Running Applications: Docker vs. Kubernetes
When using Docker, you can run a single instance of an application using a straightforward command:Remember to monitor and adjust resource limits when scaling applications to ensure optimal performance.
Kubernetes Architecture Overview
Kubernetes leverages container runtimes like Docker, Rocket, or CRI-O to execute applications within isolated containers. A Kubernetes cluster consists of multiple nodes managed by a master node that orchestrates containerized applications.Nodes
Nodes are physical or virtual machines running Kubernetes software. They act as workers where containers are deployed. A typical Kubernetes cluster includes multiple nodes to guarantee high availability; if one node fails, the remaining nodes continue to operate, ensuring uninterrupted service.Master
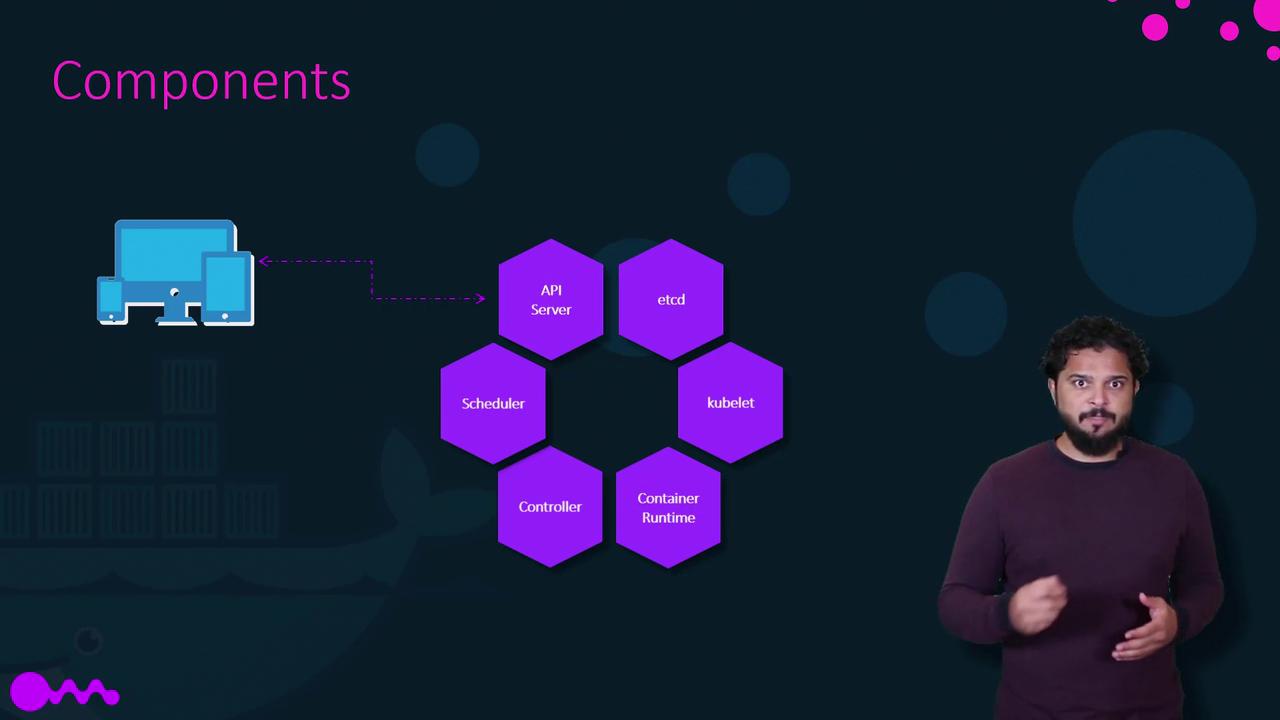
The master node runs the control plane components that manage and monitor the state of the cluster. Its responsibilities include maintaining cluster health, monitoring nodes, and reallocating workloads in the event of node failures. When installing Kubernetes, the following core components are set up:- API Server: Serves as the primary interface for all administrative tasks. It allows users, management devices, and CLI tools to communicate with the Kubernetes cluster.
- etcd: A distributed and reliable key-value store that contains all cluster data, ensuring consistency across multiple nodes.
- Scheduler: Responsible for distributing newly created containers across available nodes.
- Controllers: Detect changes in the cluster (like node failures or container issues) and initiate corrective actions by deploying new containers as needed.
- Container Runtime: The underlying software (e.g., Docker) that runs containers.
- kubelet: An agent that runs on each node to ensure containers operate as expected.
The kubectl Command-Line Tool
kubectl is the essential CLI tool for deploying and managing applications on a Kubernetes cluster. It is also used for retrieving critical cluster-related information, such as node status. Some basic commands include:Using kubectl commands effectively allows you to manage large-scale applications with simple, repeatable commands.