verbosity level (error, warn, info, debug, trace) | export TF_LOG=debug |
| TF_LOG_PATH | Specifies the file path where log output will be written | export TF_LOG_PATH=/tmp/ot.log |
TF_LOG_PATH must be set alongside TF_LOG; otherwise, no logs will be written to disk.2. Enabling Logging and Exporting Logs
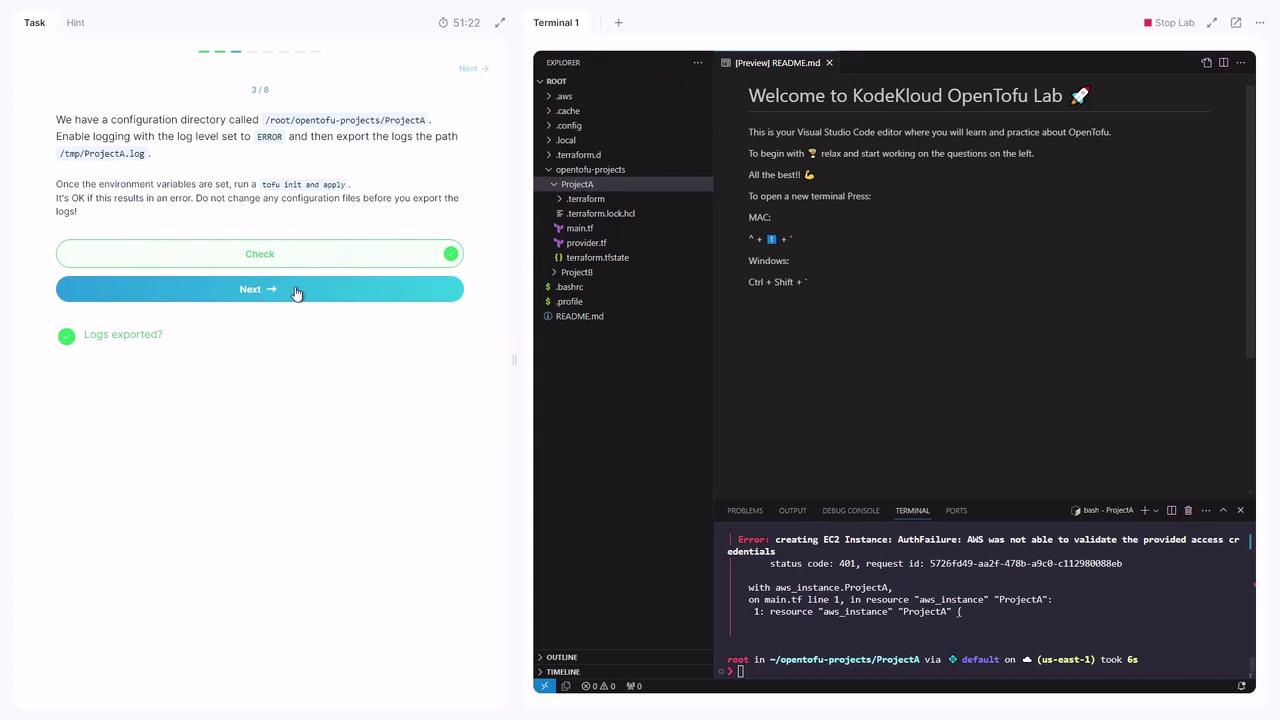
Assume your project directory is/root/OpenTofu/projects/project_a. To enable error-level logging and export output to /tmp/project_a.log, run:
yes. Authentication warnings may appear, but the log file will be created at /tmp/project_a.log.
Do not modify any configuration files before exporting logs; this ensures you capture the original error context.
trace produces the most detailed output.
3. Provisioning an EC2 Instance and Tainting
Navigate to theprojectB directory:
main.tf defines an AWS EC2 instance:
yes. After apply completes, the EC2 instance ProjectB appears in your AWS console.
Effects of Tainting
To mark the EC2 instance for replacement:Replacing a Tainted Resource
Execute the apply command with-replace: