| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Set your Compute Zone |
| 2 | Create a custom VPC |
| 3 | Add a regional subnet |
| 4 | Launch an IP-alias (VPC-native) GKE cluster |
| 5 | Verify the secondary IP ranges |
| 6 | Clean up all resources |
1. Set the Compute Zone
Configure your default compute zone tous-west1-a (or your preferred region).
2. Create a Custom VPC
Create a VPC in custom subnet mode so you can define your own IP ranges.gke-deep-dive-vpc listed, but no subnets yet.
3. Add a Regional Subnet
Define a subnet inus-west1 with a /24 CIDR block.
VPC networks are global, whereas subnets are regional. Choose the region that best suits your workload.
gke-deep-dive-subnet (10.10.0.0/24) appears under your VPC.
4. Launch an IP-Alias (VPC-native) GKE Cluster
Use IP aliasing to allocate two secondary IP ranges—one for Pods and one for Services.| Flag | Purpose |
|---|---|
--enable-ip-alias | Enable VPC-native IP aliasing |
--cluster-secondary-range-name | Name for the Pods’ secondary IP range |
--services-secondary-range-name | Name for the Services’ secondary IP range |
/21 CIDR | Allocates a block with ~2048 IPs for each range |
5. Verify Secondary Ranges
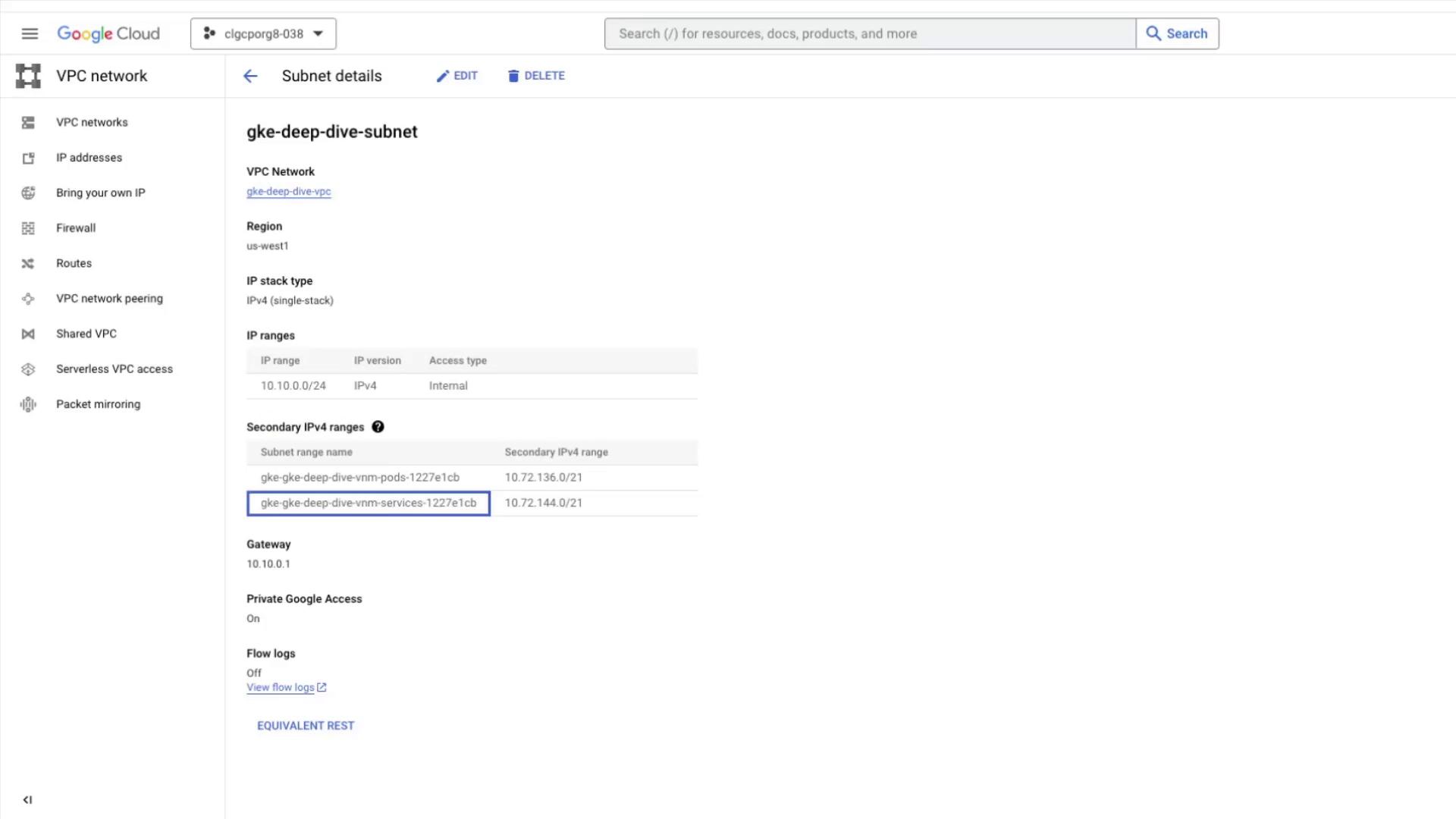
Console View
In the Cloud Console, open VPC networks → Subnets and selectgke-deep-dive-subnet. You should see two new secondary IP ranges:
CLI Verification
Describe the cluster’s IP allocation policy:clusterIpv4CidrservicesIpv4CidrclusterSecondaryRangeNameservicesSecondaryRangeName
6. Clean Up Resources
Delete the GKE Cluster
gke-deep-dive-subnet upon cluster deletion.
Remove Subnet and VPC
Resource deletion is irreversible. Ensure no critical workloads are running before you clean up.