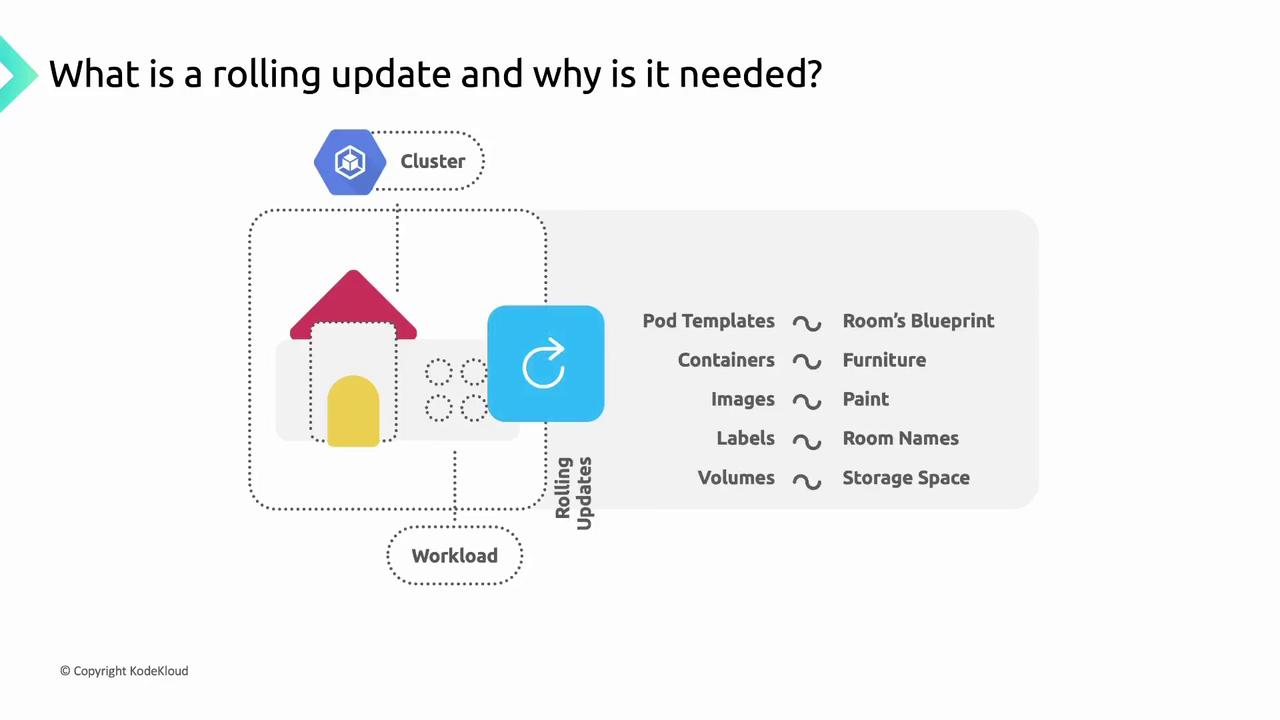
Kubernetes Rolling Update: A House Renovation Analogy
Imagine you’re renovating a house one room at a time—painting walls, upgrading appliances, replacing furniture—while keeping the rest of the home fully functional. In GKE:- The house = your GKE cluster
- The rooms = DaemonSets, Deployments, StatefulSets
- The blueprint = the workload’s Pod template
Triggering a Rolling Update
A rolling update is only triggered when you change fields under the Pod template (spec.template). Actions outside the template—such as modifying replica counts—do not automatically start a rollout.
Only changes to
spec.template (for example, containers[].image or volumes[]) trigger a rolling update. Scaling operations require separate commands or API calls.Configuring Update Strategies in GKE
GKE supports two update strategies for workload controllers:| Resource Type | Spec Field | Default Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Deployment | spec.strategy | RollingUpdate |
| DaemonSet | spec.updateStrategy | RollingUpdate |
| StatefulSet | spec.updateStrategy | RollingUpdate |
- OnDelete: Pods only update when manually deleted.
- RollingUpdate: Pods update automatically, one at a time.
1. OnDelete Strategy
With OnDelete, the controller replaces Pods only after you manually delete them. This grants you full control over when and which Pods are updated.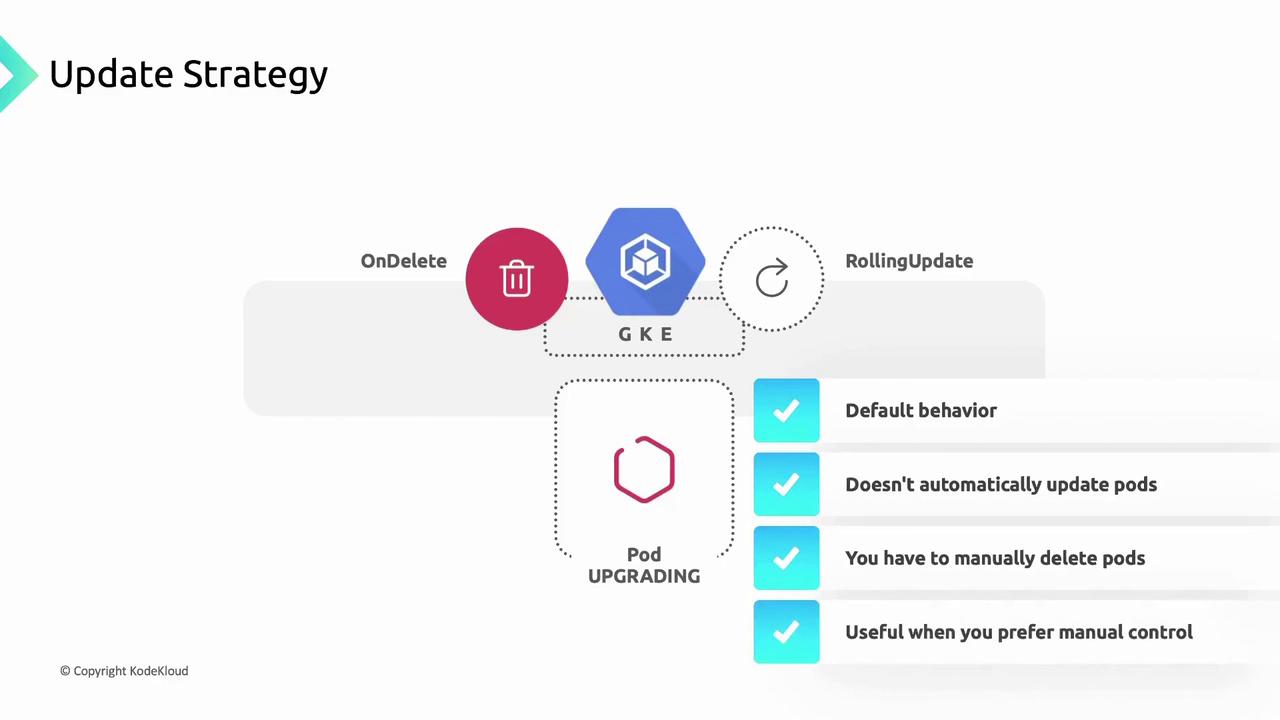
Using
OnDelete means no automatic rollout. Be prepared to manually delete outdated Pods to apply your updates.2. RollingUpdate Strategy
The RollingUpdate strategy automates Pod replacements. GKE waits for each new Pod to becomeReady before proceeding to the next. You can fine-tune rollout behavior using parameters such as maxUnavailable or partition.
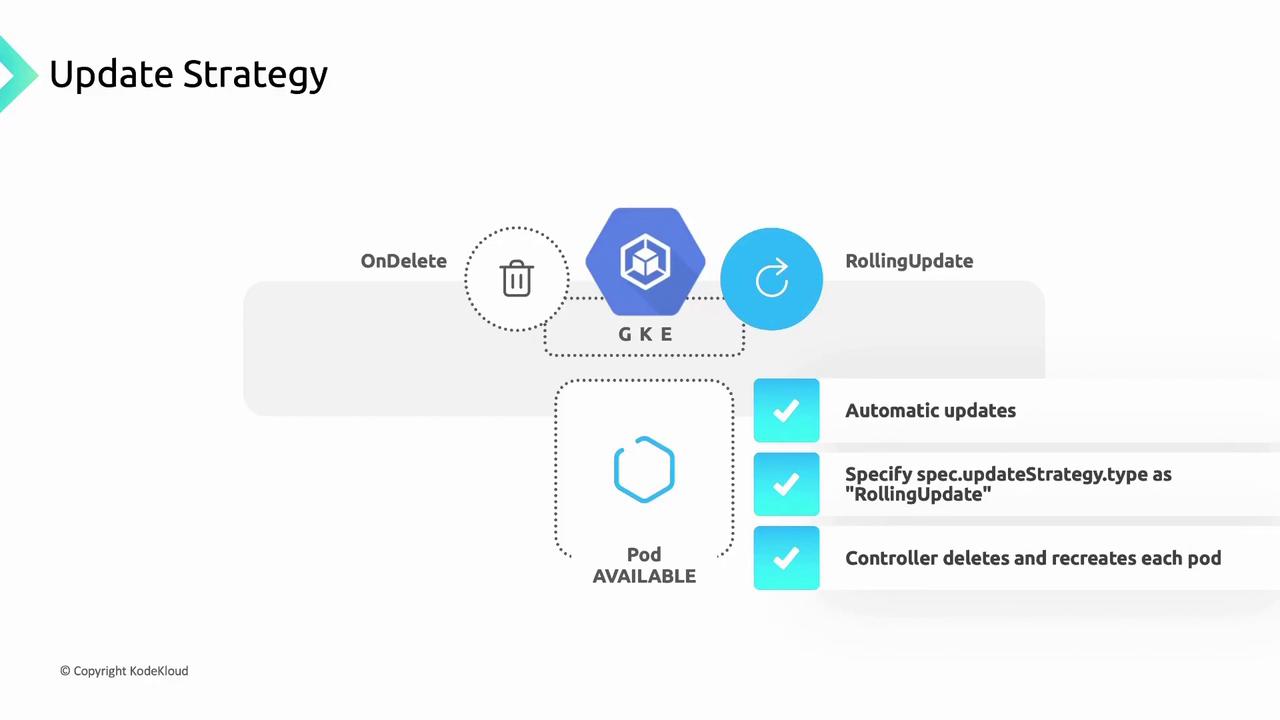
The
partition setting lets you control how many Pods remain on the old revision. Adjust maxUnavailable or maxSurge to manage availability during updates.Handling Failures During Rolling Updates
If a new Pod fails to reach theReady state, the update halts. Existing Pods on the old version remain running, ensuring your service stays available. This predictable behavior helps maintain reliability and gives you time to diagnose issues before proceeding.
Links and References
- GKE Rolling Updates Overview
- Kubernetes Deployment Strategy
- StatefulSet Rolling Updates
- DaemonSet Update Strategy