- Cloud-only users – Users who exist solely in the cloud.
- Guest users – Users invited from other tenants for B2B collaboration, appearing as guests in your tenant.
- Directory-synchronized users – Users synchronized from an on-premises Active Directory to the cloud.
Why Choose Azure Active Directory?
Azure AD is a multi-tenant, cloud-based, centralized identity and access management (IAM) solution that offers comprehensive capabilities including:- Directory services
- Access management for applications
- Identity protection
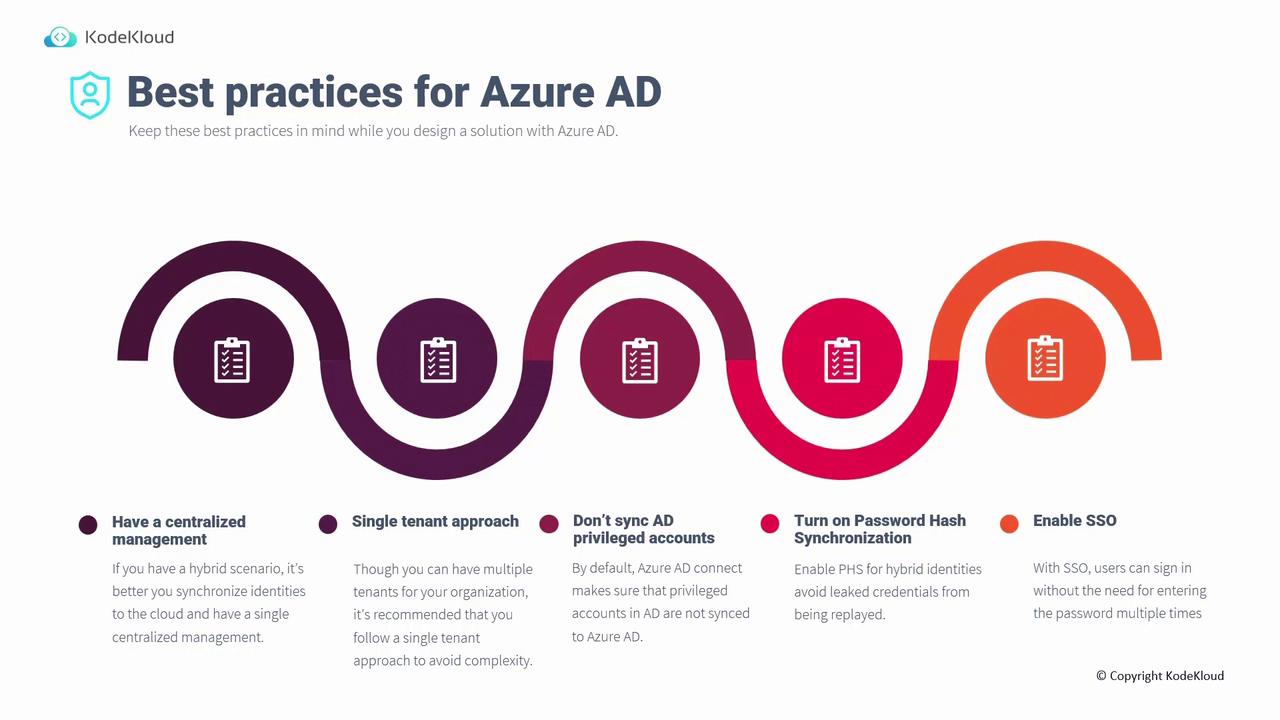
Best Practices for Azure Active Directory
When crafting your Azure AD strategy, consider the following best practices:Centralized Management with Hybrid Identities
For organizations that use both on-premises and cloud applications, synchronizing on-premises users with Azure AD enables centralized management. Without this integration, distinct authentication systems would require users to maintain multiple passwords and complicate account deactivation when employees leave.Single Tenant Approach
Although multiple tenants can be created, a single tenant approach simplifies user management. With one tenant representing the entire organization, administrative tasks—like disabling accounts for departing employees—are streamlined and less prone to error.Do not synchronize AD-privileged accounts. Privileged accounts such as enterprise or domain administrators should be excluded from synchronization to safeguard both on-premises and cloud environments. Even though these accounts are filtered out by default, custom roles may inadvertently sync them.
Enable Password Hash Synchronization
Hybrid identity solutions offer three methods for user sign-in:- Password hash synchronization (PHS) – Stores users’ hashed passwords in Azure AD, enabling direct cloud authentication.
- Pass-through authentication – Proxies login requests from Azure AD to on-premises domain controllers for authentication.
- Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) – Uses a federated model to pass authentication requests to on-premises domain controllers.
Enable Single Sign-On (SSO)
Single Sign-On (SSO) enhances productivity by letting users access multiple corporate applications after a single initial login from a domain-joined computer. Should SSO fail, users can still authenticate by manually entering their passwords, ensuring continuous access. These best practices contribute to a secure, efficient, and manageable Azure AD deployment.