Cluster Autoscaler Overview
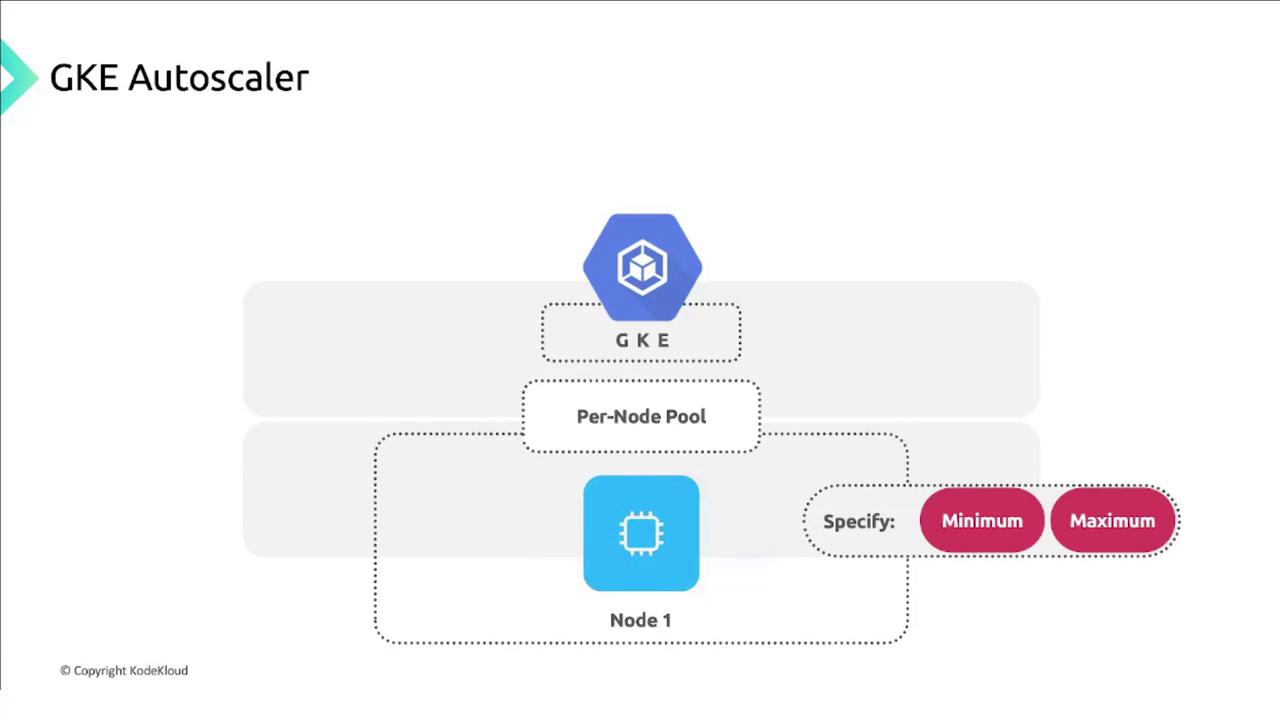
GKE’s Cluster Autoscaler watches your pods and resizes node pools within the min/max bounds you define.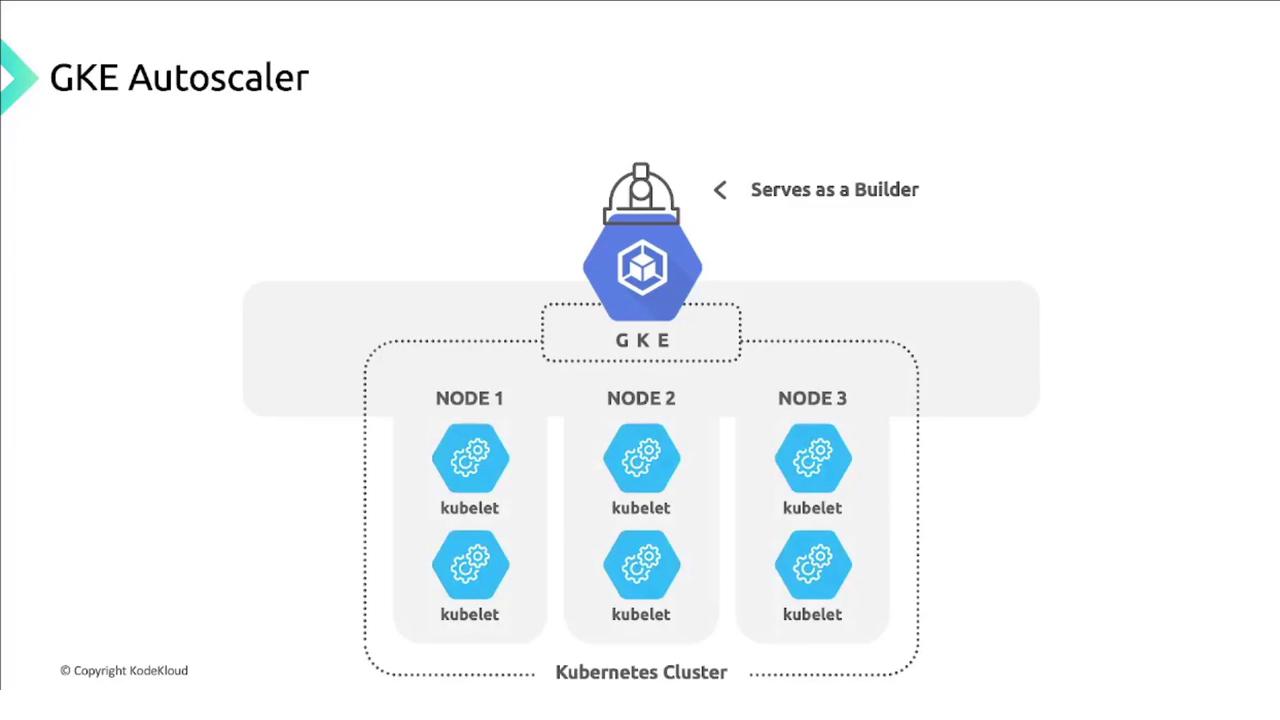
Core Functions
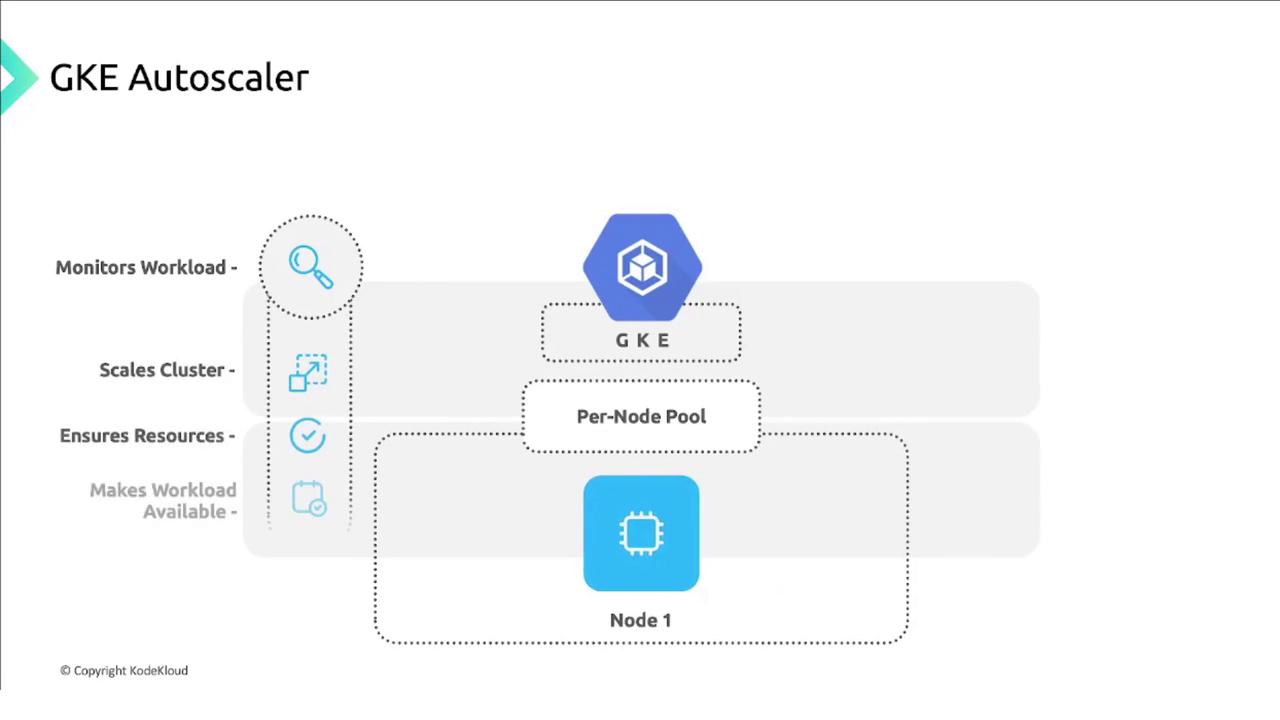
- Monitors pending pods.
- Scales up when there aren’t enough nodes.
- Scales down when nodes are underutilized.
- Ensures workloads remain available.
If your workloads don’t tolerate
pod evictions—for example, single-replica controllers—a scale-down can cause service interruption. Always use multiple replicas so pods can reschedule without downtime.
Node Pools as Managed Instance Groups
Cluster Autoscaler operates per node pool. Each pool corresponds to a Compute Engine managed instance group: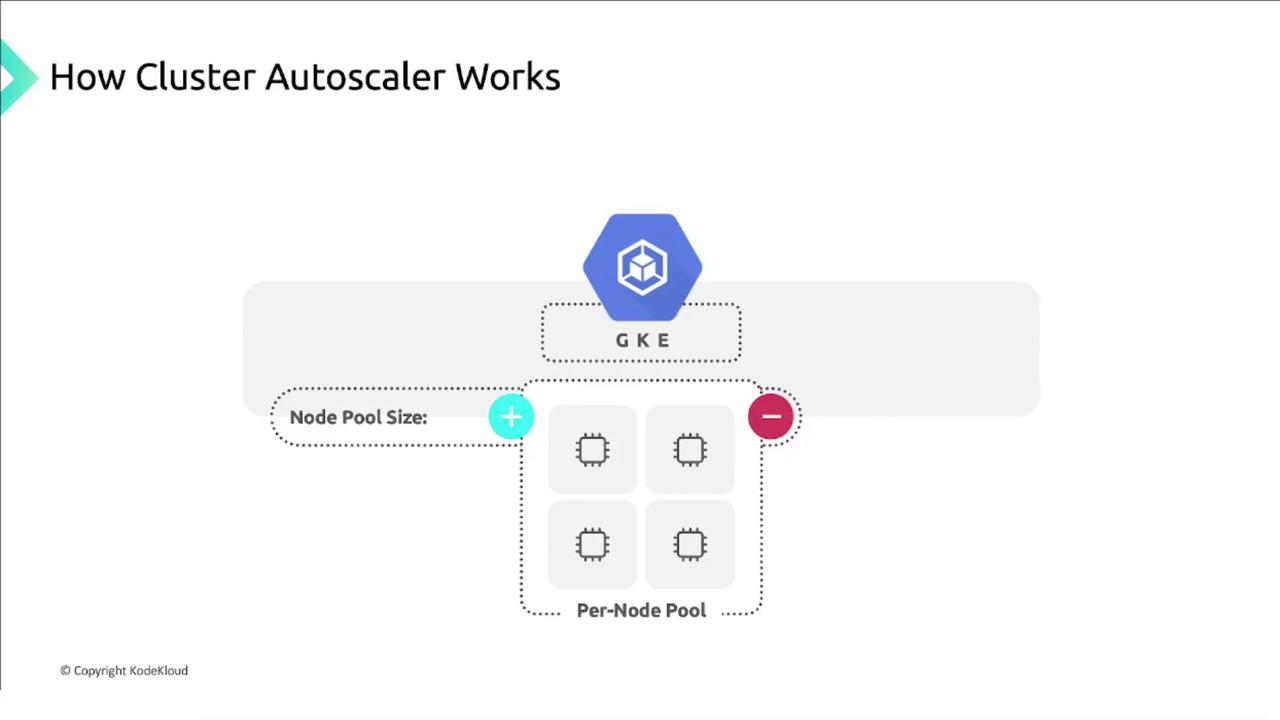
Scaling Logic
Scaling decisions rely on pending pod resource requests, not on current CPU/memory utilization:- If pods remain unscheduled due to insufficient nodes, the autoscaler adds nodes until pods fit or the pool’s max is reached.
- If nodes are underutilized and all pods fit on fewer nodes, it removes nodes down to the pool’s min.
Node Auto-Provisioning
With Node Auto-Provisioning enabled in a Standard GKE cluster, GKE creates and deletes node pools automatically based on pending pod requirements (CPU, memory, storage, affinities, taints, tolerations).
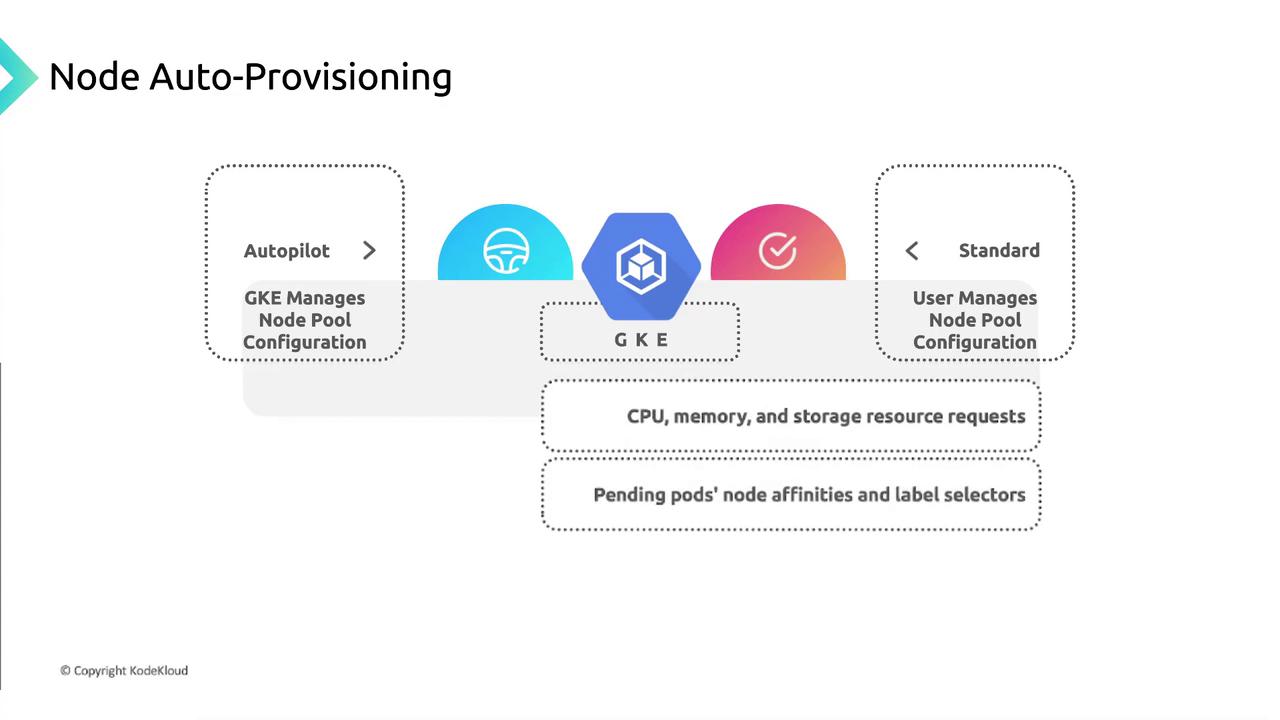
| Cluster Mode | Node Pool Management | Configuration Needed |
|---|---|---|
| Autopilot | Fully managed by GKE | None |
| Standard | User-managed node pools | Enable and configure NAP |
Key Benefits of GKE Autoscaler
- Cost Reduction: Scale down when demand is low.
- Improved Performance: Add nodes proactively to avoid resource exhaustion.
- Enhanced Reliability: Maintain availability during failures and spikes.
Autoscaling Limits
| Limit Category | Constraint |
|---|---|
| Cluster Size | Up to 15,000 nodes & 150,000 pods (project quotas apply) |
| Node Pool Size | Defined by Compute Engine quotas and zone-specific limits |
| Scaling Interval | Evaluations run approximately every 10 seconds |
| Scaling Policies | Based on pending pod requests and available project resources |
Best Practices
- Use multiple node pools to isolate workloads by resource profiles or zones.
- Enable Cluster Autoscaler and Node Auto-Provisioning to match real-time demand.
- Configure monitoring and alerts for CPU, memory, and pod scheduling metrics.
Review your Compute Engine quota limits and scaling policies regularly to prevent quota exhaustion during high-traffic periods.