You cannot delete a file share that has associated snapshots. To remove such a file share, you must first delete all its snapshots.

Taking a Manual Snapshot on the Azure Portal
- Open the Azure Portal and select one of your storage accounts.
- Navigate to the File Shares section.
- Choose an existing file share. For demonstration purposes, if the file share is empty, upload a couple of files.
- Click the Snapshot option. If manual snapshots already exist, you may see them listed here. You can delete any unwanted snapshots if necessary.
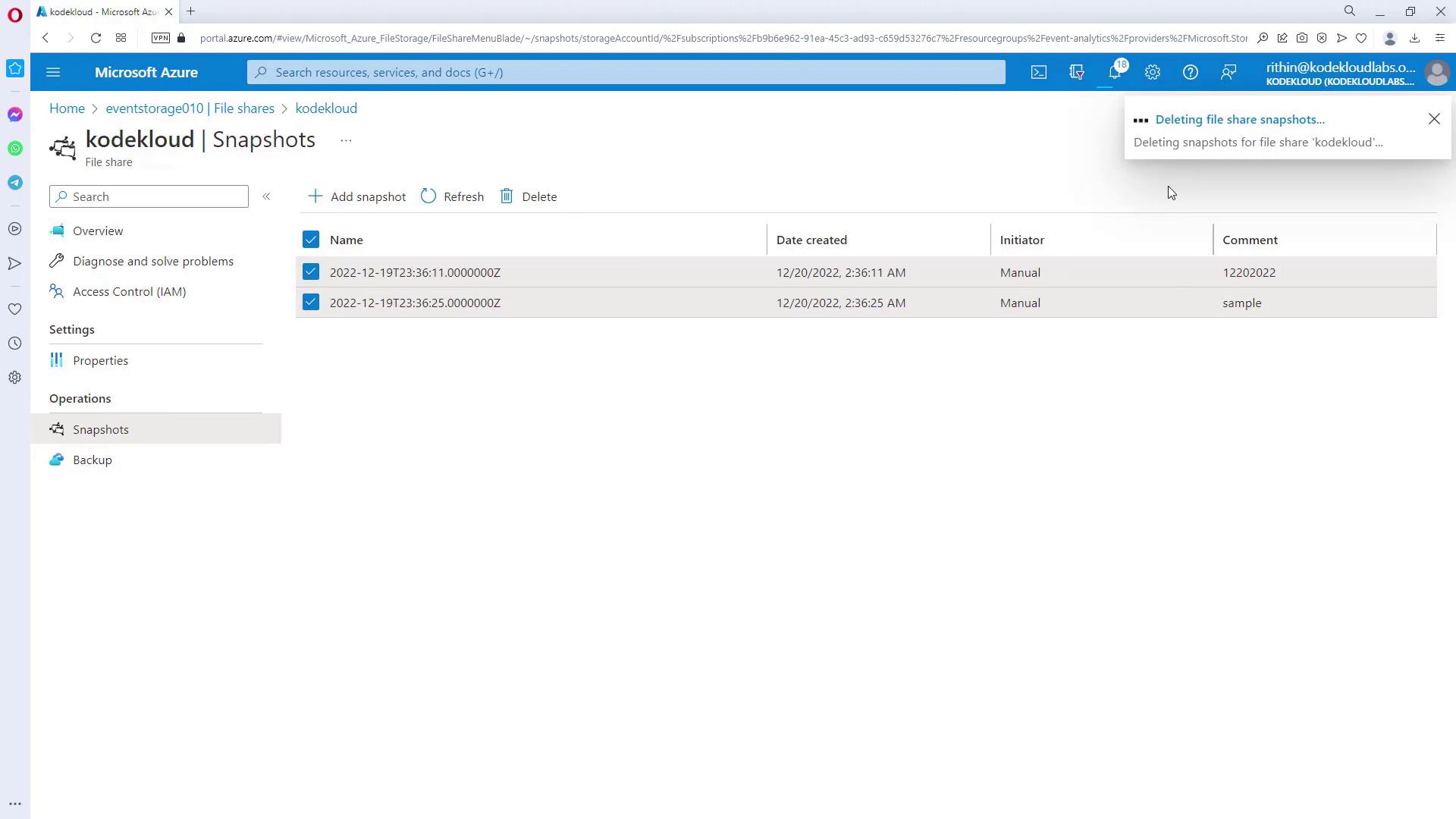
- Create a new snapshot. Once it is created, inspect its contents to confirm that all files and folders have been captured.
- For a recovery test, delete some files from the current file share. For instance, if you delete two CSV files while retaining a JSON file and an error CSV file, the snapshot will still preserve the deleted CSV files.
- Return to the snapshots list, open the most recent snapshot, and select the Restore option. During restoration, you can choose to overwrite the original file or restore it as a copy. If the original file is missing, restoring it with the same name is appropriate.
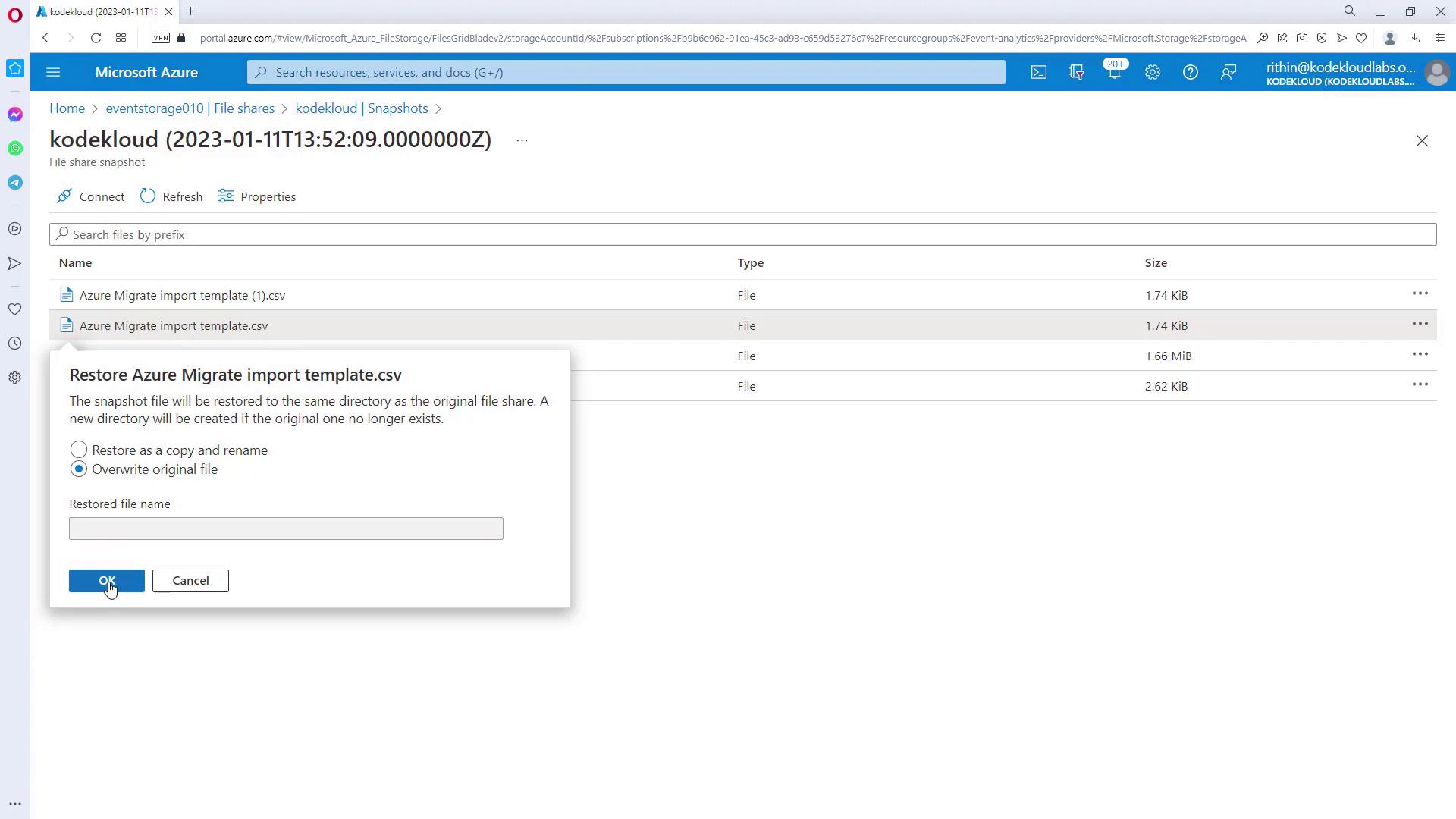
- After restoration, the file will reappear in the file share.
Automating Backups with Backup Policies
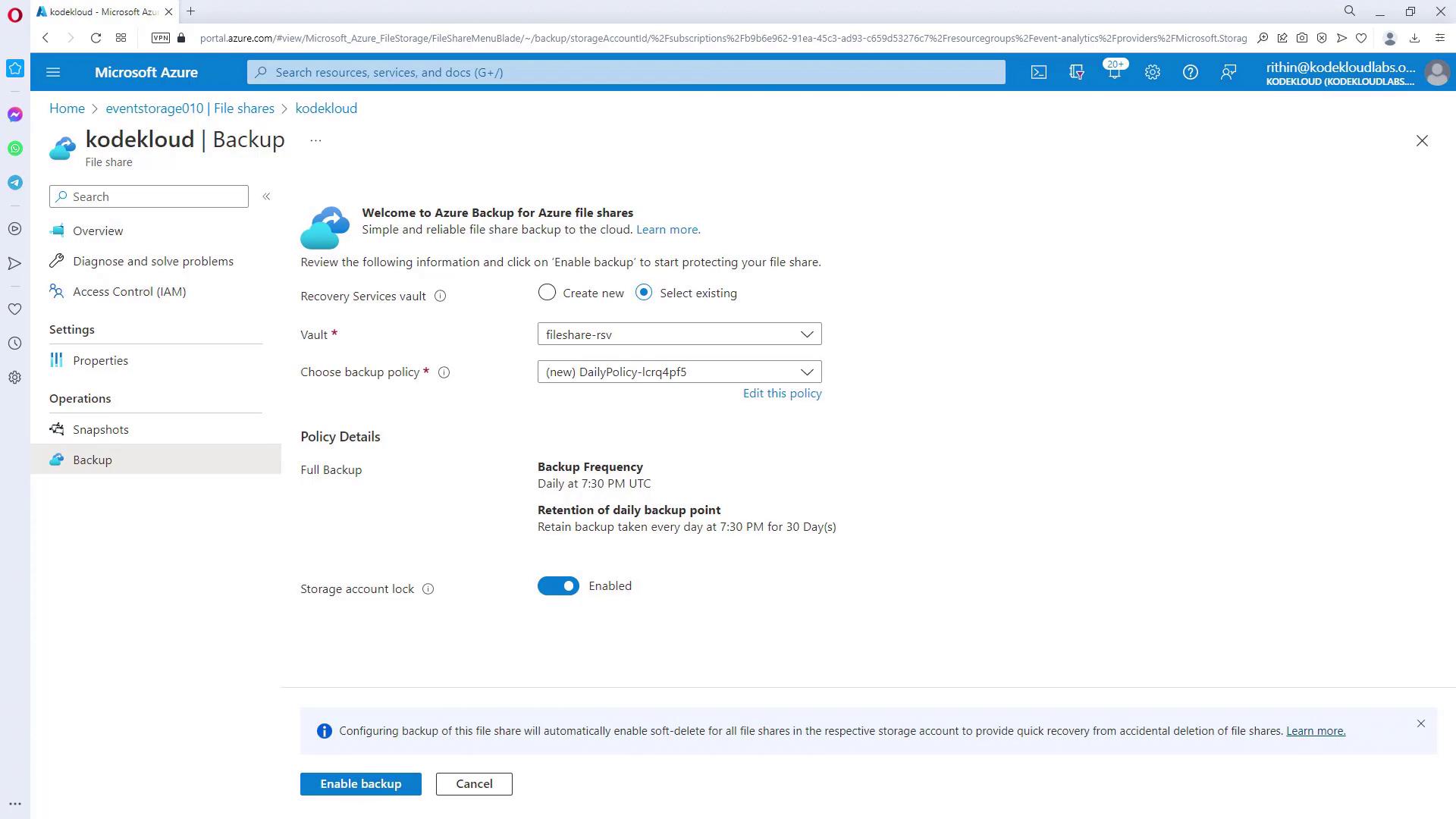
While manual snapshots are effective, automating backups ensures that your file share is consistently protected. Follow these steps to associate your file share with a backup policy in the Azure Portal:- Select a Recovery Services vault in the Azure Portal.
- Choose a backup policy that meets your requirements. Editing the policy allows you to specify the backup schedule (for example, daily at a designated time) and the retention period.
- Enable the backup for the file share. Once configured, the file share will automatically be backed up according to the defined schedule, ensuring you always have an up-to-date snapshot available for recovery.