| Prompting Method | Definition | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Zero-Shot | Perform tasks without any examples in the prompt | Multilingual translation, summarization, QA |
| Few-Shot | Provide 1–5 examples to illustrate the task to the model | Sentiment analysis, text classification, NER |
Overview
Zero-shot prompting asks the model to complete a task it has never been explicitly shown.Few-shot prompting supplies a handful of input–output pairs to guide the model’s output.
Key Topics
- Importance of Prompting
- Zero-shot Prompting
- Few-shot Prompting
- Prompt Execution
- Benefits and Challenges
- Real-world Impact
Importance of Prompting
Selecting the right prompting strategy can significantly affect accuracy, resource usage, and development speed.Zero-Shot Prompting
With zero-shot prompting, the model relies entirely on its pretraining to generalize to new tasks. This reduces the need for labeled data and shortens development cycles.
Few-Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting refines model behavior by demonstrating the task with a small set of examples. This often yields higher accuracy on specialized or nuanced tasks.Well-chosen examples should be representative and balanced to minimize bias and improve consistency.
Zero-Shot Prompting Explained
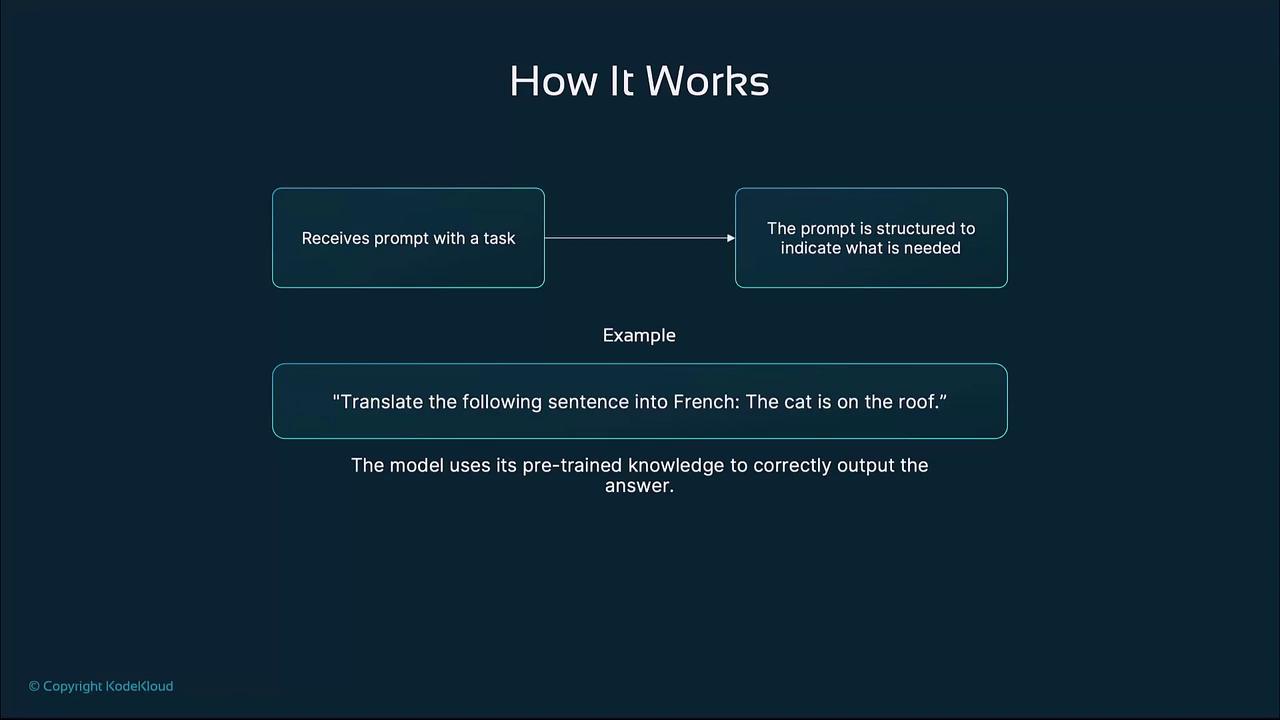
In a zero-shot scenario, you supply only a description of the desired task. The LLM uses its vast pretrained knowledge to perform the task directly.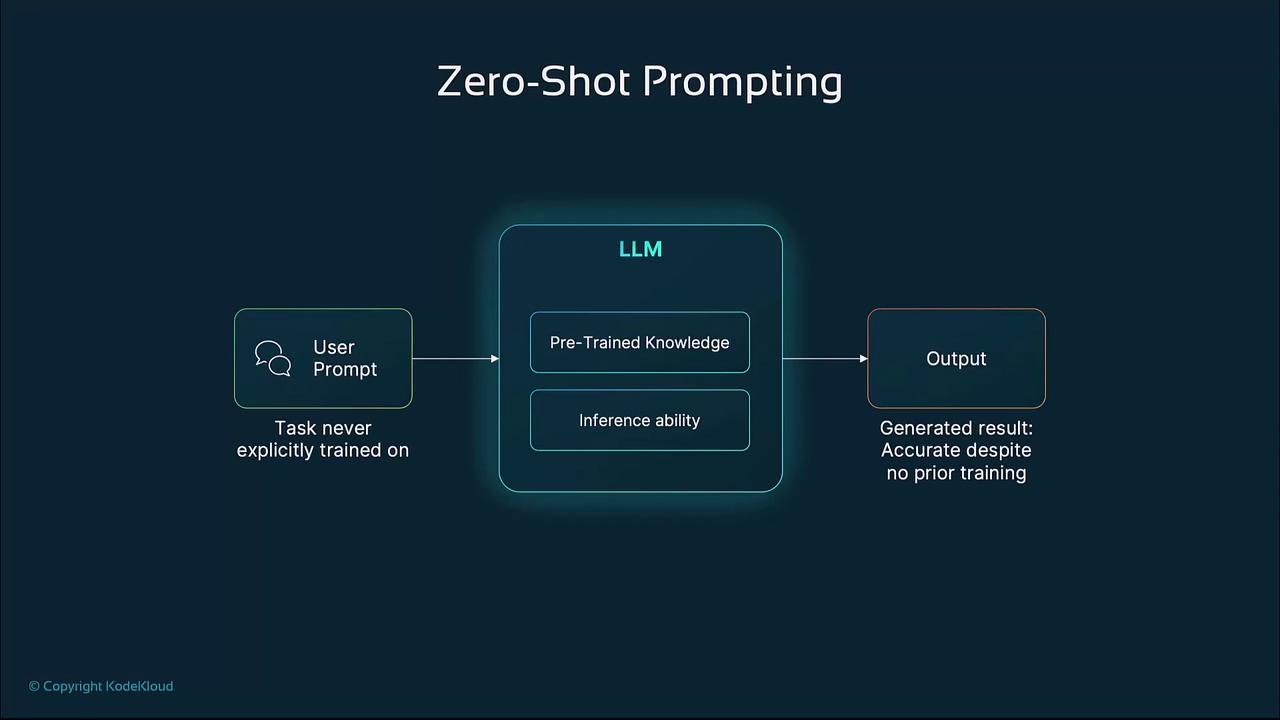
- User submits a descriptive prompt.
- The LLM applies its pretraining and inference capabilities.
- The model generates an output based on general knowledge.
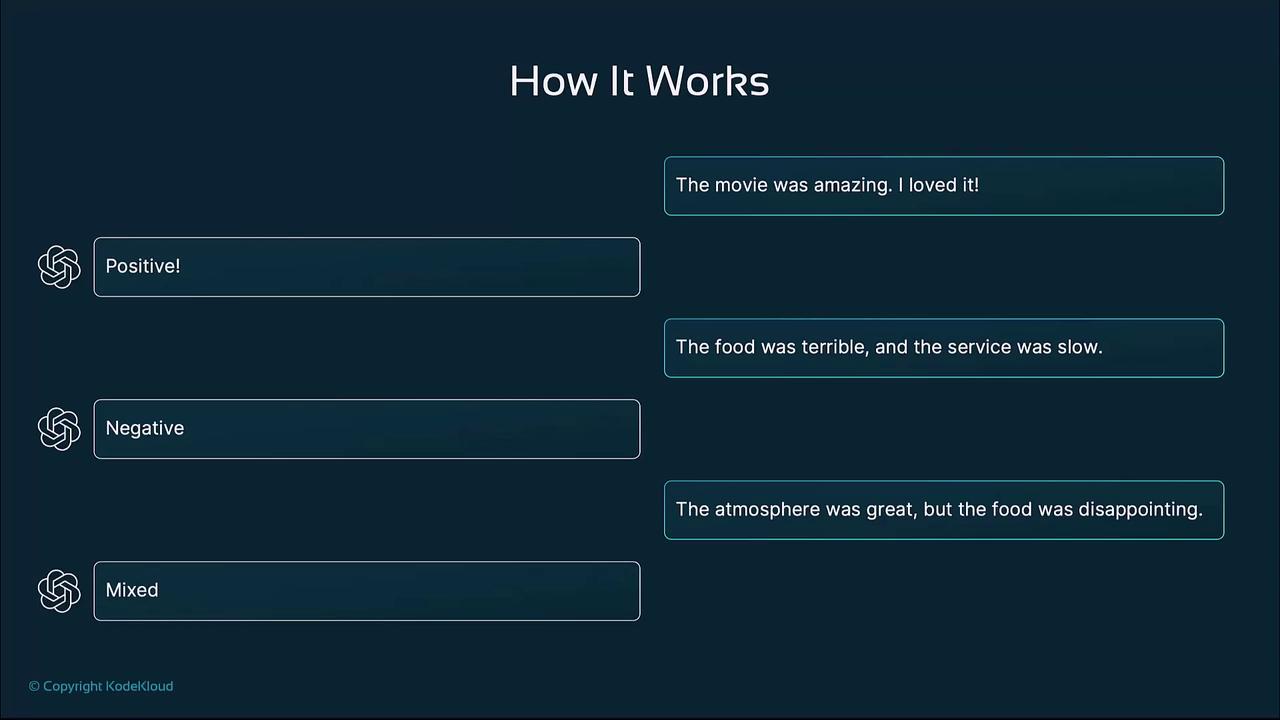
Few-Shot Prompting Explained
Few-shot prompting incorporates a handful of input–output pairs to illustrate the pattern. The model then applies the same pattern to a new instance. How to structure a few-shot prompt:- Include 1–5 example input–output pairs.
- Clearly separate each example.
- Provide a final “New Input” for the model to complete.
Prompting in Practice
Whether you choose zero-shot or few-shot, prompting unlocks powerful AI capabilities across domains.
Zero-Shot Applications
- Question answering (e.g., “Who won the World Series in 1998?”)
- Creative text generation (short stories, poetry)
Few-Shot Applications
- Sentiment analysis with labeled examples
- Code generation using sample snippets
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits

- Task flexibility: One model supports many tasks.
- Reduced data needs: No large labeled datasets required.
- Faster deployment: Skip time-consuming retraining.
- Broader use cases: AI where data is scarce.
Challenges

- Complex tasks: May falter on highly technical domains.
- Prompt ambiguity: Vague instructions can mislead the model.
- Sensitivity: Minor wording changes yield different outputs.
- Domain specificity: Few-shot requires relevant, high-quality examples.
Unclear or poorly structured prompts can significantly degrade performance—iterate on your phrasing to get consistent results.
Real-World Impact
Explore how zero-shot and few-shot prompting empower modern AI solutions:
- Natural Language Processing: On-the-fly translation, summarization, question answering.
- Code Generation: Write and refactor code in multiple languages with minimal examples.
- Creative AI: Compose music, draft stories, generate design concepts with brief prompts.