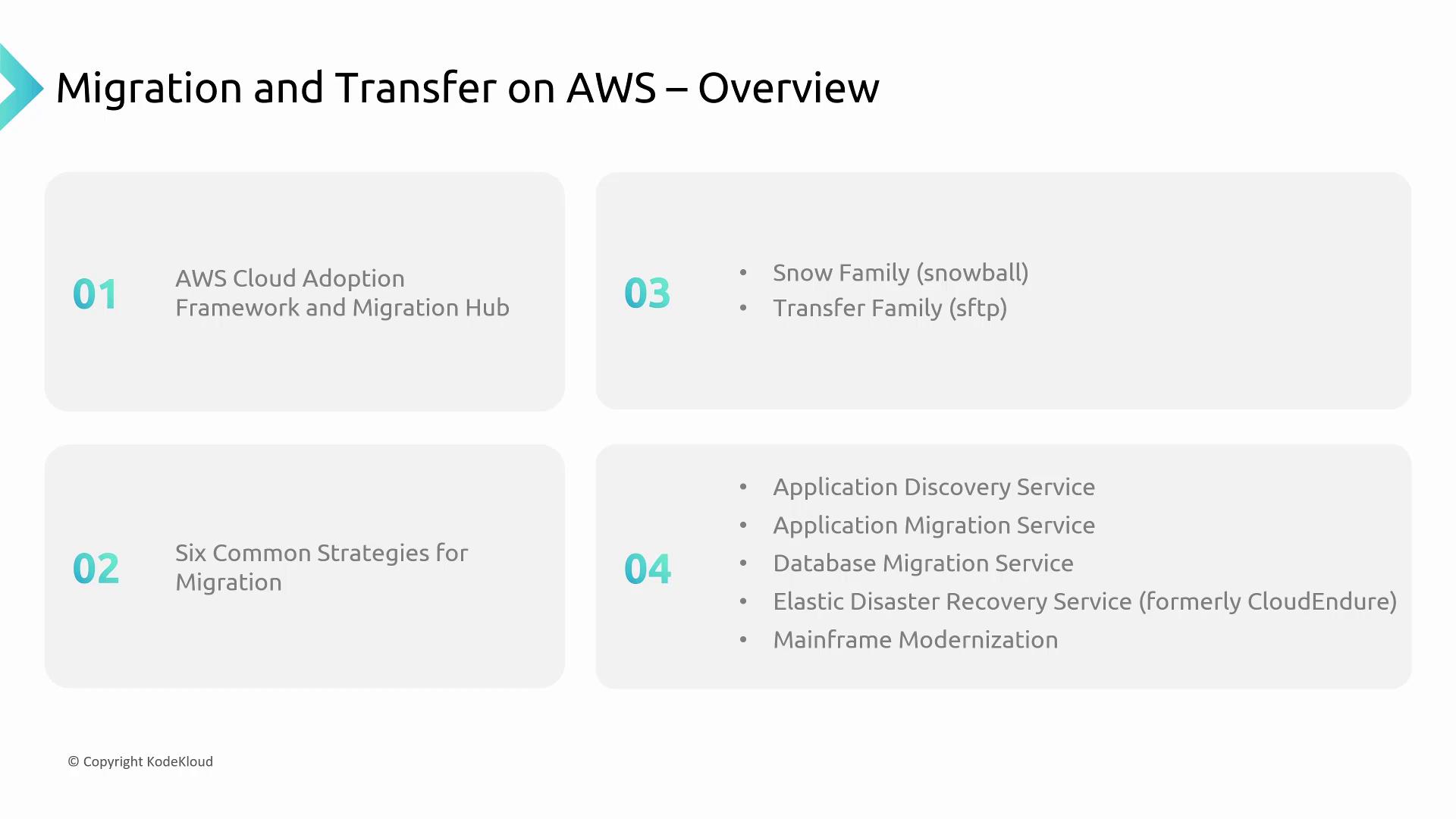
Cloud Adoption Framework and Migration Hub
The AWS Cloud Adoption Framework helps organizations evaluate questions concerning business goals, personnel, governance models, platform solutions, security measures, and operational processes. It serves as a blueprint for aligning your cloud strategy with organizational priorities.
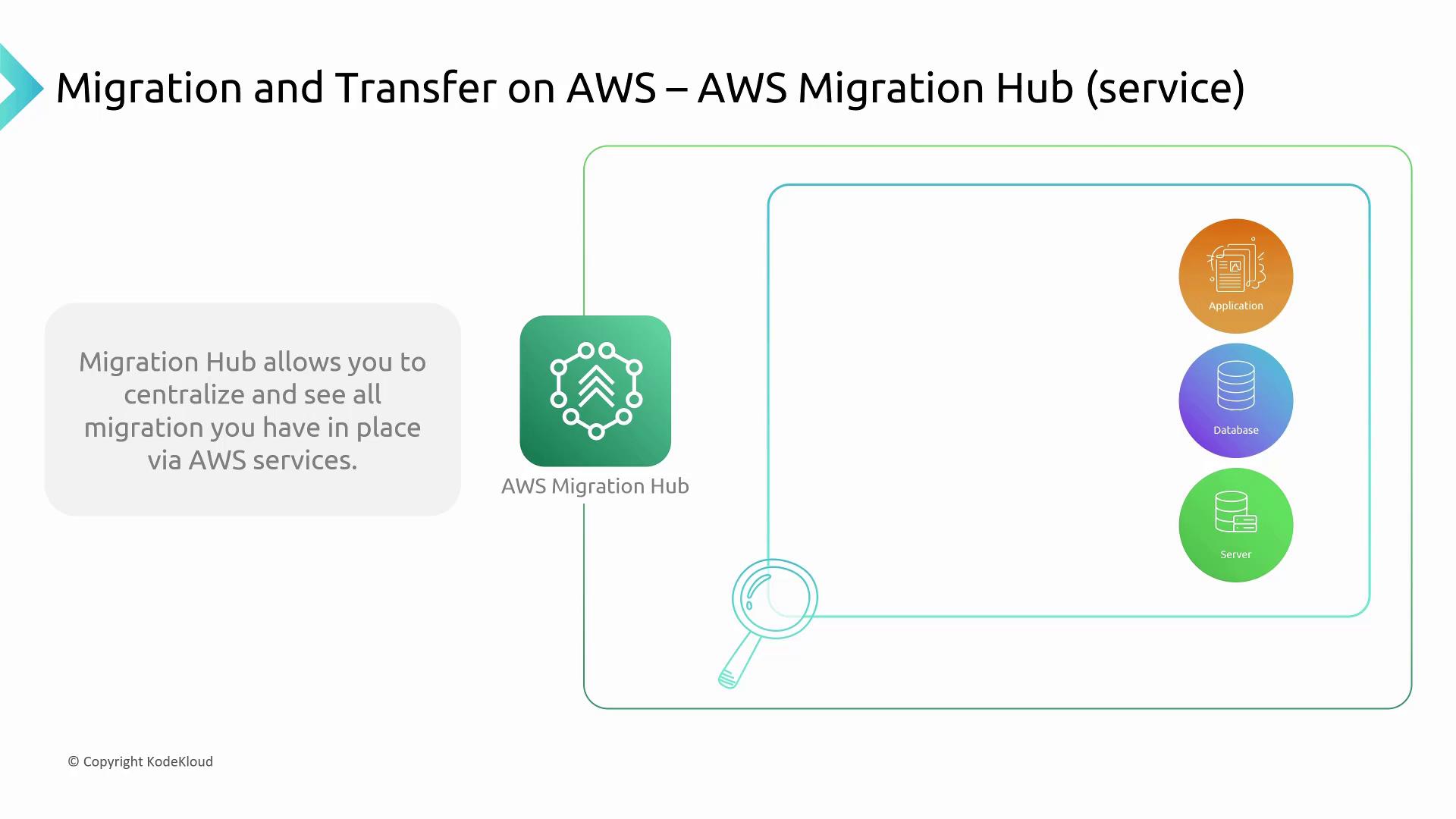
When planning your migration, consider using the AWS Migration Hub. It centralizes migration status across applications, databases, and entire data centers, providing a unified view even when using services like the Application Migration Service or the Database Migration Service.
Migration Strategies
AWS and industry experts recognize six (sometimes seven) migration strategies. Selecting the right strategy depends on factors such as time, cost, effort, and existing licensing. Below is an overview of each method:-
Rehosting (Lift and Shift):
Move your existing server, database, and application to AWS without significant modifications. This is the fastest approach but may offer limited long-term benefits. -
Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift):
Execute minor improvements—such as updating to a modern operating system or migrating to a managed service—while preserving the core structure of your application. -
Refactoring (Re-architecting):
Redesign your application architecture to take full advantage of AWS services. Although it requires more time and investment, this approach optimizes performance and scalability in the cloud. -
Repurchasing:
Replace your current solution with a cloud-based equivalent. An example is transitioning from an on-premises version of Microsoft SQL Server to its AWS-certified counterpart. -
Retaining:
Maintain the existing on-premises infrastructure until a future decommissioning plan is in place. This strategy is used when immediate migration is not feasible. -
Retiring:
Decommission systems or applications that are no longer required, effectively phasing out legacy resources.

Detailed Migration Strategies
Rehosting
Rehosting, commonly known as “lift and shift,” transfers an existing server to AWS without modifying the application, database, or operating system. This straightforward method is quick but may not fully leverage cloud benefits.Replatforming
Replatforming involves minor improvements, such as updating the operating system or migrating to managed services, all while keeping the underlying application largely unchanged. This strategy is often described as “lift, tinker and shift.”
Refactoring/Re-architecting
Refactoring is the most transformative approach, entailing a complete redesign of the application architecture to integrate seamlessly with AWS services. Although it demands more effort and time, it results in an optimized, scalable, and resilient cloud-native application.
Repurchasing
Repurchasing involves obtaining a cloud-based version of your current solution. For example, moving from an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server to an AWS-licensed version can simplify management and licensing while migrating to the cloud.
Retaining and Retiring
The retaining strategy involves deferring the migration by keeping your current on-premises infrastructure until it reaches the end of its lifecycle. Conversely, retiring focuses on decommissioning systems that are obsolete, thereby streamlining your environment.Offline Data Transfer with the Snow Family
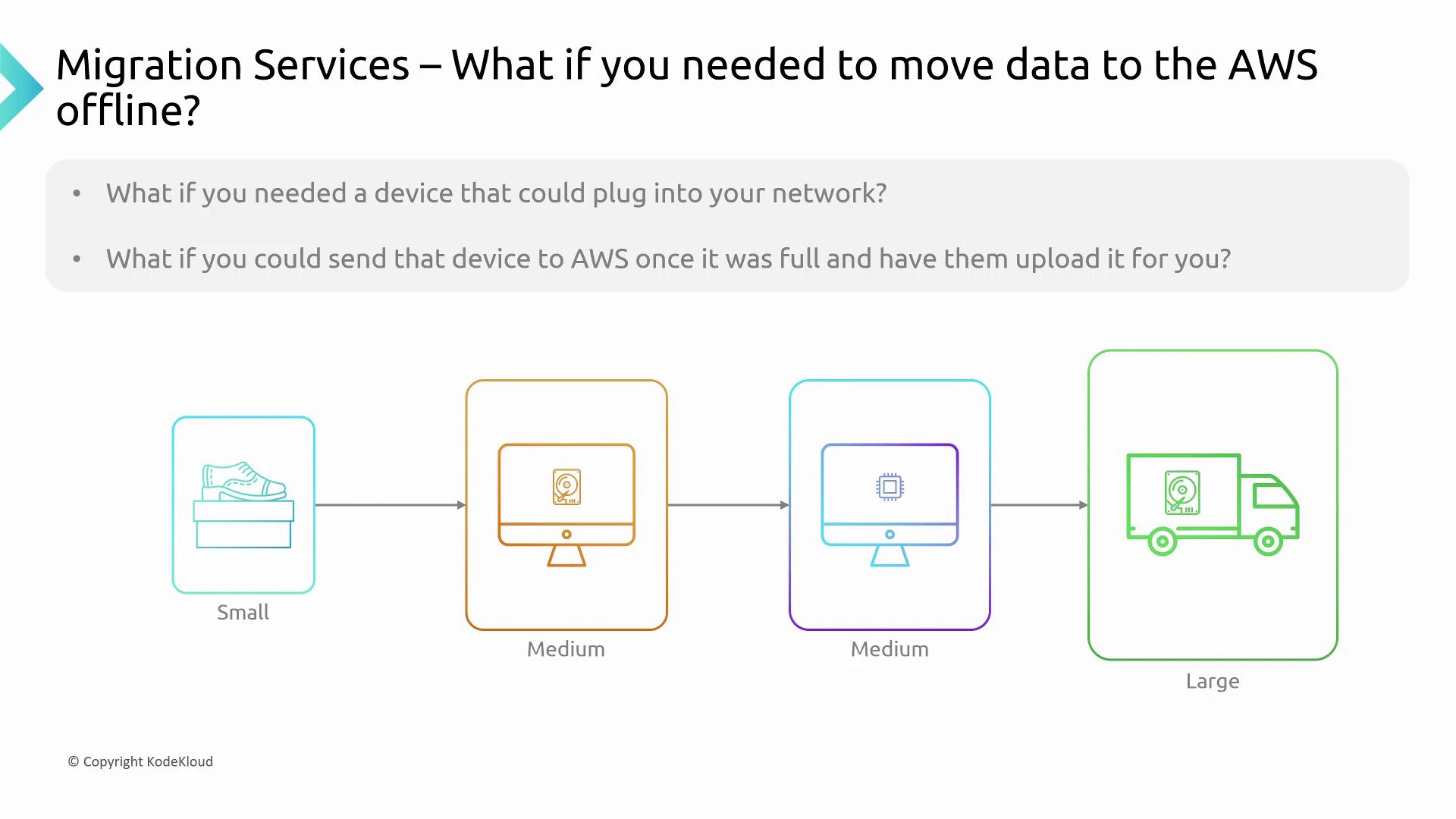
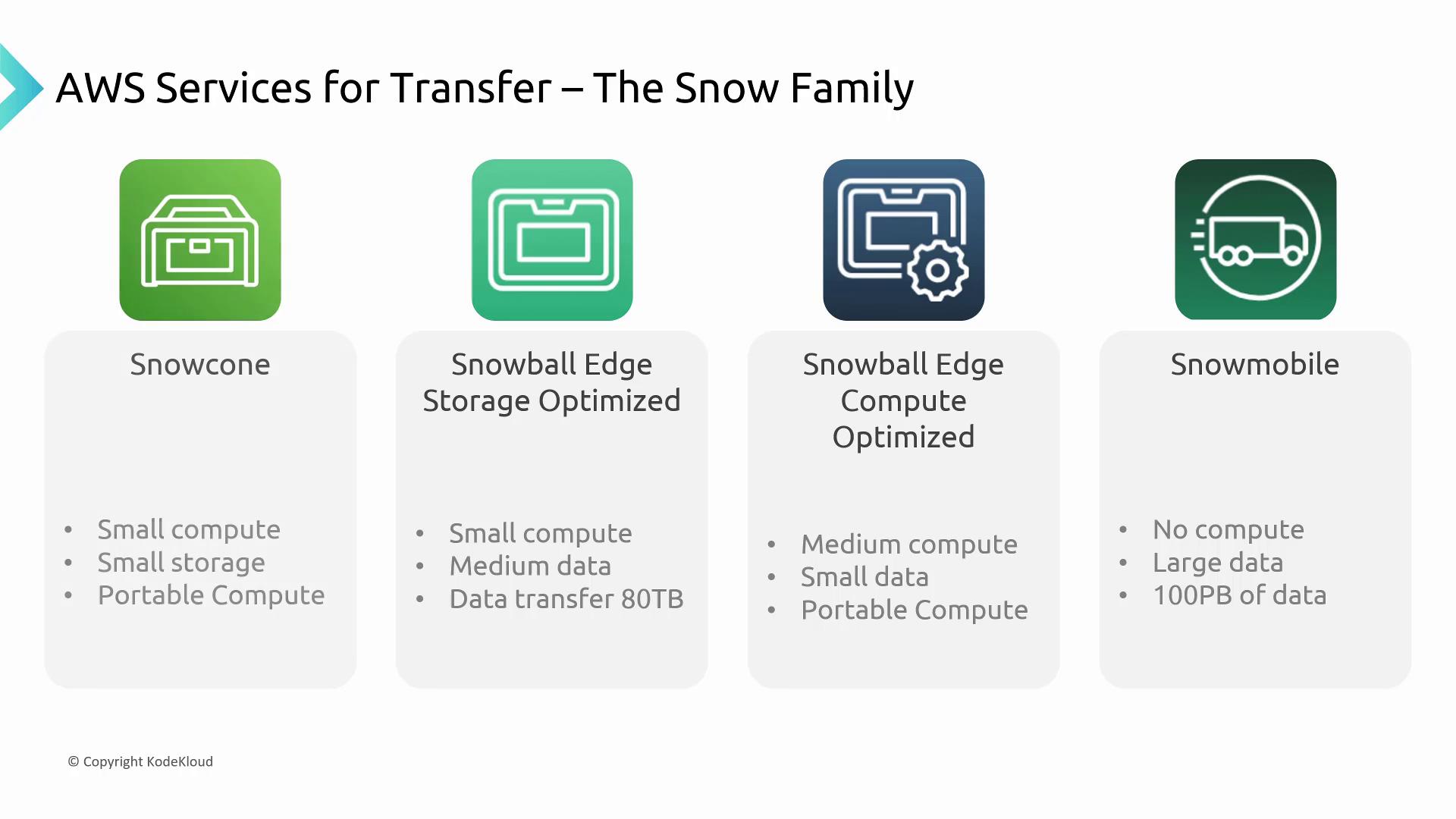
When network constraints hinder large-scale data migrations, AWS offers a range of physical data transfer devices known as the Snow Family. These devices come in various sizes to meet different data transfer needs:-
Snowcone:
A compact, shoebox-sized device ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) deployments. -
Snowball Edge (Storage Optimized and Compute Optimized):
Suitcase-sized devices capable of handling between 73 terabytes and 80 terabytes of usable data. One version is optimized for storage while the other is designed for compute-intensive tasks. -
Snowmobile:
A truck-sized solution engineered for petabyte-scale (up to 100 petabytes) data transfers, suitable for extremely large data migrations.
Online Data Transfer with the Transfer Family and DataSync
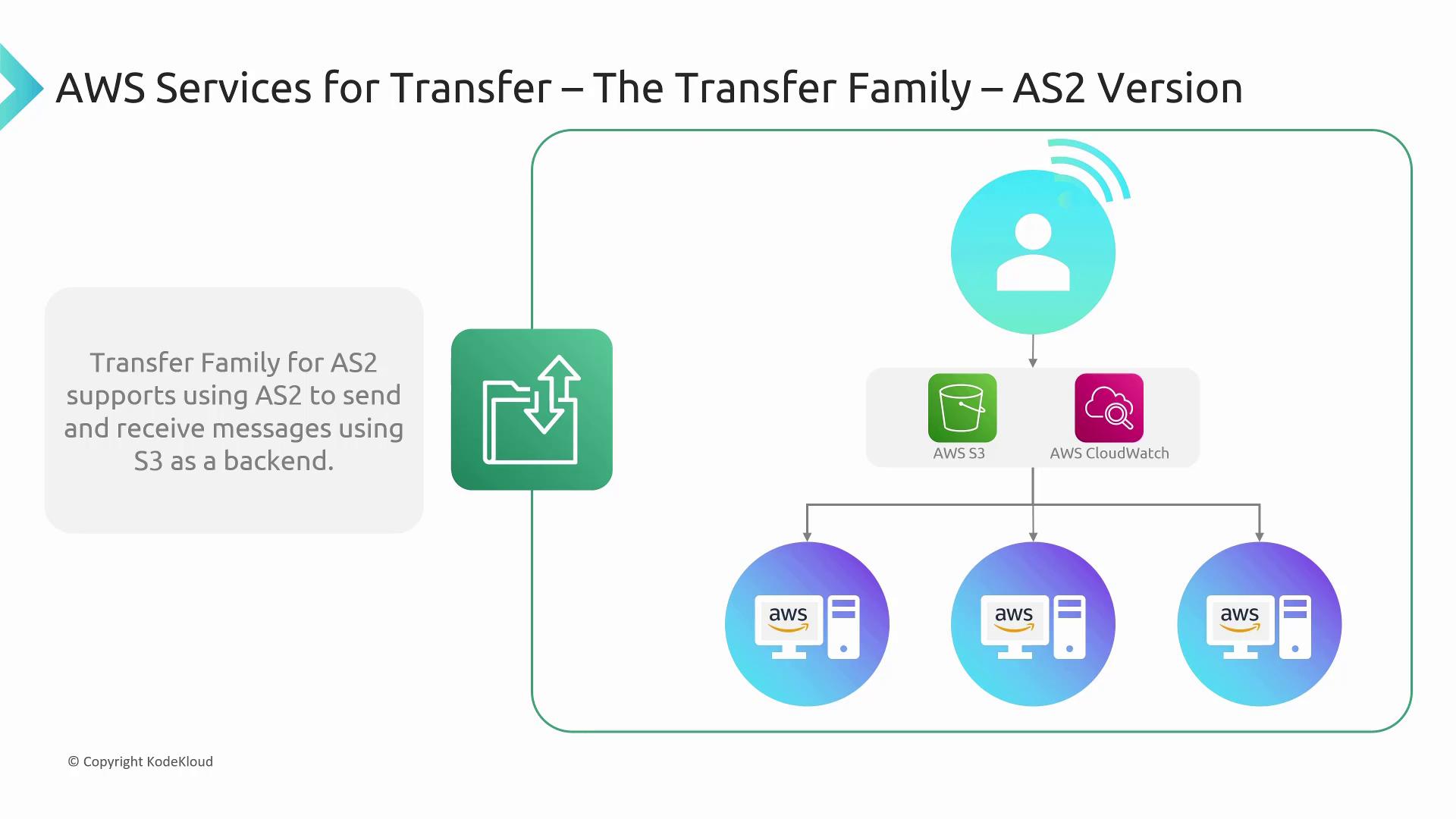
For scenarios where online data transfer is required, AWS provides the Transfer Family, which supports multiple protocols including FTP, FTPS, SFTP, and AS2 for secure transfers directly into Amazon S3 or Amazon EFS. AS2, in particular, facilitates the secure sending and receiving of messages, with CloudWatch integration for monitoring.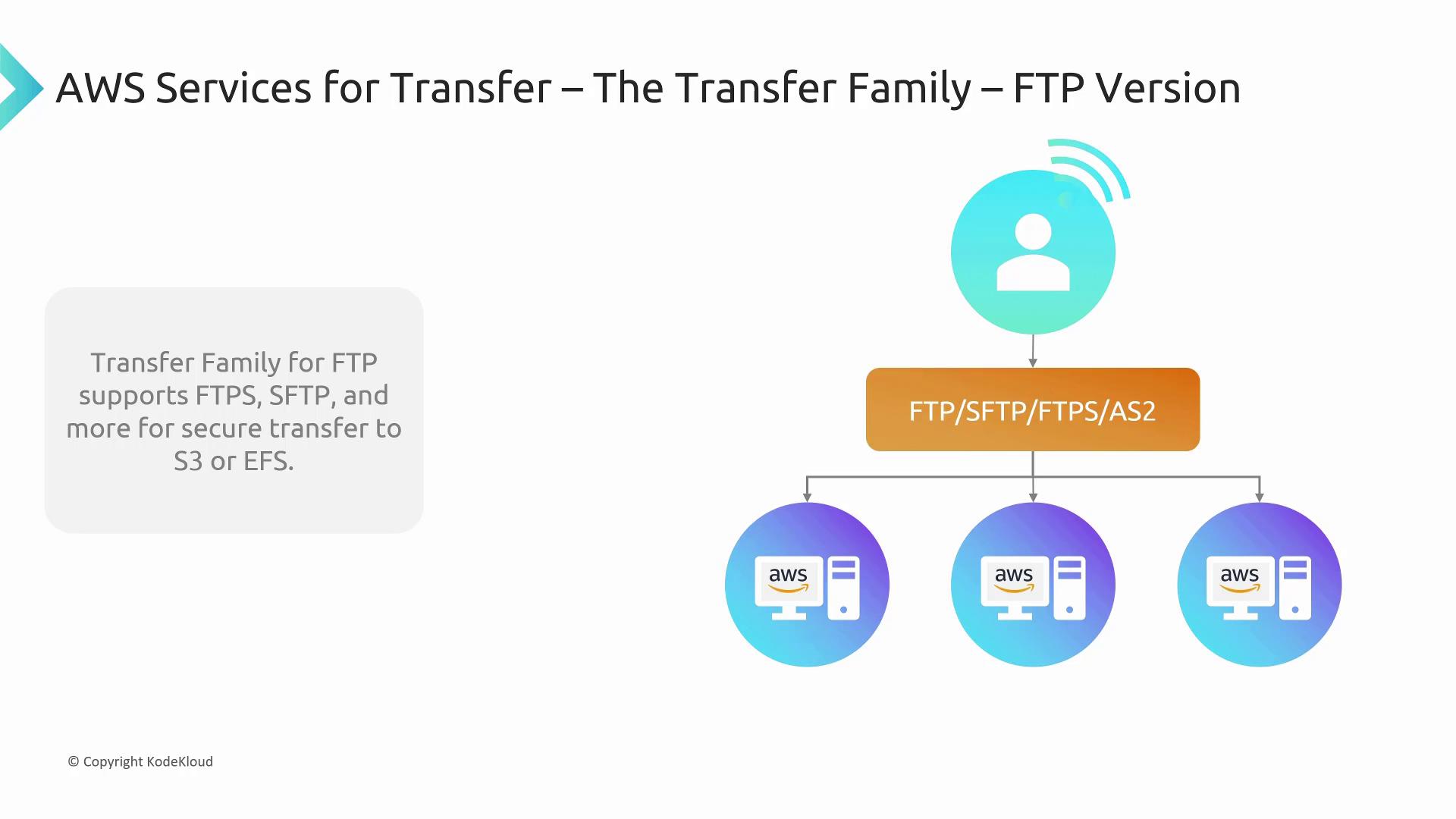
Application, Database, and Data Center Migration Services
AWS offers a suite of specialized services to address migration needs for applications, databases, and entire data centers. These tools help streamline the migration process:- Application Discovery Service:
Gathers comprehensive data about your applications, providing critical insights for planning your migration strategy.
- Application Migration Service:
Facilitates the actual migration of applications from traditional data centers to AWS, often incorporating modernization strategies.
-
Database Migration Service:
Supports both one-time migrations and continuous database replication from on-premises databases to AWS, adaptable to various migration scenarios including warm standby and cutover migrations. -
Elastic Disaster Recovery (formerly CloudEndure):
Provides automated, block-by-block replication of entire workloads, enabling a smooth cutover to live EC2 instances during disaster recovery or full data center migrations. -
Mainframe Modernization:
Assists organizations in transforming legacy mainframe environments and migrating mainframe components into modern AWS architectures.
Migration Services Summary
Effective migration is underpinned by careful planning and the strategic use of AWS services. Here are the key points to remember:- Utilize the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework to inform your cloud strategy.
- Leverage the AWS Migration Hub for a centralized view of all migration projects.
- For offline data transfers, consider using Snow Family devices, such as Snowcone, Snowball Edge, and Snowmobile.
- Take advantage of the Transfer Family for secure online transfers using protocols like FTP, FTPS, SFTP, and AS2.
- Automate large-scale file transfers with AWS DataSync.
- Employ dedicated services for application, database, and data center migrations.
- Transition legacy mainframe systems with AWS Mainframe Modernization.
