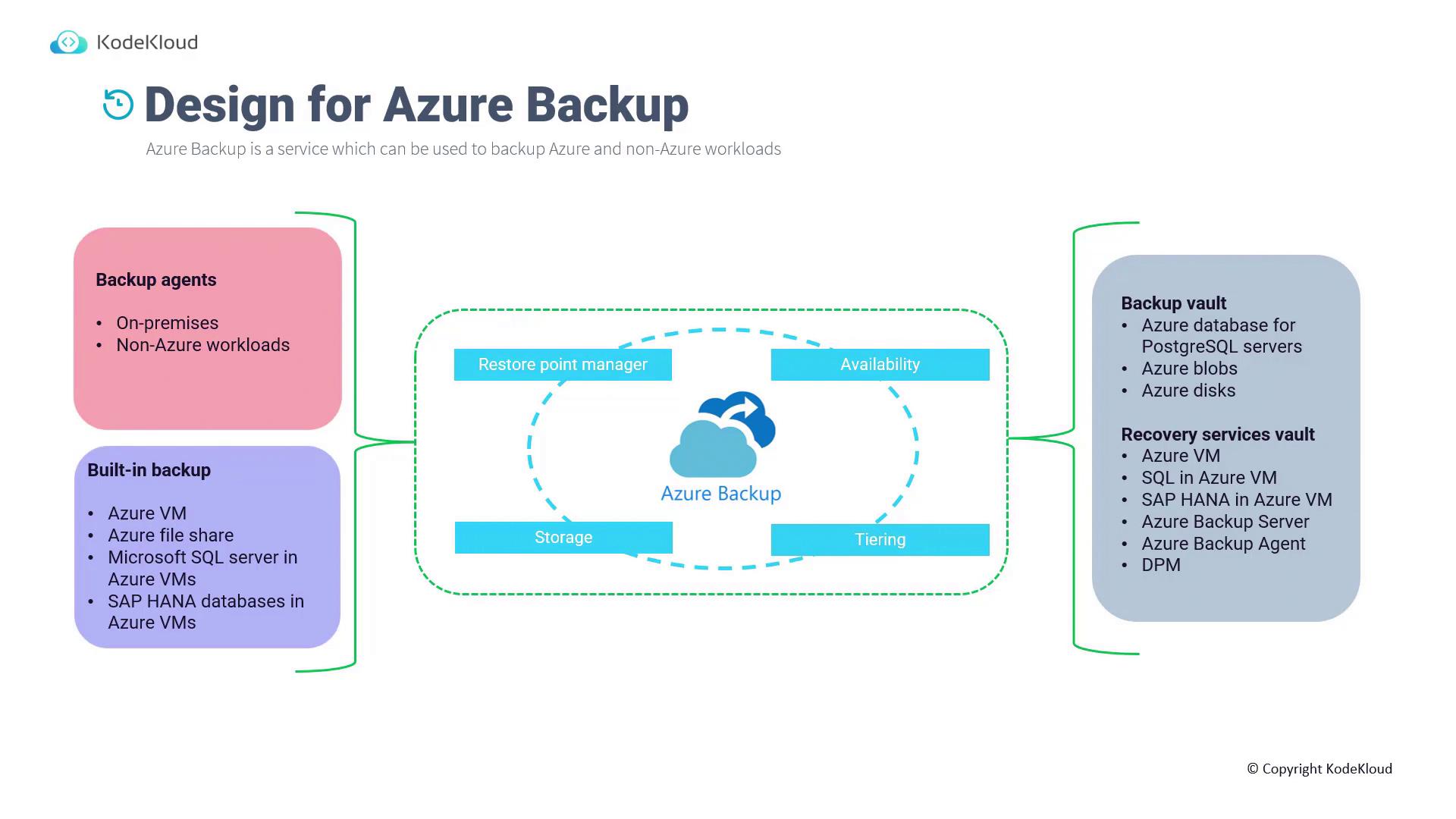
Data Collection and Backup Processes
Azure Backup employs several methods for data collection and backup:- Backup Agents: Installed on on-premises or non-Azure systems, these agents collect and send data directly to Azure Backup.
- Built-In Backup: Native backup features are available for services such as Azure Virtual Machines, Azure File Shares, Microsoft SQL Server, SAP, and more.
Backup Storage Architecture
Azure Backup categorizes backup data into dedicated vaults for optimized management:- Backup Vault: Used for storing backup data for services like Azure Database for PostgreSQL, Blob storage, and disks.
- Recovery Services Vault: Protects Azure Virtual Machines, SQL databases, SAP systems, backup servers, backup agents, and Data Protection Manager (DPM). For on-premises workloads, components such as backup agents and DPM extend backup capabilities beyond Azure.
Using dedicated vaults to store various types of backup data enhances data management and improves overall service reliability.
Vault Organization
- Maintain separate vaults for different environments (e.g., production, development, testing).
- Configure production workloads with geo-redundant storage (GRS) to ensure high availability, while development systems may use locally redundant storage (LRS).
- Organize vaults by subscription, environment, or application based on your organizational needs.
Policy Enforcement
Use Azure Policy to enforce consistent configurations and compliance rules across all vaults. This ensures every vault adheres to standard policies and best practices.Region Availability
Deploy Azure Backup components in the same region as the Recovery Services Vault. For example, if you have a Virtual Machine in the East US region, ensure the corresponding vault is also located in East US.Access Control
Access to the Recovery Services Vault is managed using Azure Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). This ensures that only authorized users can manage backup resources, enhancing overall security.Data Redundancy
By default, a newly created Recovery Services Vault is configured with geo-redundant storage (GRS). Consider the following points regarding redundancy settings:- The Azure portal does not allow changes to the redundancy option during the initial vault creation.
- Before onboarding any resources, you can modify the redundancy setting (e.g., from LRS to zone-redundant storage (ZRS)).
- Once a resource such as a Virtual Machine is backed up in the vault, the redundancy option becomes locked.
- To switch from GRS to LRS after onboarding, you must delete the existing vault, create a new one with the desired redundancy, and then onboard the resource again.
Changing redundancy settings on a vault with onboarded resources requires deleting and recreating the vault. This process can lead to service interruptions, so plan accordingly.