Discriminative AI vs. Generative AI
Deep learning approaches generally fall into two categories:| Model Type | Learning Paradigm | Primary Function | Input Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Discriminative | Supervised (labeled data) | Classification and prediction | Images, tabular |
| Generative | Unsupervised / Semi-supervised (unlabeled data) | Content generation | Text, images, video |
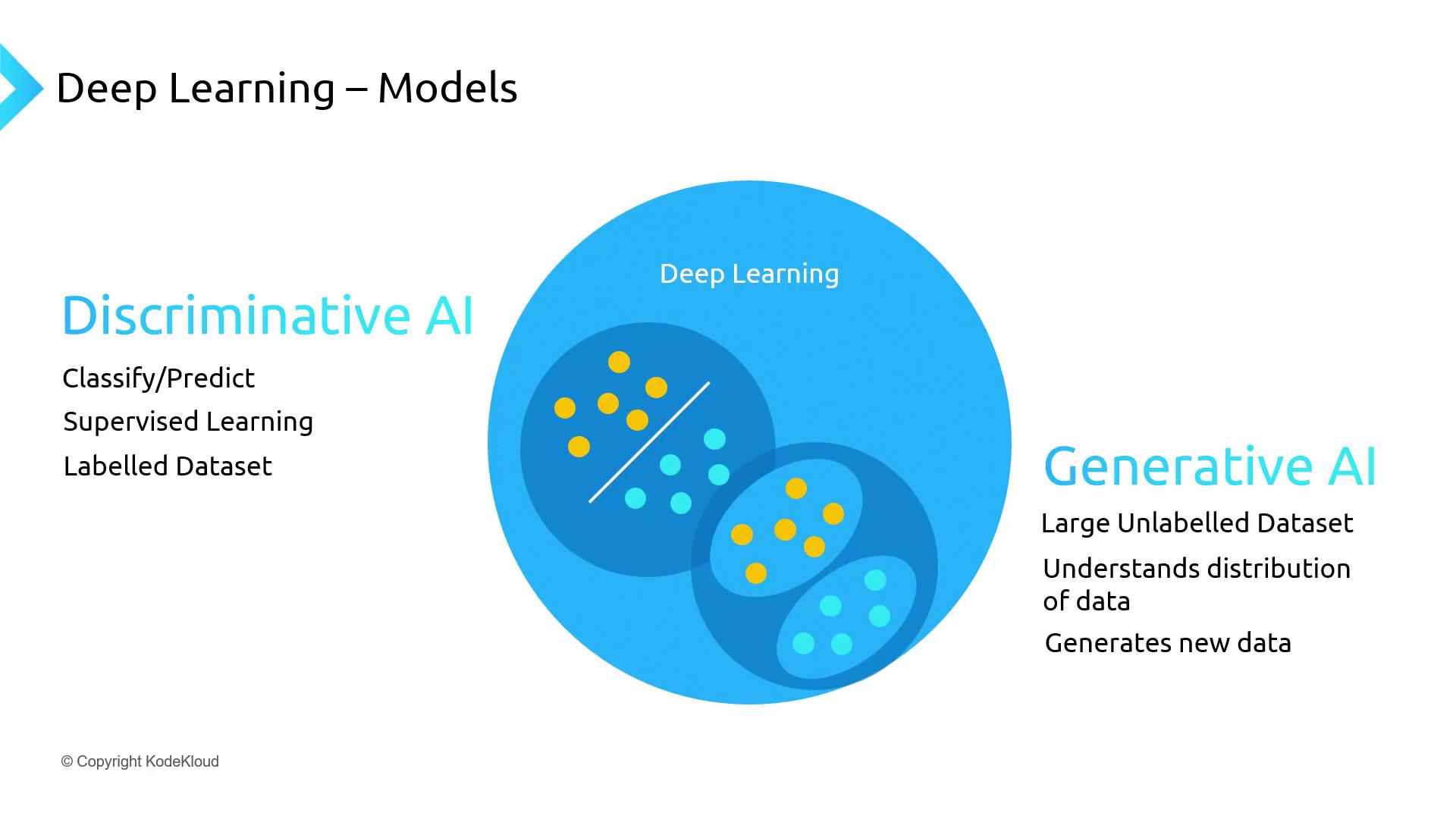
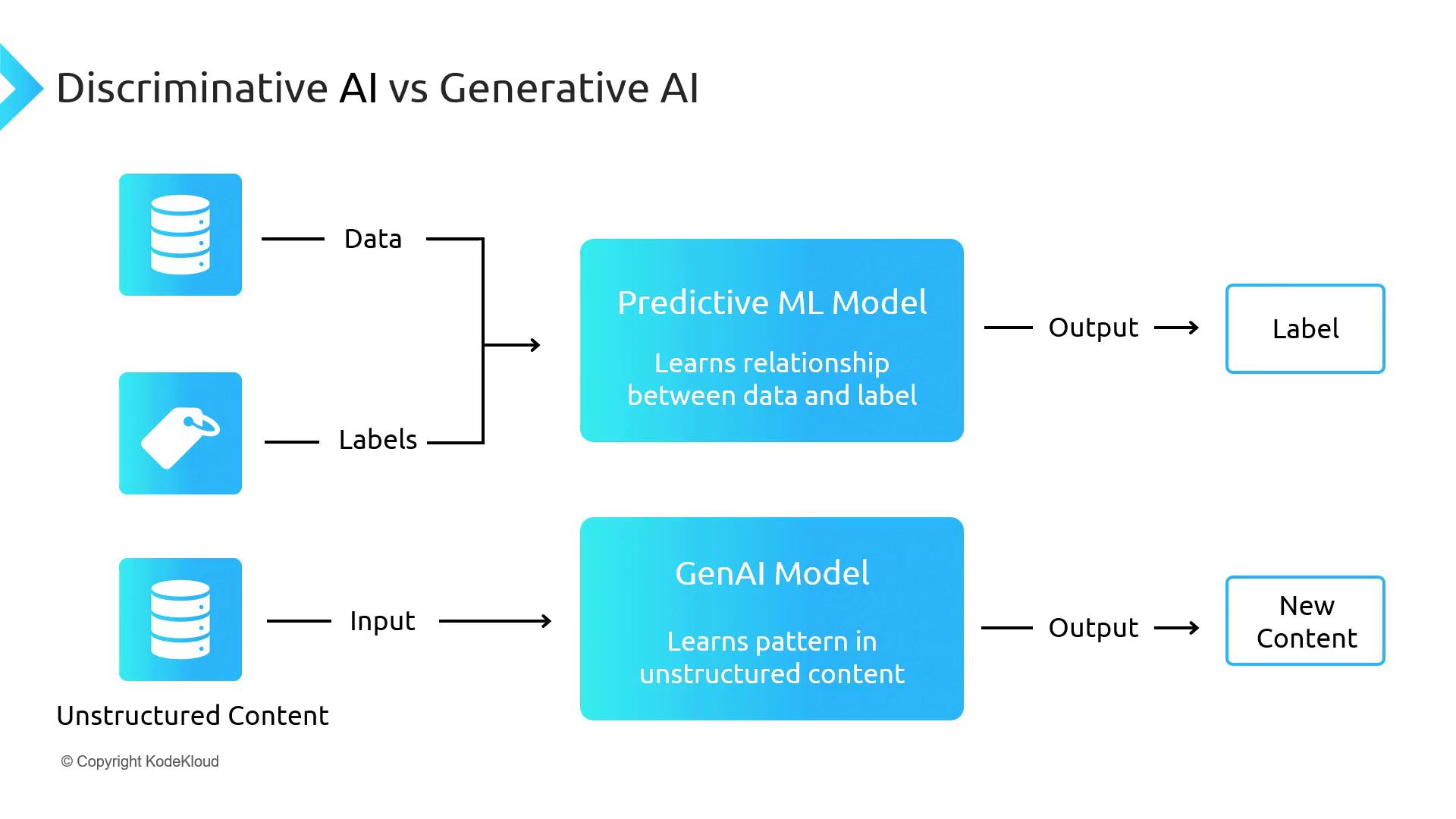
Discriminative models estimate the probability of labels given inputs (
P(y|x)), whereas generative models learn the joint probability of inputs and outputs (P(x, y)) to create fresh data.Practical Example
-
Discriminative AI
Input: Photo of a dog
Output: Label “dog” -
Generative AI
Input: Photo of a dog + prompt “dog wearing goggles”
Output: New image of a dog with goggles
Core Capabilities of Generative AI
Generative models transform raw patterns into rich, novel outputs:- Text generation
Articles, summaries, code snippets in English and multiple languages - Image and artwork creation
Photorealistic renders, illustrations, style transfers - Video sequence synthesis
Frame interpolation, short clips, animation - Audio and speech
Music composition, voice cloning, sound effects
Foundation Models: The Backbone of Generative AI
Foundation models are large-scale architectures pretrained on vast, diverse datasets. They serve as the starting point for fine-tuning on specific tasks:- Examples
- GPT family (OpenAI)
- BERT and RoBERTa (Google)
- Stable Diffusion (Stability AI)
- Benefits
- Reduced training time
- Transfer learning for specialized applications
- Robust performance on unseen inputs
Always verify generated content for factual accuracy and potential biases. Generative AI can inadvertently replicate harmful patterns from its training data.