Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) enables systems to learn patterns and make predictions from data without explicit programming. OpenAI applies self-supervised learning on massive text and image corpora, allowing models to:- Predict the next word or token in a sequence
- Learn structural patterns and semantic relationships
- Improve accuracy as more data is processed
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses algorithms and systems that perform tasks requiring human-like reasoning, decision-making, and problem solving. At OpenAI, AI underpins features such as:- Contextual text generation
- Complex language comprehension
- Automated code synthesis and debugging
Large Language Models
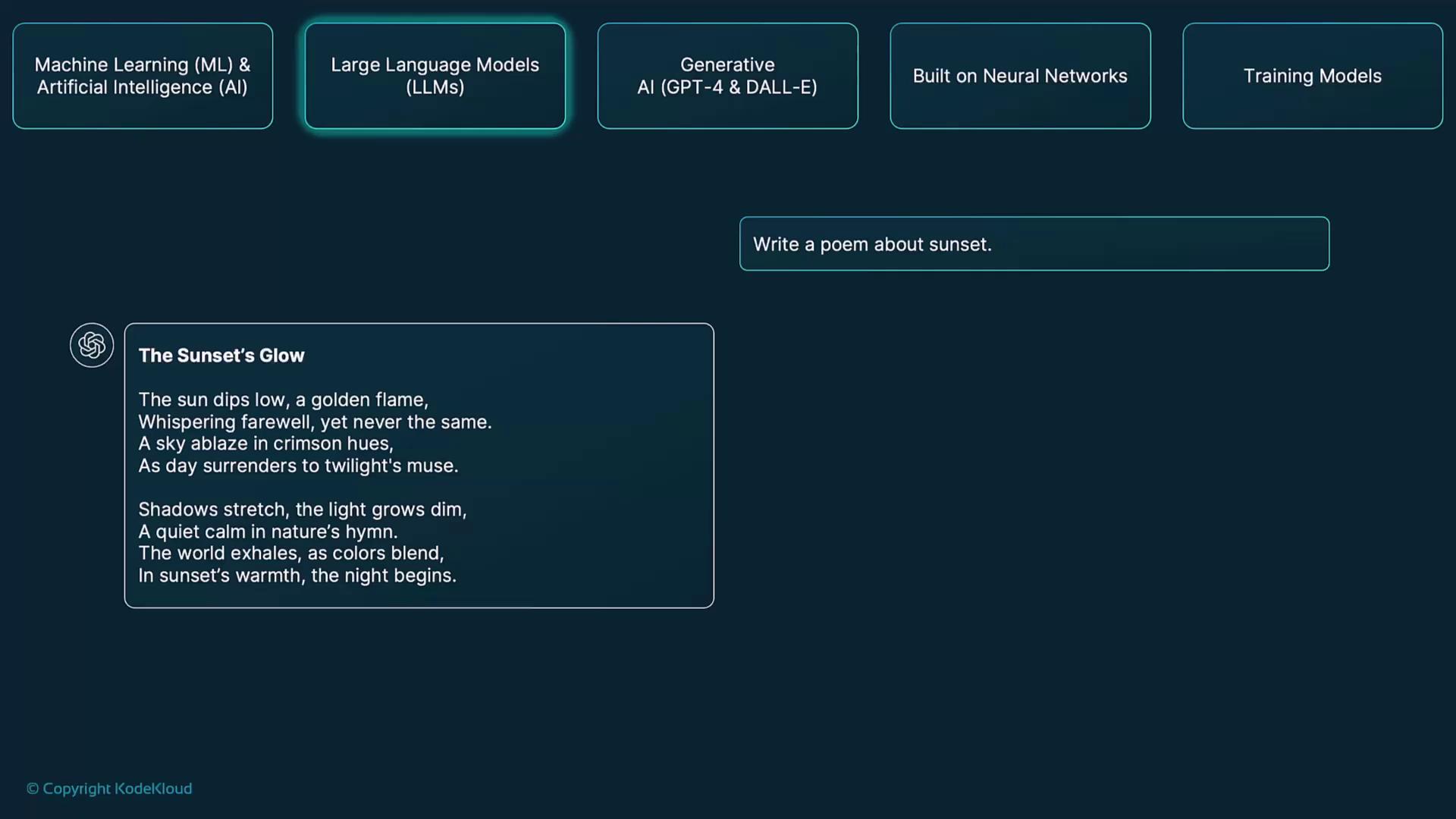
Large Language Models (LLMs) are transformer-based systems trained on billions of words. OpenAI’s GPT series (Generative Pre-trained Transformers) exemplifies this approach:- Pre-training on diverse text sources to learn linguistic structure
- Fine-tuning on specialized datasets or tasks for domain expertise
- Inference using probability distributions to generate coherent text
Generative AI
Generative AI creates entirely new content by modeling underlying data distributions. Key architectures include:- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks) for realistic image synthesis
- VAEs (Variational Autoencoders) for structured latent representations
- Transformers (e.g., GPT, DALL·E) for high-fidelity text and image outputs
Neural Networks
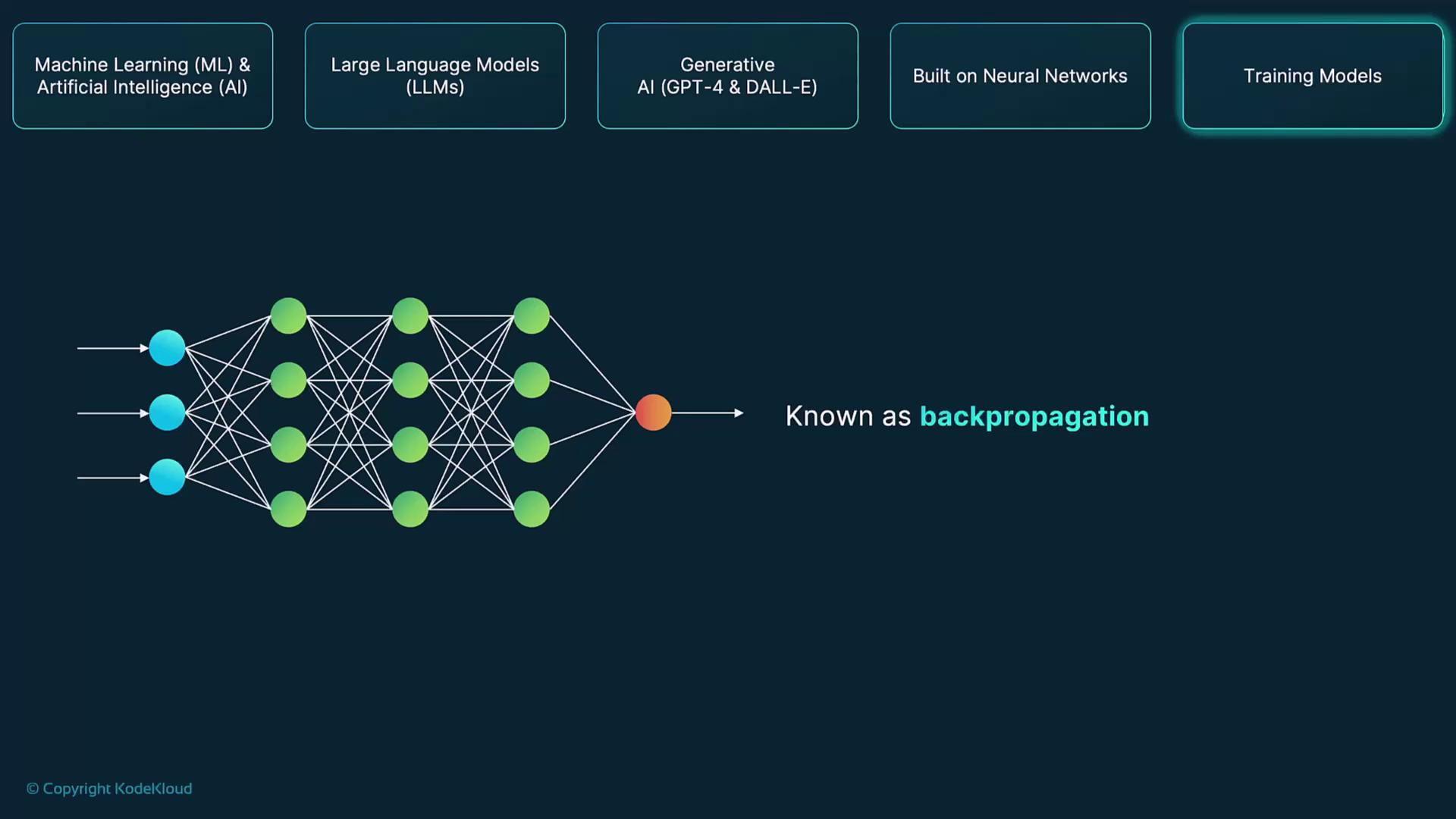
Neural networks are the computational backbone of OpenAI’s models. The Transformer architecture stands out by using self-attention mechanisms to capture long-range dependencies in sequences. Key components:- Multi-head attention layers for parallel context aggregation
- Feedforward networks for nonlinear feature transformation
- Layer normalization and residual connections to stabilize training
Training Models
OpenAI’s flagship models—GPT, CLIP, and DALL·E—undergo extensive training cycles on text, image–text pairs, and code repositories. The process involves:-
Task Definition
Assign specific objectives like next-token prediction, image captioning, or code completion. -
Backpropagation
Compute gradients to assess how each weight contributes to the model’s error, propagating corrections backward through the network. -
Optimization
Apply gradient descent variants (e.g., Adam) to update parameters in the direction that reduces the loss.
Training these models requires specialized hardware (GPUs/TPUs) and distributed computing frameworks to handle billions of parameters efficiently.
| Model | Domain | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| GPT | Text | Language generation & understanding |
| CLIP | Image-Text | Zero-shot image classification & captioning |
| DALL·E | Image | Creative image synthesis from prompts |