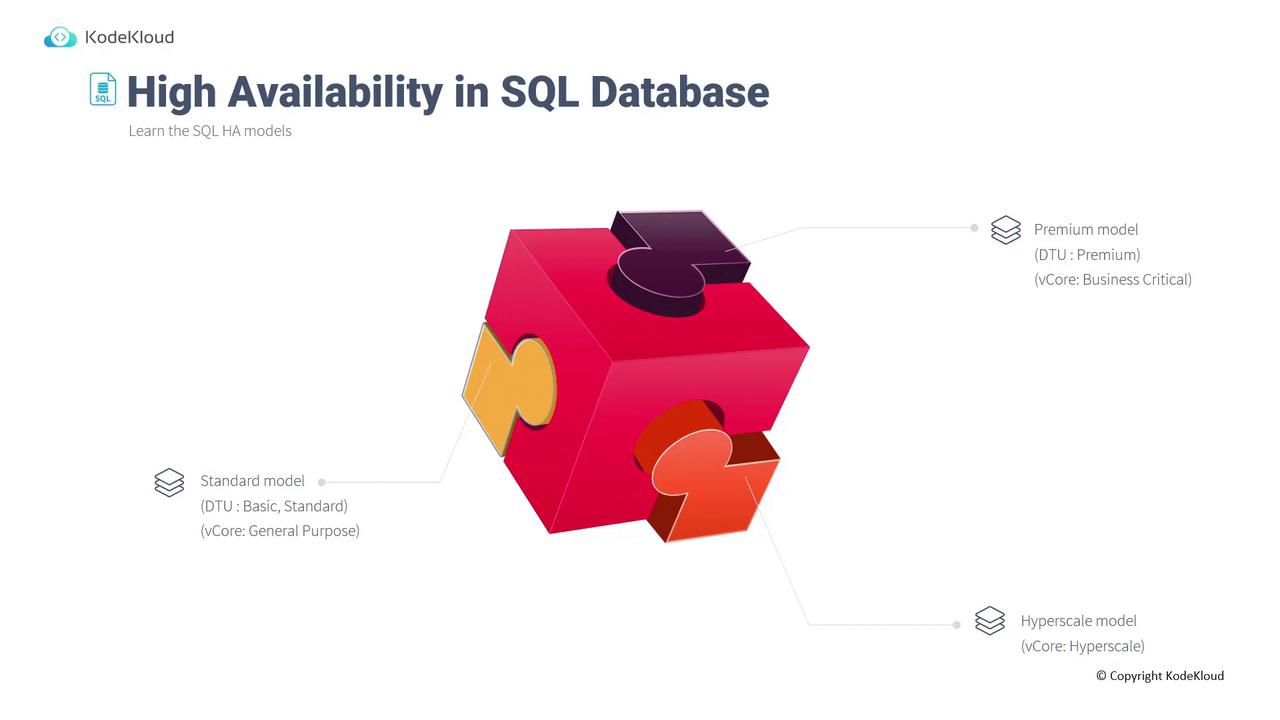
High Availability Models in SQL Database
SQL Database provides three tiers of availability based on the selected performance model:- Standard Availability Model: Activated when you select the basic/standard tier (DTU model) or the general-purpose option from the vCore model.
- Premium Availability Model: Utilized when opting for the premium tier in the DTU model or the business-critical tier in the vCore model.
- Hyperscale Model: Chosen when using the hyperscale tier.
Standard Availability Model
In the Standard Model, the compute and storage layers are decoupled:- Compute Layer: Hosts the SQL Server executable along with TempDB and cache data.
- Storage Layer: Houses the database files on Azure Premium Storage, leveraging replication options like GRS, LRS, or ZRS to maintain backup redundancy.
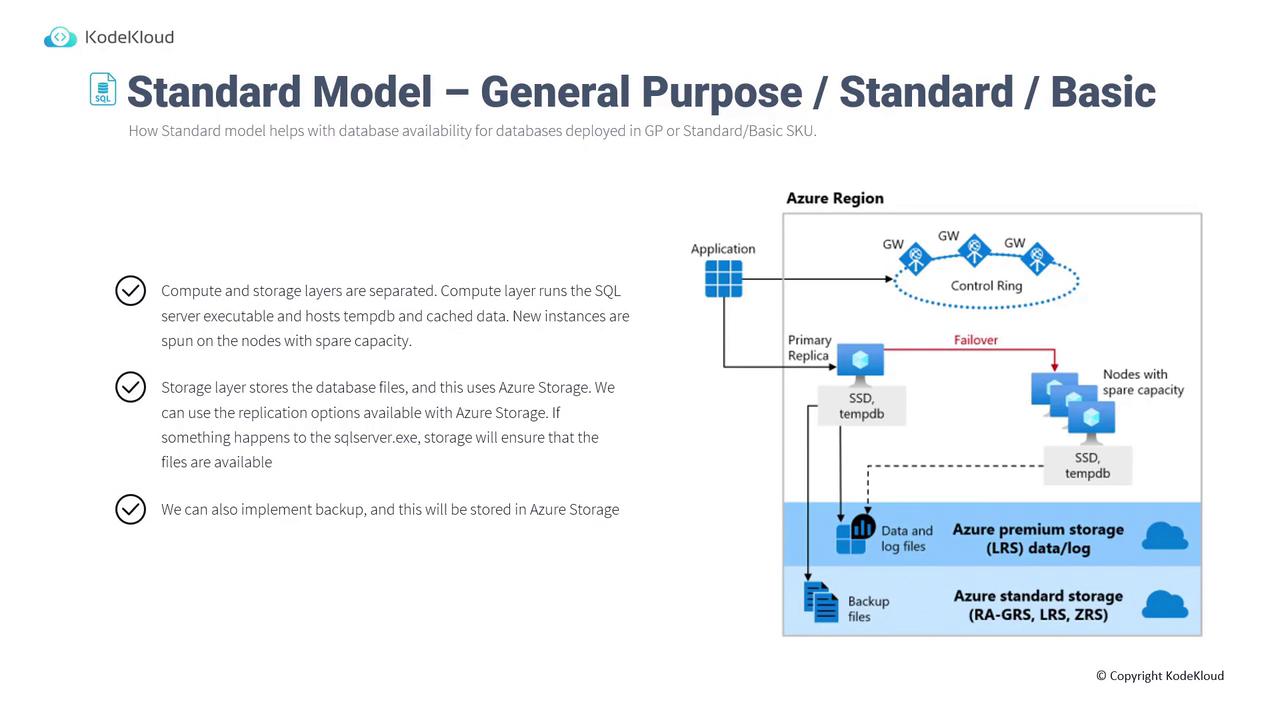
- The architecture shows a primary replica with secondary replicas across different nodes.
- The compute layer is dedicated to running SQL Server.exe, whereas the storage layer secures database files.
- Azure Storage is employed for backup operations, ensuring redundancy in case of compute layer issues.
Premium Availability Model
The Premium Model integrates both compute and storage within a single node. Key characteristics include:- Integrated Architecture: SQL Server executable and directly attached SSD storage co-exist on the same server.
- Multi-Node Cluster: Typically deployed in clusters of three or four nodes for high availability.
- Designed for OLTP Applications: Ensures high transaction rates and ultra-low I/O latency.
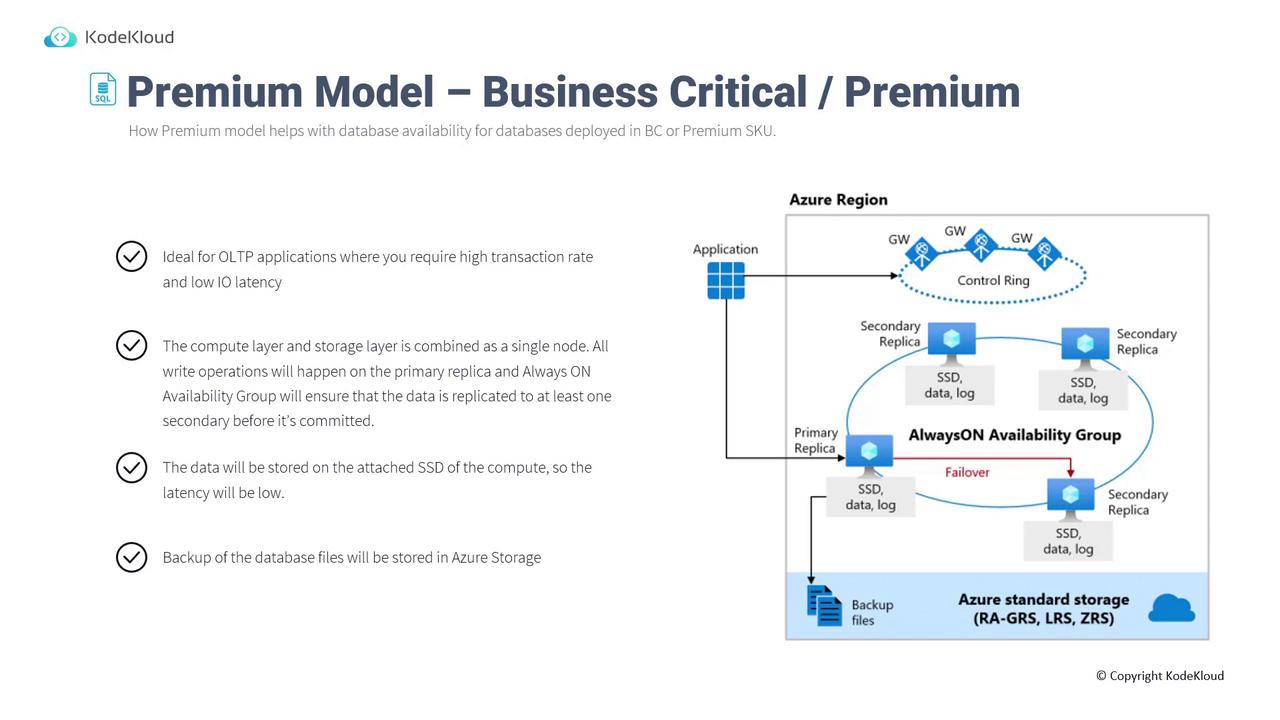
- Primary replica leverages directly attached SSD storage to minimize latency.
- All write operations occur on the primary replica. An Always On Availability Group ensures data is replicated to secondary nodes before commit.
- Backup processes continue to use Azure Storage.
- Managed entirely by Microsoft when deploying a business-critical or premium tier.
Hyperscale Model
The Hyperscale Model is designed for complex and high business-critical workloads. Its multi-layered approach includes:- Stateless Compute Layer: Runs SQL Server.exe, manages transient data, cache, and operates in a primary/secondary configuration.
- Stateless Storage Layer: A distributed storage engine, featuring page servers that cache transient and processed data.
- Stateful Transaction Log Layer: Captures all transactions from the primary compute and replicates log and cache data to secondary compute nodes.
- Stateful Storage Layer: Preserves the definitive database files, ensuring data integrity even if compute nodes encounter failures.
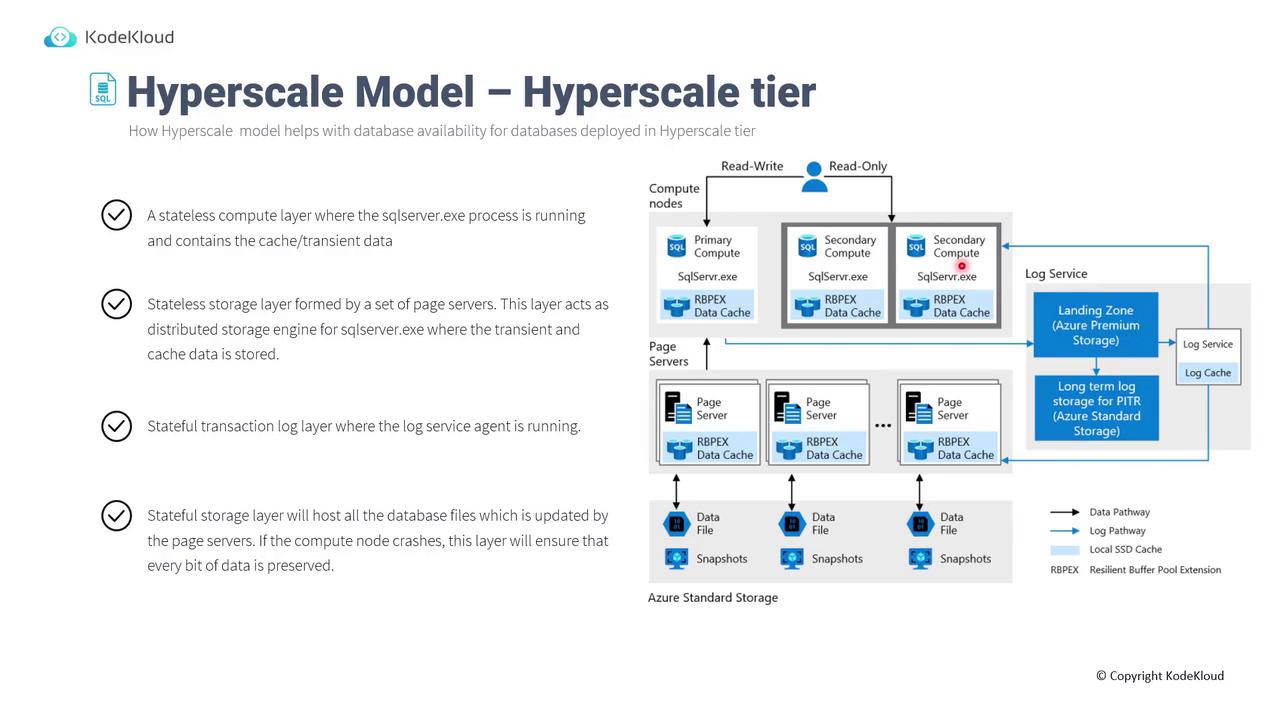
- The compute layer directly handles read/write operations along with running the SQL Server process.
- Page servers (stateless storage) manage transient and cached data.
- A dedicated log service layer ensures all transactions and cache data are replicated.
- This model is ideal for workloads that demand extremely low latency and high data integrity.
Failover Strategies
While these models are generally deployed within a single data center, additional strategies are essential to mitigate complete data center or regional failures:- Availability Zones: Within the premium tier, distributing compute nodes across multiple availability zones protects against data center-level failures. If one zone fails, the remaining zones ensure continuous operation.
- Geo-Replication: For regional failures, geo-replication involves duplicating the SQL Database to a secondary logical server in a different region. The primary server handles read/write operations while redirecting read-only requests to the secondary. In the event of a primary region failure, the secondary region assumes full operations.
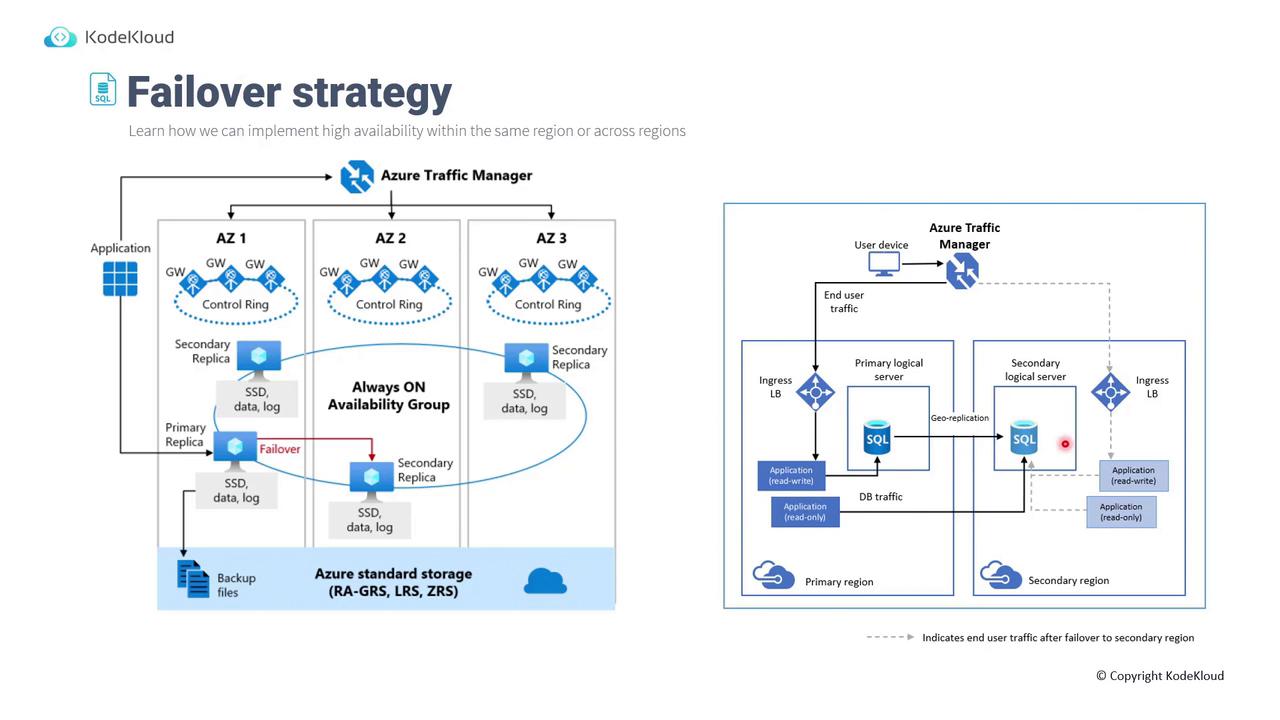
- Availability Zones: Ensure continuity within the same region.
- Geo-Replication: Provides robust protection across different regions with automatic failover capabilities.
Summary
To summarize, SQL Database availability can be achieved through different architectural models tailored for specific business needs:| Availability Model | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | Decoupled compute and storage; Azure Storage for backups; replication options (GRS, LRS, ZRS) | General-purpose workloads |
| Premium | Integrated compute and storage on SSD; Always On Availability Group for failover; low I/O latency | OLTP applications and high transaction rates |
| Hyperscale | Multi-layer architecture with stateless and stateful components; advanced transaction log replication | High business-critical workloads requiring extreme scalability and low latency |